WELCOME TO PIGS!!!
advertisement

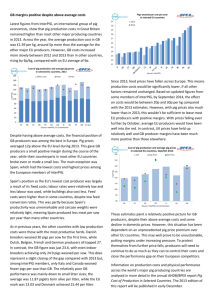
PIG PRODUCTION Why pigs? For the gals-they don’t turn into men when they get drunk For the fellas-they have at least 6 pairs of mammary glands They don’t kick or scratch Many opportunities for the “style” of employment The pay is pretty good Pigs are the major red meat consumed world-wide (43%) Diversification-welfare, economics, nutrition, engineering, public health Career opportunities-they will take you around the world! Why not pigs? They smell and bite You may not feel confident at graduation You may want to live in the city You may like one-on-one consulting You may like surgery The Australian industry has its ups and downs You will have to become a strong welfare advocate You may have to travel a lot What will you need to know to survive in the pig industry? Problem-solve: high pork production costs (cents/kg carcass weight). poor reproductive performance (pigs weaned/sow/year). poor growth performance (growth rate, mortality, feed efficiency). What happens on the pig farm? Herd profitability Volume Cost of production (Kg meat) (c/kg) Growing herd efficiency health Breeding herd efficiency nutrition management genetics environment The structure of the Australian pig industry 26th in the world 364Kt Carcass Weight vs China 41,600Kt 55kg in 1980 … 75kg in 2006 Average slaughter weight increasing Import mainly from USA, Canada and Denmark Export to Japan, Singapore and NZ We eat 18.8kg pig meat per head Ranked 23rd in the world Vs 77kg in Denmark Per capita consumption of pork-selected countriescalender year 2000 (from PigStats, 2002) The Aussie Pig Industry Percentage of sows by state 12% 1% 28% 15% 22% 22% NSW Qld Vic SA WA Tas The Aussie pig industry Number of pig producers is decreasing 49,537 in ’60……2,914 in ’01 Average herd size is increasing 2000 1997 1991 1988 1985 1994 Year 1982 1979 1976 1973 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 1970 Average herd size Average herd size is increasing (’79=16 sows…’99=101 sows) Fate of Pig meat in Australia 10/10/04 Pig meat consumed in Australia. Includes imported pork which makes up 70% of processed pork Fresh pork (40%) Butchers (22%) Supermarkets (60%) Other fresh (18%) Processed pork (60%) Ham (35%) Bacon Other Pork (40%) (25%) Overseas markets & how they impact us Recent challenges for the Australian industry Low prices High Aussie dollar hindering exports Price competition from imports High feed grain prices (drought) We import pig meat from: What type of meat is imported? We export pig meat to: We export pig meat as: How production efficiency and volume are measured in pig herds and what impacts on these parameters The production system Breeding - about 1 week after weaning Gestation - about 16 weeks Natural mating +/- AI Stalls, pens Farrowing / lactation – 3 to 5 weeks Weaner - 3-10 weeks Grower/finisher - 10-25 weeks Keys to success: Contain costs Meet mating targets Fill sheds Sell at heavy weights Use feed efficiently (no wastage) Optimise health and genetics Costs of Production - examples Average ($/kg Carcass WT) Feed Labour (paid) Other costs Total operating costs Capital costs Owners labour Total costs 1.20 0.18 0.21 1.59 0.20 0.21 2.00 Range: $1.30 > $2.35/kg carcass weight Components of cost of production 80 70 60 2001 40 2002 30 20 10 Fe ed La % bo ur O % ve rh ea d% H er d% S he d% % 0 H ea lth % 50 What determines prices? Seasonal Imports Export demand (25% pork exported) Profit is driven by the cost of feed and pig meat price Breeding herd Pigs weaned per sow per year Pigs weaned/litter Litters/sow/ yr Growing herd Kg meat sold/m2 floor space No. pigs/m2 floor space Physical herd performance Kg/pig Physical performance-efficiency targets: Litters/sow/year: 2.27 Born alive per litter: 11 Herd liveweight feed conversion efficiency 3:1 Growth rate: 600g/d Deaths (10% piglets, 2% weaners, 1% growers) Physical performance-actuals Breeding herd Parameter Farrowing rate Total Born PBA Stillborn % Mean 80 11 10 8 9 Range 61-90 10-13 9.5-11.5 4.311.6 7.4-10.3 Target >80% >11.5 >10.5 <8 % >9.5 Pigs weaned/litter Preweaning mortality% Pigs weaned /sow/yr 13 6.2-31 <1.5 18.4 15-23.9 >20 Physical performance Breeding herd Parameter Weaning age Litters per sow st Weaning 1 Service Sow death rate % Culling rate % Mean 21 2.14 8 9.6 62 Range 14- 29 1.8- 2.43 5- 10.2 1.5 -18 26 - 88 Housing types Indoors Outdoors Improved feed efficiency Reduced labour costs Lower capital costs Perceived as welfare friendly In-between bedded systems / ecoshelters Buildings: Conventional shed Straw based “ecoshelter” Capital cost high Capital cost low Operating cost low Operating cost high Intensive farming Bedded systems Especially for progeny (weaners) Estimates 30% in Australia Some breeding herds Chiefly in response to welfare Bedded systems (cont.) Cost one half/third of traditional sheds No internal penning Perceived as welfare-friendly Helps in the transition to multi-site, AIAO, Split-sex feeding, phase feeding On-going costs higher (bedding + labour) Higher feed intakes and increase in backfat Systems of raising pigs Family farms Corporate farms Contracting – breeder and grower contracting Contracting Shares production & financial risks Contractor provides land, sheds, labour Company provides pigs, feed, transport, medication, technical advice, assists in permits etc Allows for expansion with minimal capital Stable income for farmer (returns are not market-driven)