Midterm Exam * Macroeconomics
advertisement

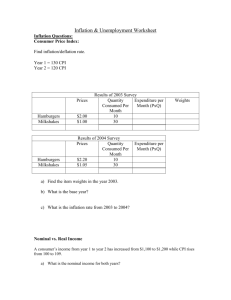
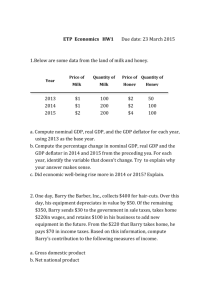
Midterm Exam – Macroeconomics (50 points) (1st Semester, 2010 –Type A) Name: Student Number: I solemnly swear NOT to cheat, therefore upholding my conscience. (Signature: ) I. Answer the multiple choice questions below: (2 points each) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 10. I. Using the loanable funds market model, explain what happens to consumption, investment, and the interest rate in the long run (1) when the government increases government expenditure, and (2) when the government decreases tax revenue. (3) How these two cases are different (similar)? (Use equations and graphs.) (10 points) II. Using the concept of money supply and money demand, derive the classical quantity equation, explain the impact of an increase in the money supply in the long run. Explain why classical economists think money is neutral? (10 points.) (10 points; Write answers on the back.) 1 I. Find the most appropriate answer to the following multiple-choice questions: (2 points each) 1. All of the following are flow variables EXCEPT: (1) consumption (2) interest rate (3) investment (4) GDP (5) government spending 2. In the national income accounts, investment includes all of the following except (1) firm’s spending on equipment (2) increase in the value of firm’s inventories (3) household’s purchase of new houses (4) firm’s purchase of stocks (5) firm’s spending on plant 3. An economy’s _________ always equals its ________________. (1) Saving; investment (2) expenditure on goods; expenditure on services (3) exports; imports (4) GDP; sum of values added at all production stages (5) government expenditure; tax revenue 4. Suppose that a farmer grows wheat and sells it to a baker for $20, the baker makes bread and sells it to a store for $30, and the store sells it to the customer for $50. This transaction increases GDP by (1) $0. (2) $20. (3) $30. (4) $50. (5) $100. 5. Which of the following is NOT a correct statement about saving? (1) Private saving equals disposable income minus consumption. (2) Public saving equals government spending minus tax revenue. (3) National saving equals the sum of private saving and public saving. (4) National saving equals income minus the sum of consumption and government spending. (5) The supply of loanable funds comes from both private saving and public saving. 6. If the amount of national production increases by 10% and all prices increase by 5%, then (1) real GDP increase by 5%. (2) real GDP increases by 15%. (3) nominal GDP increases by 10%. (4) nominal GDP increases by 15%. (5) None of the above. 2 7. Which of the following statements about the CPI and the GDP deflator is NOT true? (1) The GDP deflator is measured as nominal GDP divided by real GDP. (2) The CPI measures the price of a basket of goods and services for the typical consumer. (3) The GDP deflator is broader than CPI in the coverage of goods and services. (4) Prices of imported goods are not included either in CPI. (5) The composition of basket is fixed for CPI and but not for the GDP deflator. 8. According to the Fisher equation: (1) a 10 percent rise in the rate of inflation causes a 10 percent rise in the wage rate. (2) a 10 percent rise in the rate of inflation causes a 10 percent rise in the real interest rate. (3) a 10 percent rise in the rate of inflation causes a 10 percent rise in the nominal interest rate. (4) a 10 percent rise in the real interest rate causes a 10 percent rise in the rate of inflation. (5) a 10 percent rise in the nominal interest rate causes a 10 percent rise in the rate of inflation. 9. When the government raises revenue by printing money, it imposes an "inflation tax" because the (1) Printing money to raise revenue causes inflation and this will cause nominal value of money holdings increases. (2) Printing money to raise revenue causes inflation and this will cause the real interest rate to increase. (3) Printing money to raise revenue causes inflation and this will cause the nominal interest rate to increase. (4) Printing money to raise revenue causes inflation and people will have to pay more taxes under inflation. (5) Printing money to raise revenue causes inflation which is like a tax on people who hold money. 10. One effect of an unexpected rise in inflation is that wealth is redistributed from (1) poor people to wealthy people. (2) wealthy people to poor people. (3) lenders to borrowers. (4) borrowers to lenders. (5) young people to old people. 11. According to the classical economists, which of the following variables is NOT affected by monetary policy? (1) the nominal wage rate (2) the nominal interest rate (4) inflation rate (5) real interest rate 3 (3) the nominal GDP 12. Hyperinflation usually occurs when (1) people spend too much money. (2) workers demand higher and higher wages. (3) governments collect more and more taxes. (4) governments print too much money to finance their spending. (5) the economy grows too fast. 13. Frictional unemployment occurs because (1) the minimum wage is too high. (2) labor unions put pressure in the labor market. (3) rigidities exist in the wage-setting process. (4) it takes time to match firms and workers. (5) All of the above. 14. Which of the following policies would reduce the amount of frictional unemployment? (1) A reduction in corporate taxes (2) An increase in unemployment insurance (3) An increase in the minimum wage (4) An increase in the public retraining programs (5) An decrease in the labor union power. 15. Structural unemployment results when (1) the minimum wage is set to increase in the near future. (2) there is generous unemployment insurance. (3) workers are temporarily laid off due to weather conditions. (4) the real wage is below its market-clearing level. (5) Labor unions put pressure in the labor market. 4 <<보너스 문제>> 16. 다음 중 한국의 실업률 계산방법과 관련한 설명 중 틀린 것? (1) 조사대상월 30일 현재 만 18세 이상 인구 중 경제활동인구를 대상으로 고용지표를 조 사 (2) 조사대상주간에 수입을 목적으로 1시간 이상 일한 자는 취업자로 분류 (3) 동일가구내 가구원이 운영하는 농장이나 사업체의 수입을 위해 주당 18시간이상 일한 무급가족종사자는 취업자로 분류 (4) 직업 또는 사업체를 가지고 있으나 일시적인 병 또는 사고, 연가, 교육, 노사분규 등의 사유로 일하지 못한 일시 휴직자는 취업자로 분류 (5) 조사대상주간에 수입있는 일을 하지 않았고, 지난 4주간 일자리를 찾아 적극적으로 구 직활동을 하였던 사람으로서 일자리가 주어지면 즉시 취업이 가능한 사람은 실업자로 분류 17. 2010년 3월 현재 우리나라의 실업률은? (1) 2.1% (2) 3.1% (3) 4.1% (4) 5.1% (5) 6.1% 18. 한국의 2009년도 GDP에 관한 설명 중 옳지 않은 것은? (1) GDP에 대한 지출을 민간최종소비지출, 정부최종소비지출, 총고정자본형성, 재고증감, 재 화와서비스의 수출, 재화와 서비스의 수입, 통계상 불일치로 구분할 수 있다. (2) 위의 부분 중 민간최종소비지출의 비중이 54%로 가장 크다. (3) 정부최종소비지출은 총고정자본형성의 비중보다 크다. (4) 2009년도 실질GDP는 전년도에 비하여 플러스 성장하였다. (5) 2009년도 일인당 GDP는 미 달러기준으로 2만 달러에 미달하였다. 19. 다음 중 우리나라의 소비자물가지수 계산에서 가장 가중치가 큰 부문은? (1) 식료품, 비주류음료 (2) 주거 및 수도 광열비 (3) 외식, 숙박 (4) 교육 (5) 교통 5