Sexually Transmitted Diseases
advertisement

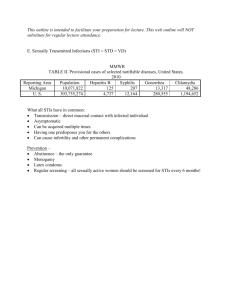
Sexually Transmitted Diseases Peter Tran, D.O Garden City Hospital Objectives HSV Chancroid Syphilis Lymphogranuloma Venereum Chlamydia/Gonorrhea Trichomoniasis HPV Molluscom Contagiosum Scabies Pubic lice Epidemiology 15 million new cases reported each year 65 million infected with incurable viral STD HPV Prevalence – 20 million Incidence – 6.2 million ½ of all men and women acquire at some point in their lives At 50 y/o, 80% of women would acquire HPV. Epidemiology Chlamydia Rates steadily rising 2003 – 900,000 cases reported 2x the reported cases of gonorrhea Chlamydia — Reported rates: United States, 1984–2001 Rate (per 100,000 population) 300 240 180 120 60 0 1984 86 88 90 92 94 96 98 2000 Chlamydia — Rates by state: United States and outlying areas, 2001 231.3 212.7 104.9 165.4 217.9 169.2 156.3 303.6 241.2 169.9 244.5 194.7 231.0 187.3 241.8 307.8 279.6 331.7 352.0 250.9 134.5 301.0 343.8 225.0 303.7 129.7 259.1 249.3 219.7 274.6 273.5 272.3 382.1 Guam 278.4 414.6 326.6 413.4 334.5 399.2 437.7 VT NH MA RI CT NJ DE MD 312.8 235.4 Rate per 100,000 population (n= 7) <=150 150.1-300 (n= 29) (n= 17) >300 332.7 Puerto Rico 72.2 104.8 111.9 163.8 277.8 226.6 193.9 356.4 295.3 Virgin Is. 120.6 Note: The total rate of chlamydia for the United States and outlying areas (including Guam, Puerto Rico and Virgin Islands) was 275.5 per 100,000 population. Chlamydia — Rates by sex: United States, 1984–2001 Rate (per 100,000 population) 450 360 270 Men Women 180 90 0 1984 86 88 90 92 94 96 98 2000 Chlamydia — Age- and sex-specific rates: United States, 2001 Men 3,000 Rate (per 100,000 population) 2,400 1,800 1,200 600 0 9.9 375.9 604.9 284.7 140.4 70.3 37.1 15.9 5.5 2.2 114.2 Age 10-14 15-19 20-24 25-29 30-34 35-39 40-44 45-54 55-64 65+ Total Women 0 600 1,200 1,800 2,400 3,000 139.8 2,536.1 2,447.0 824.6 301.9 119.1 51.4 18.1 5.1 2.9 436.3 Epidemiology Gonorrhea Rates have decreased slightly since 1998. Higher for non-hispanic blacks (24x the rate for whites) High for homosexual men Fluoroquinolone resistance increasing Not recommend in Hawaii and Calif. Gonorrhea — Reported rates: United States, 1970–2001 and the Healthy People year 2010 objective Rate (per 100,000 population) 500 Gonorrhea 2010 Objective 400 300 200 100 0 1970 73 76 79 82 85 88 91 94 97 Note: The Healthy People 2010 (HP2010) objective for gonorrhea is 19.0 cases per 100,000 population. 2000 Gonorrhea — Rates by state: United States and outlying areas, 2001 50.7 11.5 11.1 8.7 33.4 54.9 5.9 112.1 38.3 15.6 117.5 48.5 116.0 69.5 87.9 74.2 76.4 186.4 193.4 114.7 9.8 68.8 57.2 VT 12.5 NH 14.2 MA 50.6 RI 79.2 CT 74.8 NJ 106.0 DE 221.2 MD 178.0 172.3 99.3 138.6 40.5 155.9 156.7 88.8 206.0 178.3 172.2 269.3 Guam 31.0 272.8 251.4 231.1 Rate per 100,000 population 144.0 274.2 72.9 134.7 <20 20-100 >100 (n= 9) (n= 21) (n= 23) 49.9 Puerto Rico 15.5 Virgin Is. 31.3 Note: The total rate of gonorrhea for the United States and outlying areas (including Guam, Puerto Rico and Virgin Islands) was 126.9 per 100,000 population. The Healthy People year 2010 objective is 19.0 per 100,000 population. Gonorrhea — Rates by region: United States, 1981–2001 and the Healthy People year 2010 objective Rate (per 100,000 population) 600 West Midwest Northeast South 2010 Objective 480 360 240 120 0 1981 83 85 87 89 91 93 95 97 99 2001 Gonorrhea — Rates by sex: United States, 1981–2001 and the Healthy People year 2010 objective Rate (per 100,000 population) 600 Male Female 2010 Objective 480 360 240 120 0 1981 83 85 87 89 91 93 95 97 99 2001 Gonorrhea — Rates by race and ethnicity: United States, 1981–2001 and the Healthy People year 2010 objective Rate (per 100,000 population) 2,500 2,000 White Black Hispanic Asian/Pac Isl Am Ind/AK Nat 2010 Objective 1,500 1,000 500 0 1981 83 85 87 89 91 93 95 97 99 2001 Gonorrhea — Age- and sex-specific rates: United States, 2001 Men 750 Rate (per 100,000 population) 600 450 300 150 0 8.2 307.5 563.6 328.4 203.9 134.3 90.5 46.8 17.2 4.5 128.6 Age 10-14 15-19 20-24 25-29 30-34 35-39 40-44 45-54 55-64 65+ Total 0 Women 150 300 450 600 750 51.8 703.2 664.1 249.4 112.7 57.8 31.2 9.4 2.0 0.9 128.5 Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project (GISP) — Percent of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates with resistance or intermediate resistance to ciprofloxacin, 1990–2001 Percent 3.0 2.4 Resistance Intermediate resistance 1.8 1.2 0.6 0.0 1990 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 Note: Resistant isolates have ciprofloxacin MICs >1 mg/mL. Isolates with intermediate resistance have ciprofloxacin MICs of 0.125 - 0.5 mg/mL. Susceptibility to ciprofloxacin was first measured in GISP in 1990. 2000 01 Epidemiology Syphilis Rates have remained steady since 2000 Incidence 2.5/100,000 people in 2003. 27% increase in males 21% decrease in females Higher in southern states and among blacks Primary and secondary syphilis — Reported rates: United States, 1970–2001 and the Healthy People year 2010 objective Rate (per 100,000 population) 25 P&S Syphilis 2010 Objective 20 15 10 5 0 1970 73 76 79 82 85 88 91 94 97 Note: The Healthy People 2010 (HP2010) objective for primary and secondary syphilis is 0.2 case per 100,000 population. 2000 Primary and secondary syphilis — Rates by state: United States and outlying areas, 2001 1.0 0.0 0.1 0.0 0.4 0.7 0.1 0.4 0.1 0.2 1.6 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.5 3.3 1.6 0.5 3.5 0.9 1.7 1.0 2.5 0.7 0.3 0.5 1.4 1.2 5.5 5.8 1.8 5.9 Guam 7.8 4.9 3.2 5.1 2.3 3.9 0.0 VT NH MA RI CT NJ DE MD 4.3 3.0 Rate per 100,000 population <=.2 .21-4 >4 1.0 Puerto Rico 6.4 0.5 0.1 0.7 0.9 0.4 1.6 1.8 5.0 Virgin Is. 0.0 Note: The total rate of primary and secondary syphilis for the United States and outlying areas (including Guam, Puerto Rico and Virgin Islands) was 2.2 per 100,000 population. The Healthy People year 2010 objective is 0.2 per 100,000 population. (n= 10) (n= 34) (n= 9) Primary and secondary syphilis — Counties with rates above and counties with rates below the Healthy People year 2010 objective: United States, 2001 Rate per 100,000 Population <=0.2 (n=2,533) >0.2 (n=606) Primary and secondary syphilis — Rates by region: United States, 1981–2001 and the Healthy People year 2010 objective Rate (per 100,000 population) 50 West Midwest Northeast South 2010 Objective 40 30 20 10 0 1981 83 85 87 89 91 93 95 97 99 2001 Primary and secondary syphilis — Rates by sex: United States, 1981–2001 and the Healthy People year 2010 objective Rate (per 100,000 population) 25 Male Female 2010 Objective 20 15 10 5 0 1981 83 85 87 89 91 93 95 97 99 2001 Primary and secondary syphilis — Rates by race and ethnicity: United States, 1981–2001 and the Healthy People year 2010 objective Rate (per 100,000 population) 150 White Black Hispanic Asian/Pac Isl Am Ind/AK Nat 2010 Objective 120 90 60 30 0 1981 83 85 87 89 91 93 95 97 99 2001 Primary and secondary syphilis — Age- and sex-specific rates: United States, 2001 Men Rate (per 100,000 population) 7.5 6.0 4.5 3.0 1.5 0.0 0.0 1.4 5.0 5.9 6.4 7.2 5.3 3.4 1.4 0.4 3.0 Age 10-14 15-19 20-24 25-29 30-34 35-39 40-44 45-54 55-64 65+ Total 0.0 Women 1.5 3.0 4.5 0.2 2.5 3.8 3.1 3.0 2.9 2.0 0.9 0.2 0.0 1.4 6.0 7.5 STD’s with Genital Ulcers Disease Lesion Lymphadeopathy Systemic Symptoms Primary Syphilis Painless, indurated, single, clean base Non-tender, B/L None Genital Herpes Painful vesicles, multiple Tender, B/L Primary lesion Chancroid Tender, painful papules Tender, B/L, suppurative None Lymphomgranuloma Small, painless vesicle or papules Painful, matted, possible fistula After genital lesions heal HSV HSV-2 50 million in US HSV-1/HSV-2 85-90% of cases HSV-1 Cold sores Can also be transmitted during oral sex Incubation period - 1 week Typically presents as painful ulcers of the genitalia or anus and bilateral painful inguinal adenopathy. A group of vesicles on an erythematous base that does not follow a neural distribution is pathognomonic. Often associated with flu-like symptoms Urethral lesions can cause retention Asymptomatic viral shedding can occur 3 months after presentation HSV HSV Diagnosis Classic presentation occurs in a small percentage of patient. Women can present with atypical lesions abrasions, fissures or itching Viral culture with subtyping Sensitivity - 30-95% Depends on stage of lesion and whether primary or recurrence. Treatment Antiviral acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir Used as first episode, episodic or suppressive If episodic, must be used during the prodrome phase or 1 day of onset of lesions. Chancroid Caused by H.ducreyi Most common STD worldwide M:F – 3:1 Incubation – 1-3 weeks 10% are co-infected with HSV or syphilis Painful, nonindurated ulcer with a friable base. Can spread laterally by apposition to the inner thighs. It is associated with inguinal adenopathy that is typically unilateral and tender with tendency to become suppurative and fistulize. H. ducreyi is fastidious and difficult to culture. Gram-stain more helpful. gram-negative streptobacilli, which are usually arranged in short, parallel chains Chancroid Chancroid Treatment Azithromycin 1g PO Rocephin 250mg IM Cipro 500mg BID 3 days Erthromycin 500mg qid x 7 days Treat sexual partners Relief of inguinal tenderness by I&D/needle aspiration of the buboes. Syphilis Caused by the spirochete Treponema Pallidum Direct contact with lesion, body fluids or in utero. Incubation – 10 days – 3 months Primary syphilis is characterized by a single painless, indurated ulcer occurring at the site of inoculation that appears about 3 weeks after inoculation and persists for 4 to 6 weeks. associated with bilateral, nontender inguinal or regional lymphadenopathy Often goes unnoticed since its asymptomatic and heals without treatment Latent syphilis Defined as seroreactivity with no clinical evidence of disease. Early latent – within 1 year Late Latent – beyond 1 year or unknown duration Syphilis Secondary Syphilis Typically presents several months – 2 years from initial infection Mucocutaneous, constitutional symptoms Maculopapular rash Trunks, palms, soles Generalized nontender lymphadenopathy Condyloma lata – very infectious Secondary Syphilis Tertiary Syphilis 1/3 of untreated patients will develop tertiary syphilis systemic disease that can affect almost any organ or system, especially the cardiovascular, skeletal, and central nervous systems, and skin. Aortitis, meningitis, uveitis, optic neuritis, general paresis, tabes dorsalis, and gummas of the skin and skeleton. Syphilis Tests Non-treponemal RPR & VDRL Sensitivity (78% and 86% in primary) about 100% in secondary/tertiary. Correlate with disease activity. Negative after 1 year 4-fold decrease titer represents successful Tx Treponemal TP-PA FTA-ABS + results stay for life. Does not correlate with disease activity. Syphilis Treatment Primary/Secondary 2.4 mil units Benzthiazide PCN G IM Jarisch-Herxheimer Rxn Allergic Doxy 100mg BID x 14 days Tertiary Aqueous crystalline PCN G 3-4 mil units IV q4h x 14 days or Procaine PCN G IM 2.4 mil units qd with probenecid 500mg qid x 14 days Lymphogranuloma Venereum Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis types L1, L2, L3. Rare in the US. Mostly tropical regions. Incubation – 3 days – 1 month Presents as single painless ulcer on the genitalia. Painful unilateral, suppurative inguinal lymphadenopathy and constitutional symptoms that occur 1 month after ulcer heals. Can lead to significant tissue damage with anorectal fistula formation, elephantiasis, urethral destruction. Treatment Doxycycline 100 bid x 3 weeks Erythromycin 500mg qid x 3 weeks Lymphogranuloma Venereum Chlamydia Trachomatis Types D-K Most common bacterial STD in US and worldwide. Most common cause of epididymitis in young men. 40% of untreated infection in women will lead to PID. Over half of infected men and women are asymptomatic. Tests PCR & endocervical or urethral cultures Can be done on urine samples Treatment Primary Zithromax 1g Doxycycline Alternatives Erythromycin, levaquin, amoxicillin Treat sexual partners Treat for gonorrhea coinfection Chlamydia Trachomatis N. Gonorrhea Caused by intracellular gram-negative diplococci. Incubation – 1-2 weeks Symptoms include LUTS and pelvic discomfort or dysuria in women. Can lead to PID Rare but can manifests as systemic disease Reiter’s Syndrome Often coinfected with C. trachomatis Tests “Can’t see, can’t pee, can’t climb a tree” (arthritis, urethritis, conjuctivitis) PCR/culture Can be obtained from urine Treatment Primary - Rocephin 125mg IM Flouroquinolones except in parts of Asia, Pacific, Hawaii, Calif. Pregnancy – Rocephin or Spectinomycin 2gm IM Treat for coinfection with C. trachomatis Treat all sexual partners within 2 months of contact N. Gonorrhea Trichomoniasis Most common STD worldwide Caused by the flagellated protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis Incubation – Days – 1 month ½ of infected women are asymptomatic Men can present with LUTS/discharge Clinically presents with frothy white-green foul-smelling vaginal discharge “strawberry cervix” Vaginal wet-mount or microscopic exam of urine Treatment Flagyl 2g or 500mg Trichomoniasis Genital Warts Caused by HPV via direct skin-skin contact Over 100 different types Type 6,11 are common Low risk for conversion to invasive carcinoma Type 16,18,31,33,35,39,45,51 associated with cervical dysplasia and neoplasm in women and SIN in men >85% of cervical/anal cancer caused by type 16, 18 Diagnosis Visual – nontender cauliflower like genital lesions Acetic acid 3-5% may show subclinical infection ? Limited cystoscopy for urethral lesions Treatment Patient-Applied Podofilox 0.5% Imiquimod 5% cream Physician-Applied Cryosurgery, laser, electrosurgery, surgical excision, TCA, BCA HPV Molluscum Contagiosum Caused by MCV-1 virus Incubation – 2 weeks – 2 months Considered an STD in adolescents and adults Diagnosis Smooth, round, papule 2-5mm with central umbilication Biopsy Henderson-Patterson bodies Treatment Benign and self-limiting. Lesions usually resolve by 1 year. Can be treated by cryo, laser, cautery. Molluscum Contagiosum Scabies Caused by mites – Sarcoptes Scabiei Usually STD, but not in children Incubation 2-6 weeks Symptoms Pruritis (“7 year itch”) due to an immune reaction to the mites or their eggs/feces Wavy, elongated, erythematous papules due to mite burrows Microscopic exam for the mites or their eggs Treatment 5% permethrin cream 1% lindane lotion/cream Ivermectin 200mcg po x 1 Not indicated in children < 2y/o, after a bath, pregnant/lactating women, or severe dermatitis Equally effective as the creams Clean all bed linen and clothing Scabies Pediculosis Pubis Pubic lice (Phthirus pubis) Nits and lice can be found mostly on areas with hair Saliva of lice causes intense pruritis Lice or their eggs can be seen with the naked eye Treatment 5% permethrin cream 1% lindane shampoo Bactrim? Clean clothing, linen. Treat sexual partners Pediculosis Pubis