breast
advertisement

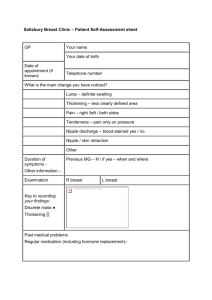
Breast Hend almalki Station 1 a young lactating female she gave a history of 24 hr tenderness and redness a) The pic. show ?? b) the causative organism is ? c) DDx ? d ) list 2 Rx ? e) the affected parts r ??? nipple & the areola ???!! a- what dose the picture show? Swelling ,redness, pus discharge of the breast B- what is the causative organism? Staphylococcus aureus C- what is the differential diagnosis? Breast abscess proceeded by early phase acute mastitis D- what is the treatment? Antibiotic (dicloxacillin)needle aspiration with culture taken and if large abscess incision and drainage should be done E- what are the affected parts? Breast lobule will be affected via the nipple ,duct system and circulation Station 2 A- name the abnormality that you see in the picture? B- what is your DDx? c- what is the 1st underlying structure that will concern us if it get attached to this lesion? D- what maneuver that done to make this lesion more clear ? E- list the groups of axillary Lymph node? f- what is the different between benign and malignant breast cancer? A- name the abnormality that you see in the picture? Skin dimpling caused by tethering note :puckering is multiple dimpling of the skin(this note is from doc kurdi session) B- what is your Dx? Breast cancer c- what is the 1st underlying structure that will concern us if it get attached to this lesion? The fibrous septa (cooper`s ligament) that separate breast lobule which may block the lymphatic that run alongside them causing edema of the breast and peau d` orange apperance D- what maneuver that done to make this lesion more clear ? Ask the patient to raise the hand above the head E- list the groups of axillary Lymph node? There are six groups can be easily remembered by the acronym 'APICAL' -anterior, posterior,infraclavicular, central,apical and lateral : 1- anterior or medial (pectoral) 2- posterior or inferior (subscapular) 3- lateral ( humeral) 4-(central) or intermediate ( they drain from ant , post and lat then efferents drain into apical) 5- ( infraclavicular or subclavicular) 6-( apical) : the final group , receives its afferents from all other groups and from the mammary tail and its efferents form the subclavian trunk. That was the anatomical classification Surgically, axillary lymph nodes r classified into 3 levels going from lateral to medial in relation to pectoralis minor p.m. muscle: level 1 : lat to p.m. ( mainly ant , post & lat groups) , level 2 : behind p.m. Mainly ( central and some apical nodes) , level 3 : medial to p.m. ( mainly infraclavicular group+ some apical ) f- what is the different between benign and malignant breast cancer? Malignant Benign Anywhere Commonly in the axillary tail presnted as smooth, rubbery, discrete, well-circumscibed brest mass, non-tender, mobile, hormone dependent Solid mass ,painless , roughly spherical breast mass, fixed , not mobile Age <40 Age > 40 none Nipple(discharge, rash , retraction) skin dimpling,edema Axillary ,supraclavicular lymph node -Mammogram - US - FNA to R/O solid lesion Triple assement (history & examination, imaging: mammogram-US,pathology) Metastatic screen(chest,liver,bone ,brain) Benign Generally conservative – serial observation -Excision if: mass rapidly growing, if >5cm in size or if Pt. wants Malignant Stage I,II BCS ( breast conservative surgery): Lumpectomy with free margin +radiation +/- Axillary clearance (ALND) +/- chemotherapy If there is any contraindication of conservative as to radiation (skin excoriation , pregnancy , CTD )we go for non conservative Stage III, IV Modified radical mastectomy (MRM Simple mastectomy (it’s MRM without LN dissection) +Chemotherapy Nowadays all breast cancer pt receive chemotherapy except for pt who can`t tolerate it as old women who can die by post chemo infection we give her tamoxifen if ER receptor +ve Benign Malignant Circumscribed mass Spiculated mass Fat-containing lesion Architectural distortion with no history of prior surgery Macrocalcifications :Widely scattered Microcalcifications (<0.5 mm) :Tightly clustered Round, uniform density, large, coarse Linear, branching, pleomorphic, casting Long axis of the lesion is along the normal tissue planes Lesion is taller than it is wide Homogeneous internal echotexture Decreased hyperechogenicity Hyperechogenicity Marked acoustical shadowing Smoothly marginated Spiculation Station 3 *describe what u see.? *Dx? *give 3D.Dx for bloody discharge from nipple? A- describe what you see? Retracted nipple b- what is your differential diagnosis? Congenital retraction, duct ectasia, carcinoma C- give3 differential diagnosis for bloody discharge from nipple? Intraductal Carcinoma ,Intraductal papilloma Paget’s disease Station 4 Q. describe Q. mention 3 important points that you should ask about in the Hx (risk factors) ? Q. what is the most proper diagnosis ? A- describe what you see? Bilateral breast enlargement b- mention 3 important points that you should ask about in the Hx (risk factors) ? *Drugs(antihistamine ,cimetidine , anabolic steroid, diuretics spironolactone,estrogen for prostatic cancer ,digoxin decreased testosterone) sign and symptoms of * liver cirrhosis or * bronchial carcinoma D -what is the most proper diagnosis ? gynaecomastia NB Common Breast Lumps: Young Women: Fibroadenoma / Abscess Pregnant : Galactocoele / abscess Middle aged and elderly women: Cancer higher up the differential diagnosis list. Galactocele: a cystic tumour containing milk or a milky substance Galactocele is usually round and freely mobile Needle aspiration is the choice for diagnosis and treatment with large gauge needle as the content of a galactocele is thick and creamy Surgery is performed when needle aspiration is not possible or when it becomes infected. Thank you