Amino Acids and Peptides
advertisement

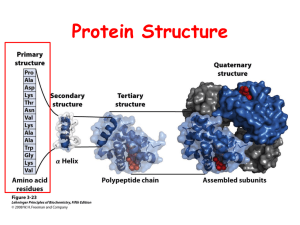
Chapter Outline Amino Acids Amino acid classes Bioactive AA Modified AA Peptides Proteins Protein structure Fibrous proteins Globular proteins Stereoisomers Titration of AA AA reactions 5P1-1 5.1 Amino Acid: Definition An alpha amino acid is a carboxylic acid with an amino group on the carbon alpha to the carboxylic acid . The alpha carbon also has an R group side chain except for glycine which has two Hs. O Generic amino acid at physiological pH: zwitterion form C O + H3N C H R aC 5P1-2 Definition, cont. If the R group is not H, the AA can exist in two enantiomeric forms (nonsuperimposable mirror image) forms.) O C + H3 N a carbon C R1 O O H H Mirror plane O C C + NH3 R1 5P1-3 Amino Acids General form: 1. an amino acid (AA); 2. two AA linked to form the peptide bond. O C + H3N L-form C R1 HO H HO + H3N C C N C C O R1 R1 H O PEPTIDE BOND 5P1-4 Amino Acids-2 Only the L form of amino acids is commonly found in proteins. Depending on the nature of the R group, AA are classified into four groups. nonpolar polar acidic basic 5P1-5 AA with nonpolar side chains-1 H3N + COO C H CH3 alanine, Ala H3N + H3N + COO C CH2 phenylalanine, Phe COO C H CH2 CH CH3 CH3 leucine,Leu H H3N + COO C H CH3 CH CH2 CH3 isoleucine, Ile 5P1-6 AA with nonpolar side chains-2 H 3N + COO C H CH CH3 CH3 valine, Val COO H 2N + CH2 C H CH2 CH2 proline, Pro H 3N + COO C H CH2CH2S CH3 methionine, Met COO H 3N + C H CH2 C CH N H tryptophan, Trp 5P1-7 AA with polar side chains-1 H3N + COO C H H Glycine, Gly H3N + H3N + COO C CH2 OH Serine, Ser COO C H CH2 SH cysteine, Cys H H3N + COO C H CH OH CH3 threonine, Thr 5P1-8 AA with polar side chains-2 H3N + COO C H CH2 O C NH2 asparagine, Asn H3N + COO C H CH2 H3N + COO C H CH2 CH2 C O NH2 glutamine, Gln tyrosine, Tyr OH 5P1-9 AA: acidic and basic H3N + COO H3N C H CH2 O C O aspartic acid, Asp H3N + CH2 CH2 NH + H2N C NH2 arginine, Arg C H CH2 glutamic acid, CH2 Glu O C O COO C H CH2 + COO H3N + COO C H CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 + NH3 lysine, Lys H3N + H C + HN COO C H CH2 C NH C H histidine, His 5P1-10 Amino Acid Titration At physiological pH, the carboxyl group of the AA is negatively charged and the amino group is positively charged. Amino acids without charged side chains are zwitterions and have no net charge. H3+N-CHR-COO-. A titration curve shows how the amine and carboxyl groups react with hydrogen ion. 5P1-11 Amino Acid Titration-2 At low pH a nonacidic/nonbasic amino acid is protonated and has the structure below. H3N+CHRCOOH The charge behavior of acidic and basic AAs is more complex. 5P1-12 Titration of Alanine B=C pK2=9.73 10 C O H3N CHC OH R1 A O + H3N CH C O R1 B O + H3N CH1C O R1 C + pH 5 1 B, pI=pH=6.0 A A=B pK1=2.3 1 mole base added 2 5P1-13 Isoelectric point The isoelectric point (pI) for an AA occurs when there is no net charge. For a neutral AA, the pI is calculated using the equation pK1 + pK2/2 Eg.: alanine: 2.34 + 9.7 / 2 = 6.0 For acidic or basic AAs, the pI is the average of the two pKa values bracketing the isoelectric structure. 5P1-14 Isoelectric point-2 In general the pI is the average of the two pKa’s bracketing the isoelectric structure. Eg.: glutamic acid, pI = 3.2 pK3=9.9 pK2=4.3 pK1=2.2 5P1-15 5.2 Peptides Peptide: a polymer of about 2-100 AAs linked by the peptide(amide) bond. As the amino group and the carboxyl group link, water is lost. H H O H O O + + + H3N C C O H3N C C O H3N C C O R1 -H2O R1 -H2O R1 H O H O H O + H3N C C N C C N C C O H H R1 R1 R1 Peptide bonds 5P1-16 Peptides-2 A peptide is written with the N-terminal end to the left and the C-terminal end to the right. H2N-Tyr-Ala-Cys-Gly-COOH Name = Tyrosylalanylcysteinylglycine The peptide bond is rigid and planar due to the resonance contribution shown right. C C H H + a a C N C N Ca Ca - O O 5P1-17 Peptides-3 The peptide bond angles force specific conformations of proteins and, on extended chains, successive R groups are on opposite sides. 5P1-18 Physiologically Interesting Peptides carbon O + - H3N CH2CH2C NH CH COO -alanyl-L-histidine CH2 C HC NH N C Common name: carnosine found in muscle tissue 5P1-19 Physiologically Interesting Peptides - COO + O O - H3N CH CH2 CH2 C NH CH C NH CH2COO CH2 SH -glutamyl-L-cysteineylglycine Glutathione: the reduced form reduces oxidizing agents by dimerizing to form the disulfide bond with release of 2 H. 5P1-20 Physiologically Interesting Peptides Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu N-terminal AA C-terminal AA Short form description for a peptide. Leucine enkephalin: a natural analgesic found in the brain 5P1-21 Physiologically Interesting Peptides H3 3 + N -Cys-Tyr-Ile Oxytocin Induces labor and aids in forcing milk from the mammary glands. | | S Gln | | S -Cys-Asn | 8 Pro-Leu-Gly-NH2 Vassopressin has a Phe at position 3 instead of Ile and an Arg at position 8 instead of a Leu. Its role is in regulating blood pressure. 5P1-22