NETWORKS
advertisement

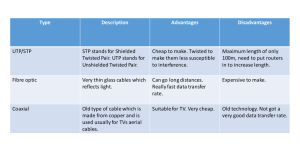
Networks “Each time you use the telephone you use the world’s largest computer network – the telephone system” Networks Slide 1 A Computer Network • A system of linked computers that allow messages to be transmitted from one to another • Messages can be text, sound, video and graphics Networks Slide 2 Purpose of Networks • Allows sharing of hardware • Allows sharing of software • Allows easy exchange and sharing of data between different locations – Tele-working – Video Conferencing – Electronic data interchange (EDI) Networks Slide 3 Components of a Network • Hardware – A sending device – A communications link – A receiving device • Communications software Networks Slide 4 Network Terms • Node – A point on a network to which a device is attached • Channel – The path over which data is transmitted • Host Computer (Server) – A computer that manages the network Networks Slide 5 Types of Networks • There are 2 basic types of networks – LAN – Local Area Network – WAN – Wide Area Network Networks Slide 6 LAN • ‘Hardwired’ within the same building – Components are in fixed positions – Computers are in close ‘proximity’ to each other – Computers have immediate access to CPU – no dial-up required – Terminals/computers are directly linked to each other and to the host computer Networks Slide 7 WAN • Uses a telecommunications service to link computers over a distance • Needs a modem to convert signals from digital to analog for transmission • May use a combination of telecommunications services • Connects many types of computers Networks Slide 8 Hardware Required • Network Card • Cables/wires for interconnection • Modem to convert signals • Satellites to relay data • Microwave stations to relay data Networks Slide 9 Network Card (NIC) • Network card also called a Network Interface Card (NIC) • NICs are needed to connect the network cable to the computer Networks Slide 10 Communications Channel • The route for digital information to pass through the network – Wired and wireless – The channel capacity is the number of bits of information it can transmit per second Networks Slide 11 How is Data Transmitted? • Both LANS and WAN use the following to link computers – Twisted pair wire – Coaxial Cable – Fiber-optic cable Networks Slide 12 Twisted Pair Wire • Two copper wires are twisted together to form a cable and then insulated – Inexpensive – Used in normal telephone lines so are already in place in buildings – Susceptible to noise or interference – Slow data transmission Networks Slide 13 Coaxial Cable • Used to connect computers and terminals in a LAN • Heavily insulated single wire • Can be laid underground or under the sea • Much faster data transmission than twisted wire • Less interference than twisted wire Networks Slide 14 Fiber Optic Cable • Fiber optic technology uses light, not electricity, to send data • Cables are made of glass fibers that guide light beams for miles • Fiber optics is faster, lighter, and less expensive than wire cables Networks Slide 15 Fiber Optics • Used higher frequencies so less interference • Has high bandwidth thus faster transmission of data Networks Slide 16 Modem • Modems convert digital signals to analog and analog signals to digital • Modem is short for Modulate/Demodulate Networks Slide 17 Modem Speeds • Modem speed is measured in bits per second • This is how many bits per second (bps) are being transmitted over the channel • Current speed for modems is 56.6 kbps Networks Slide 18 ISDN • ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) is designed to transmit a computer’s digital signal directly over a network • The entire network is digital Networks Slide 19 Benefits of ISDN • No digital to analog conversion • Speed—data can be transmitted at 128,000bps much faster than modem • Voice and data transmission can happen at same time Networks Slide 20 •Disadvantages of ISDN • • • • • High initial costs On-going monthly fees Possibly, a newer phone line is needed Not available in some geographic areas Newer technologies like DSL now becoming available Networks Slide 21 Microwave Transmission • Data is sent as signals through the atmosphere from one relay station to another • Line-of-sight transmission only Networks Slide 22 Microwave Transmission • Since signals cannot bend - needs relay stations (in high places) about 30 miles apart to continue transmission • Microwave transmissions are fast and cost-effective Networks Slide 23 Satellites • This form of communications link requires earth stations and transponders • Earth stations send and receive signals. Transponders amplify the signal, change the frequency, and retransmit the data to a receiving earth station Networks Slide 24 Satellite Transmission • Requires – Earth Stations - which send and receive signals – Transponders – receives the signal from an earth station, amplifies it, changes the frequency and sends it on to another earth station near the destination Networks Slide 25 Wireless Networks • Use radio waves and/or microwaves to maintain communication channels between computers • The data is beamed out over the airwaves • Advantages of wireless include mobility and elimination of unsightly cables Networks Slide 26 Advantages of Wireless • Users with personal digital assistant (PDA) handheld computers such as Palm Pilots or with laptops can use wireless technology to allow them to move about while maintaining their network connectivity Networks Slide 27 Advantages of Wireless • The ability for users to network desktop computers at various locations without the trouble or expense of wiring Networks Slide 28 Disadvantages of Wireless • Slower than wired networks • Equipment more expensive • Wireless networks are affected by obstructions such as walls etc in their vicinity • Interference from other wireless devices such as cell-phones • Interference from weather Networks Slide 29 Mix and Match • Most networks will be a combination of the many technologies that have been looked at here Networks Slide 30