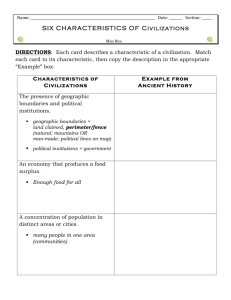
SIXTH GRADE CURRICULUM
advertisement

Unit 1- Human Beginnings Essential Standards – H.1.3, H.2.3, G&EL.1.1, G&EL.1.2, G&EL.1.3, G&EL.1.4, G&EL.2.1, C&G.1.1, C&G.1.4, E&FL.1.1, E&FL.1.2, C.1.1, C.1.3 HISTORY GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY CULTURE Unit Overview In this unit, students will examine the origins of human society. Students should develop an understanding of the role of paleontologists, archaeologists, and anthropologists in the context of social studies and prehistory. Students should be able to analyze the origins of human society and trace its transition from nomadic hunter-gatherer cultures to agrarian civilizations, including the introduction and subsequent developments of tools and agricultural technology. Generalizations 1. Anthropologists, archaeologists, and paleontologists work together to create our understanding of prehistoric cultures since the defining trait of prehistory is its lack of a writing system. 2. The development and use of tools enabled the nomadic hunter-gatherers to settle into a more agrarian civilization, which in turn led to the creation of villages and permanent settlements. 3. Essential resources such as access to food, water, and shelter are necessary for a society to thrive. Essential Questions 1. What is social studies? Why do we study it? 2. How do anthropologists, archaeologists, and paleontologists work together to create our modern understanding of the prehistoric era? 3. How did the development of tools lead to more stable societies? 4. What caused the transition from nomadic societies to agrarian civilizations? 5. What are the most essential resources for a society to thrive? 6. How are the Stone and Bronze Ages similar and different? 7. How are Cro-Magnons and Neanderthals similar and different? 8. What is the Neolithic Revolution, and how did it impact the cultures of the Prehistoric Era? Unit Vocabulary Agrarian Homo sapiens Nomadic Anthropologist Human community Origin Archaeologist Hunter-gatherer Paleolithic cave painting Artifact Ice Age Paleontologist Bronze Age Innovation Prehistoric Clovis Location Resources Cro-Magnon Migration Scarcity Decline Neanderthal Social studies Hominid Neolithic Revolution Stone Age Donald Johanson Lucy Key People Mary and Louis Leakey Unit 1- Goals What do students need to KNOW? What do students need to be able to DO? A working definition of social studies Define “social studies” The reasons we study history Explain the reasons for studying history What anthropologists, archaeologists, and paleontologists do How anthropologists, archaeologists, and paleontologists work together to create an understanding of a prehistoric culture Explain what anthropologists, archaeologists, and paleontologists do Analyze how they work together to create an understanding of a prehistoric culture Identify the tools developed during the Prehistoric Era Analyze the impact of tool development and use on the cultures of that time period Explain why many nomadic societies settled into agrarian civilizations The timeline of tool development from the Prehistoric Era The impact of tool development and use on the cultures of that time period Why many nomadic societies settled into agrarian civilizations The essential resources necessary for a society to thrive The defining characteristics of the Stone Age and the Bronze Age Identify the essential resources necessary for a society to thrive The defining characteristics of Cro-Magnons and Neanderthals Identify the characteristics of the Stone Age and the Bronze Age The causes and effects of the Neolithic Revolution Compare and contrast the Cro-Magnons and Neanderthals Analyze the causes and effects of the Neolithic Revolution I Can… Statements I Can… define “social studies.” I Can… explain the reasons we study history. I Can… explain what anthropologists, archaeologists, and paleontologists do. I Can… analyze how these people work together to create an understanding of a prehistoric culture. I Can… identify the tools developed during the Prehistoric Era. I Can… analyze the impact of tool development and use on the cultures of that time period. I Can… explain why many nomadic societies settled into agrarian civilizations. I Can… identify the essential resources necessary for a society to thrive. I Can… identify the characteristics of the Stone Age and the Bronze Age. I Can… compare and contrast the Cro-Magnons and Neanderthals. I Can… analyze the causes and effects of the Neolithic Revolution. Unit 1- Essential Standards HISTORY H.1.3 Use primary and secondary sources to interpret various historical perspectives. H.2.3 Explain how innovation and/or technology transformed civilizations, societies, and regions over time (e.g., agricultural technology, weaponry, transportation, and communication). GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY G&EL.1.1 Explain how the physical features and human characteristics of a place influenced the development of civilizations, societies, and regions (e.g., location near rivers and natural barriers, trading practices, and spread of culture). G&EL.1.2 Explain the factors that influenced the movement of people, goods, and ideas and the effects of that movement on societies and regions over time (e.g., scarcity of resources, conquests, desire for wealth, disease, and trade). CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT C&G.1.1 Explain the origins and structures of various governmental systems (e.g. democracy, absolute monarchy and constitutional monarchy). C&G.1.4 Compare the role (e.g. maintain order and enforce societal values and beliefs) and evolution of laws and legal systems (e.g. need for and changing nature of codified system of laws and punishment) in various civilizations, societies and regions. ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY E&FL.1.1 Explain how conflict, compromise, and negotiation over the availability of resources (natural, human and capital) impacted the economic development of various civilizations, societies and regions (e.g. competition for scarce resources, unequal distribution of wealth and the emergence of powerful trading networks). E&FL.1.2 Explain how quality of life is impacted by economic choices of civilizations, societies and regions. CULTURE C.1.1 Analyze how cultural expressions reflected the values of civilizations, societies and regions (e.g., oral traditions, art, dance, music, literature, and architecture). C.1.3 Summarize systems of social structure within various civilizations and societies over time (e.g. Roman class structure, Indian caste system and feudal, matrilineal and patrilineal societies). G&EL.1.3 Compare distinguishing characteristics of various world regions (e.g., physical features, culture, political organization, and ethnic make-up). G&EL.1.4 Explain how and why civilizations, societies and regions have used, modified and adapted to their environments (e.g., invention of tools, domestication of plants and animals, farming techniques and creation of dwellings). G&EL.2.1 Use maps, charts, graphs, geographic data and available technology tools to draw conclusions about the emergence, expansion, and decline of civilizations, societies, and regions. Academic Vocabulary: agrarian, artifact, Stone Age, Bronze Age, Neolithic Revolution, anthropologist, archaeologist, paleontologist Academic Vocabulary: resources, agrarian, hunter-gatherer, nomadic, Neolithic Revolution, migration, location, scarcity Academic Vocabulary: agrarian civilization, nomadic culture Academic Vocabulary: domestication, innovation, scarcity Academic Vocabulary: cuneiform, domestication, agricultural innovation, resources, cave paintings, community, artifact Unit 1- Common Core Standards READING WRITING CMS CCSS Power Standards: CMS CCSS Power Standards: R.6-8.1 Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources. W.6-8.1 Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. R.6-8.10 Read and comprehend history/social studies texts in the grade 6 text complexity band independently and proficiently. W.6-8.2 Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/ experiments, or technical processes. Additional Reading Standards: Additional Writing Standards: R.6-8.2. Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of the source distinct from prior knowledge or opinions. W.6-8.4 Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. R.6-8.6 Identify aspects of a text that reveal an author’s point of view or purpose (e.g., loaded language, inclusion or avoidance of particular facts). R.6-8.7 Integrate visual information (e.g., in charts, graphs, photographs, videos, or maps) with other information in print and digital texts. R.6-8.8 Distinguish among fact, opinion, and reasoned judgment in a text. R.6-8.9 Analyze the relationship between a primary and secondary source on the same topic. W.6-8.5 With some guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on how well purpose and audience have been addressed. W.6-8.9 Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. Unit 1- Concepts with Subtopics Aligned to Unit Generalizations HISTORY GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY H.1.3, H.2.3 G&EL.1.1, G&EL.1.2, G&EL.1.3, G&EL.1.4, G&EL.2.1 C&G.1.1, C&G.1.4 E&FL.1.1, E&FL.1.2 Time: Era 1-2, may touch the beginning of Era 3 Ice Age Stone Age Bronze Age Paleolithic Mesolithic Neolithic Location: (absolute and relative) Olduvai Gorge Africa Fertile Crescent Asia Europe Indus River Valley Yellow River Valley Leadership: Government Structure: Military Innovation: Citizenship: Rules and Laws: Historical Figures: Mary Leakey Louis Leakey Place: (physical & human characteristics) Fertile soil Mountainous Access to resources River valleys Economic Development Division of labor Trade Development of agriculture Population growth Access to resources leading to exploration, conquest, and settlement Technological Developments: Agricultural Tools Communication Cultural Developments: Nomadic cultures Agrarian cultures Connections to Today: Archaeologists Paleontologists Anthropologists Natural Resources: Stone Bronze Wood Metal Water Animals Food sources—huntergatherer to agrarian Irrigation Agriculture Movement: Nomads Hunter-gatherer Neolithic Revolution Migration settlement The need for all these things stems from the development of permanent civilizations: As people live together in closer proximity and as population grows due to agricultural and technological developments, communities expand and eventually develop the need for leaders, social structures, military, citizenship, and rules and laws. Quality of Life Population growth Surplus of food due to agricultural developments CULTURE C.1.1, C.1.3 People: Cro-Magnon Neanderthal Hominids Lucy Australopithecine Homo habilis Homo erectus Homo sapiens Cultural Expression: Cave paintings Artifacts Tools Religion Art Social Structure Settling of nomadic cultures into agrarian civilizations Division and specialization of labor Formalized religion Unit 2- Geography of Ancient Civilizations Essential Standards – H.2.3, G&EL.1.1, G&EL.1.2, G&EL.1.3, G&EL.1.4, G&EL.2.1, C&G.1.1, C&G.1.4, E&FL.1.1, E&FL.1.2, C.1.1 HISTORY GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY CULTURE Unit Overview In this unit, students will study the 4 cradles of civilization in order to understand how physical geography shaped the social, economic and political development of ancient civilizations. Students should develop an understanding of how ancient societies used technology to change their environment as well as how the environment shaped the development of that technology. Students should draw conclusions about ancient civilizations based upon patterns of migration and settlement. Geographical features and resources and how they influenced ancient civilizations should be emphasized. Generalizations 1. Physical geographical features and resources of an area determine the ability of a culture to create a successful permanent civilization in that area. 2. For a permanent civilization to thrive successfully, it should have access to food sources (meat and vegetation), fertile soil for agricultural development, sources of shelter such as forests or the ability to create shelter (wood, animal skins, etc), and water for drinking and irrigation. 3. The needs created by the environment directly contribute to the types of technology developed by the culture that settles in that environment. 4. Once a culture settles in an environment, it develops technology to shape that environment into that which will best improve and propagate that culture. 5. When geographical features change, the settled cultures must adapt or move. 6. Social structures often stem from a culture’s needs in relation to the environment (e.g., the need for huntergatherers, domestication of work and food animals, development of agriculture). 7. Political structures become necessary as populations grow and permanent civilizations expand. 8. With technological and agricultural advancements, ancient civilizations improved their economies through such techniques as irrigation, planting, surplus, domestication, travel, and trade. Essential Questions 1. What geographical features are beneficial to the establishment of a permanent civilization? 2. What geographical features are detrimental to the establishment of a permanent civilization? 3. How did geography shape the social development of ancient civilizations? 4. How did geography shape the economic development of ancient civilizations? 5. How did geography shape the political development of ancient civilizations? 6. How did ancient civilizations use technology to change their environment? 7. How did the environment shape the development of a civilization’s technology? 8. What conclusions can you draw about ancient civilizations based upon patterns of migration and settlement? 9. What are the beneficial geographical features of the Mesopotamian region that encouraged permanent civilization? 10. What are the beneficial geographical features of the Egyptian region that encouraged permanent civilization? 11. What are the beneficial geographical features of the Indian region that encouraged permanent civilization? 12. What are the beneficial geographical features of the Yellow River Valley that encouraged permanent civilization? Unit Vocabulary Agriculture Migration Aryan Mohenjo-Daro Civilization Mountains Conquest Movement Cooperation Nile River Domestication Place Fertile Crescent Region Fire Resources Flood Silt Harappa Tigris & Euphrates Rivers Human-environment interaction Vegetation zones Innovation Irrigation Yellow (Huang He) River Unit 2- Goals What do students need to KNOW? Beneficial geographical features and resources Detrimental geographical features The geographical features and resources that contributed to the success of Mesopotamia The geographical features and resources that contributed to the success of Egypt What do students need to be able to DO? Identify beneficial and detrimental geographical features and resources Explain the geographical features and resources of Mesopotamia Explain the geographical features and resources of Egypt Explain the geographical features and resources of India Explain the geographical features and resources of China The geographical features and resources that contributed to the success of India Identify the types of technology these cultures developed The geographical features and resources that contributed to the success of China Analyze how these cultures used technology to change their environments The types of technology developed by the cultures that settled in these areas Analyze how the environment determined the types of technology these cultures developed How these cultures used technology to change their environment Identify the geographical changes that influence a culture’s ability to remain settled in that area How the environment determined the types of technology these cultures developed Analyze the connection between social structures and the society’s relationship with the environment The geographical changes that influence a culture’s ability to remain settled in that area Analyze how economies develop based on agricultural and technological developments How social structures arise from the society’s relationship with the environment Analyze the development of political systems as populations grow and civilizations expand How economies develop based upon environmental (agricultural and technological) advances How political systems become necessary as populations grow and civilizations expand I Can… Statements I Can… identify beneficial and detrimental geographical features and resources. I Can… explain the geographical features and resources of Mesopotamia. I Can… explain the geographical features and resources of Egypt. I Can… explain the geographical features and resources of India. I Can… explain the geographical features and resources of China. I Can… identify the types of technology developed in the 4 cradles of civilization. I Can… analyze how these cultures used technology to change their environments. I Can… analyze how the environment determined the types of technology these cultures developed. I Can… identify the geographical changes that influence a culture’s ability to remain settled in that area. I Can… analyze the connection between social structures and the society’s relationship with the environment. I Can… analyze how economies develop based on agricultural and technological developments. I Can… analyze the development of political systems as populations grow and civilizations expand. Unit 2- Essential Standards HISTORY H.2.3 Explain how innovation and/or technology transformed civilizations, societies, and regions over time (e.g., agricultural technology, weaponry, transportation, and communication). GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY G&EL.1.1 Explain how the physical features and human characteristics of a place influenced the development of civilizations, societies, and regions (e.g., location near rivers and natural barriers, trading practices, and spread of culture). G&EL.1.2 Explain the factors that influenced the movement of people, goods, and ideas and the effects of that movement on societies and regions over time (e.g., scarcity of resources, conquests, desire for wealth, disease, and trade). G&EL.1.3 Compare distinguishing characteristics of various world regions (e.g., physical features, culture, political organization, and ethnic make-up). CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT C&G.1.1 Explain the origins and structures of various governmental systems (e.g. democracy, absolute monarchy and constitutional monarchy). C&G.1.4 Compare the role (e.g. maintain order and enforce societal values and beliefs) and evolution of laws and legal systems (e.g. need for and changing nature of codified system of laws and punishment) in various civilizations, societies and regions. ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY E&FL.1.1 Explain how conflict, compromise, and negotiation over the availability of resources (natural, human and capital) impacted the economic development of various civilizations, societies and regions (e.g. competition for scarce resources, unequal distribution of wealth and the emergence of powerful trading networks) CULTURE C.1.1 Analyze how cultural expressions reflected the values of civilizations, societies and regions (e.g., oral traditions, art, dance, music, literature, and architecture). E&FL.1.2 Explain how quality of life is impacted by economic choices of civilizations, societies and regions. G&EL.1.4 Explain how and why civilizations, societies and regions have used, modified and adapted to their environments (e.g., invention of tools, domestication of plants and animals, farming techniques and creation of dwellings). G&EL.2.1 Use maps, charts, graphs, geographic data and available technology tools to draw conclusions about the emergence, expansion, and decline of civilizations, societies, and regions. Academic Vocabulary: Agriculture, irrigation, domestication, innovation, cooperation Academic Vocabulary: resources, irrigation, trade routes, silt, flood, fire, Fertile Crescent, Harappa, Aryan, Yellow River Valley, Tigris & Euphrates Rivers, vegetation zones, Mohenjo-Daro, migration, Nile River Academic Vocabulary: Pharaoh, emperor, conquest, civilization, cooperation, dynasty, Hammurabi’s code Academic Vocabulary: domestication, agricultural, innovation, resources, social class, irrigation, artisan, trade routes Unit 2- Common Core Standards READING WRITING Academic Vocabulary: cuneiform, domestication, agricultural, innovation, resources, social class, polytheism, hieroglyphics, trade routes, cooperation CMS CCSS Power Standards: CMS CCSS Power Standards: R.6-8.1 Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources. W.6-8.1 Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. R.6-8.10 Read and comprehend history/social studies texts in the grade 6 text complexity band independently and proficiently. W.6-8.2 Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/ experiments, or technical processes. Additional Reading Standards: Additional Writing Standards: R.6-8.2. Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of the source distinct from prior knowledge or opinions. W.6-8.4 Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. R.6-8.6 Identify aspects of a text that reveal an author’s point of view or purpose (e.g., loaded language, inclusion or avoidance of particular facts). R.6-8.7 Integrate visual information (e.g., in charts, graphs, photographs, videos, or maps) with other information in print and digital texts. R.6-8.8 Distinguish among fact, opinion, and reasoned judgment in a text. R.6-8.9 Analyze the relationship between a primary and secondary source on the same topic. W.6-8.5 With some guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on how well purpose and audience have been addressed. W.6-8.9 Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. Unit 2- Concepts with Subtopics Aligned to Unit Generalizations HISTORY GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT CULTURE H.2.3 G&EL.1.1, G&EL.1.2, G&EL.1.3, G&EL.1.4, G&EL.2.1 C&G.1.1, C&G.1.4 E&FL.1.1, E&FL.1.2 Time: Eras 2 and 3 Location: (absolute and relative) Fertile CrescentMesopotamia Egyptian River Valley Indus River Valley Yellow River Valley Leadership: Emperor Pharaoh King Military Ruler Conflict & Compromise: Trade routes Expanding markets Competition for resources and goods Access to natural resources Access to human capital People: Mesopotamians Egyptians Indians Chinese Economic Development Trade routes Math systems Writing systems Record-keeping Supply, demand, and surplus Values & Beliefs, Religion: Religious artifacts Religious structures Religious records Religious traditions Innovations: Agricultural technology Weaponry Travel Trade Irrigation Surplus Math systems Writing systems Planting-harvesting developments Place: (physical & human characteristics) Rivers and bodies of water Natural barriers Fertile soils Temperate climate Natural Resources: Leather Iron Wood Silver Stone Bronze Water Vegetation Animals Government Structure: Development of political structures due to permanent settlement Military Innovation: Weaponry Organized military invasions and conquests Rules and Laws: Hammurabi’s Code Quality of Life Permanent settlements Political and social structures Improving economies with agricultural developments Movement: Trade routes Migration due to natural disasters Conquest & colonization C.1.1 Cultural Expression: Art Religion Architecture Literary tradition Social Structure Development of social classes, caste systems Division and specialization of labor Unit 3- Rise and Fall of Civilization Essential Standards –H1.3, H2.3, H2.4, G1.1, G1.4, G2.1, C&G1.4, E&FL1.1, C1.1, C1.2, C1.3 HISTORY GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT ECONOMICS AND FINANCIAL LITERACY CULTURE Unit Overview During this unit, students identify and analyze the 5 primary factors that relate to the emergence, rise, expansion, and fall of civilizations: technology, environment, leadership, governmental and social structures, and cultural value systems. When choosing civilizations, teachers should represent a variety of areas. If teachers are following a chronological study format, they can choose civilizations from Era 3: 1000 BCE – 300 CE; however, teachers may also choose to represent multiple eras in order to reinforce the connection that all civilizations across time are subject to the same primary factors in their developmental arc. Students will use the primary factors to examine different global civilizations in analyzing similarities and differences among those civilizations over time. Based on the evidence, students will then need to be able to provide explanations of the impacts these factors have on civilizations. Students may also want to develop their own civilizations as a project-based learning experience using the factors to guide their product. Generalizations 1. Throughout time, civilizations have emerged, expanded, and declined due to 5 primary factors: technology, environment, leadership, governmental and social structures, and cultural value systems. 2. Technological developments influence the development of a civilization. 3. Access to resources contributes to the success and/or failure of a civilization. 4. Leadership impacts the growth and/or decline of a civilization. 5. The structures of both the government and the society play important roles in the rise and fall of a civilization. 6. A civilization’s cultural value system influences its success and/or failure. Essential Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What advantages does civilization offer society? How do technological developments impact the growth or decline of a civilization? How have competition, conflict and compromise over natural resources impacted development? How have key historical figures and cultural groups influenced society? How do a society’s governmental and social structures affect its development? What impact does a civilization’s cultural value system have on its success and/or failure? Unit Vocabulary agricultural artisan city-state cuneiform domestication dynasty emperor Great Wall of China Hammurabi's Code hieroglyphics innovation irrigation law pharaoh polytheism resources social class trade routes Unit 3- Civilizations to Consider for Case Study Civilization Time Period (Era) Leader(s) Egypt 3000-800 BCE (Era 2-3) Ramses II Carthage 650-146 BCE (Era 3) Hannibal Mali 1230-1600 CE (Era 5+) Mansa Musa Songhai Empire 1340-1591 CE (Era 5+) Sonni Ali, Askia Muhammed the Great Olmec 1200-400 BCE (Eras 2-3) Unknown Aztec 1300-1581 CE (Era 5+) Moctezuma I or II, Tlacaelel Central America Mayans 1800 BC-800 CE (Eras 2-4) Dynastic rule of city-states by hereditary position South America Incans 1438-1533 CE (Era 5+) Atahualpa, Pachacuti Babylonia 1894-539 BCE (Eras 2-4) Hammurabi, Nebuchadnezzar I Sumer 4500-1700 BCE (Eras 1-2) Gilgamesh, Sargon Mongol Empire 1206-1370 CE (Era 5) Genghis Khan Indus Valley 3000-1700 BCE (Era 2) Unknown Phoenicia 2300-1200 BCE (Era 2) Nebuchadnezzar, King Hiram, King David, King Solomon Persia 550-330 BCE (Era 3) Cyrus the Great Shang Dynasty 1600-1046 BCE (Era 2) Wu Ding Zhou Dynasty Western 1029-771 BCE (Eras 23) King Zhao, Confucius, Laozi Area/Region Northern Africa Southern Africa Mexico Mesopotamia Northern Asia Southwest Asia Eastern 770-256 BCE (Era 3) China Qin Dynasty Han Dynasty Japan Heian Period 221-206 BCE (Era 4) Qin Shi Huangdi Western 206 BCE-9 CE (Era 4) Liu Bang, Emperor Wu, Wang Mang Eastern 25-220 CE (Era 4) 794-1185 CE (Eras 4-5) Fugiwara no Michinaga Greece 1000-323 BCE (Era 3) Alexander the Great, Homer, Pericles Roman Empire 27 BCE-476 CE (Eras 3-4) Julius Caesar, Augustus, Constantine Western Europe Reminder: Teachers are NOT expected to teach ALL these civilizations. Students need 3-5 civilizations to learn the objectives of the unit. Unit 3- Goals What do students need to KNOW? What do students need to be able to DO? Biographical information about notable leaders of 35 major civilizations Use primary and secondary sources to develop an understanding of 3-5 major civilizations Governmental and social structures of 3-5 major civilizations Major technological developments of 3-5 major civilizations Use maps, charts, and geographic data to support conclusions about the development of 3-5 major civilizations Explain how technological developments influence the growth of 3-5 major civilizations Identify and analyze the role of the environment in the rise and decline of 3-5 major civilizations Analyze how competition, conflict, and compromise over natural resources affect the development of 3-5 major civilizations Explain the governmental and social structures of 35 major civilizations Explain the cultural value systems of 3-5 major civilizations, including references to cultural expressions and religion, for several major civilizations Analyze the roles of those structures in the rise and fall of their respective civilizations Analyze the effects of key historical figures and cultural groups within 3-5 major civilizations Compare and contrast the rise and fall of 3-5 major civilizations Environmental factors for 3-5 major civilizations Cultural value systems of 3-5 major civilizations I Can… Statements I Can… explain the advantages of civilization. I Can… identify the technological developments of a variety of civilizations HISTORY H1.3 Use primary and secondary sources to interpret various historical perspectives. H2.3 Explain how innovation and/or technology transformed civilizations, societies and regions over time (e.g. agricultural technology, weaponry, transportation and communication). GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY G1.1 Explain how the physical features and human characteristics of a place influenced the development of civilizations, societies and regions (e.g., location near rivers and natural barriers, trading practices and spread of culture). G1.4 Explain how and why civilizations, societies and regions have used, CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT ECONOMICS AND FINANCIAL LITERACY C&G1.4 Compare the role (e.g. maintain order and enforce societal values and beliefs) and evolution of laws and legal systems (e.g. need for and changing nature of codified system of laws and punishment) in various civilizations, societies and regions. E1.1 Explain how conflict, compromise, and negotiation over the availability of resources (natural, human and capital) impacted the economic development of various civilizations, societies and regions (e.g. competition for scarce resources, unequal distribution of wealth and the emergence of powerful CULTURE C1.1 Analyze how cultural expressions reflected the values of civilizations, societies and regions (e.g. oral traditions, art, dance, music, literature, and architecture). C1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations, and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, H2.4 Explain the role that key historical figures and cultural groups had in transforming society (e.g., Mansa Musa, Confucius, Charlemagne, and Qin Shi Huangdi). modified and adapted to their environments (e.g., invention of tools, domestication of plants and animals, farming techniques and creation of dwellings). trading networks) Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam and Judaism). C1.3 Summarize systems of social structure within various civilizations and societies over time (e.g. Roman class structure, Indian caste system and feudal, matrilineal and patrilineal societies). G2.1 Use maps, charts, graphs, geographic data and available technology tools to draw conclusions about the emergence, expansion, and decline of civilizations, societies and regions. Academic Vocabulary: Academic Vocabulary: Academic Vocabulary: Academic Vocabulary: Academic Vocabulary: city-state, pharaoh, dynasty, domestication, Great Wall of China, emperor, Hammurabi, Qin Shi Huangdii, Ramses II resources, irrigation, trade routes, domestication, agricultural city-state, pharaoh, dynasty, domestication, Great Wall of China, emperor, Hammurabi, Shi Huang Di, Ramses II domestication, agricultural, innovation, resources, social class, irrigation, artisan, trade routes cuneiform, domestication, agricultural, innovation, resources, social class, polytheism, hieroglyphics, trade routes Unit 3- Common Core Standards READING WRITING CMS CCSS Power Standards: CMS CCSS Power Standards: R.6-8.1 Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources. W.6-8.1 Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. R.6-8.10 Read and comprehend history/social studies texts in the grade 6 text complexity band independently and proficiently. W.6-8.2 Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/ experiments, or technical processes. Additional Reading Standards: Additional Writing Standards: R.6-8.2. Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of the source distinct from prior knowledge or opinions. W.6-8.4 Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. R.6-8.7 Integrate visual information (e.g., in charts, graphs, photographs, videos, or maps) with other information in print and digital texts. W.6-8.5 With some guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on how well purpose and audience have been addressed. Unit 3- Concepts with Subtopics Aligned to Unit Generalizations GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY HISTORY H1.3, H2.3, H2.4 Technology Agricultural technology weaponry transportation communication Leadership Gilgamesh Sargon of Akkad Hammurabi King David Genghis Khan Ramses II G1.1, G1.4, G2.1 Environment Location near rivers and natural barriers Natural, physical environment Access to natural resources Trading practices Spread of cultures Invention of tools Domestication of plants and animals Farming techniques Creation of dwellings Maps, charts, graphs CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT C&G1.4 Leadership Hammurabi Qin Shi Huangdi Confucius Atahualpa Askia Muhammed the Great Hannibal ECONOMICS AND FINANCIAL LITERACY E1.1 Environment Competition over natural resources Distribution of wealth Trade networks Economic development due to natural resources Governmental & Social Structures Type of government Social classes or castes Legal systems and laws Land ownership Centralized/ decentralized Citizenship Skill development due to natural resources (e.g., shipbuilding, invention of the wheel) Leadership Social classes vs. government Specialization of labor and organized workforces Governmental policies regarding natural resources and wealth CULTURE C1.1, C1.2, C1.3 Cultural Value Systems Cultural expressions (e.g., oral traditions, art, dance, music, literature, and architecture) Religion (e.g., beliefs, practices, and spread) Gender roles Slavery Governmental & Social Structures Social structures (e.g., Roman class structure, Indian caste system, feudal, matrilineal, and patrilineal societies) Gender roles Slavery Unit 3- Concepts with Subtopics Aligned to Unit Generalizations GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY HISTORY H1.3, H2.3, H2.4 Technology Agricultural technology weaponry transportation communication Leadership Gilgamesh Sargon of Akkad Hammurabi King David Genghis Khan Ramses II G1.1, G1.4, G2.1 Environment Location near rivers and natural barriers Natural, physical environment Access to natural resources Trading practices Spread of cultures Invention of tools Domestication of plants and animals Farming techniques Creation of dwellings Maps, charts, graphs CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT C&G1.4 Leadership Hammurabi Qin Shi Huangdi Confucius Atahualpa Askia Muhammed the Great Hannibal ECONOMICS AND FINANCIAL LITERACY E1.1 Environment Competition over natural resources Distribution of wealth Trade networks Economic development due to natural resources Governmental & Social Structures Type of government Social classes or castes Legal systems and laws Land ownership Centralized/ decentralized Citizenship Skill development due to natural resources (e.g., shipbuilding, invention of the wheel) Leadership Social classes vs. government Specialization of labor and organized workforces Governmental policies regarding natural resources and wealth CULTURE C1.1, C1.2, C1.3 Cultural Value Systems Cultural expressions (e.g., oral traditions, art, dance, music, literature, and architecture) Religion (e.g., beliefs, practices, and spread) Gender roles Slavery Governmental & Social Structures Social structures (e.g., Roman class structure, Indian caste system, feudal, matrilineal, and patrilineal societies) Gender roles Slavery Unit 3- “Case Study” Ideas In order to conduct “case studies” of selected civilizations, teachers may consider collecting a variety of items such as: Primary and secondary texts Video clips (Discovery Ed, BBC, National Geographic, internet resources) Maps of the areas at that time period (Maps 101, internet resources) Biographical information about the key historical figures or groups (textbooks, internet resources, video clips, Discovery Ed) Information about the government type and structure as well as the social structure of the civilization (textbooks, articles, internet resources) Information about the religion and value systems of the culture (religious documents—may be primary sources, textbooks, internet resources) Information about the policies regarding crime and punishment (legal documents, law codes, primary sources, articles, textbooks, internet resources) Information about the technological developments of the civilization such as agricultural technology, weaponry, transportation, and communication (textbook, video clips, Discovery Ed, internet resources) Unit 3- List of Additional Concepts with Subtopics (may be used in this unit or in other units) HISTORY GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT ECONOMICS AND FINANCIAL LITERACY CULTURE H1.3, H2.3, H2.4 G1.1, G1.4, G2.1 C&G1.4 E1.1 C1.1, C1.2, C1.3 Time: Unit Three – Rise and Fall of Civilization Location: (absolute and relative) Fertile CrescentMesopotamia (Tigris & Euphrates Rivers) & Egyptian (Nile River Valley) Afroerasia Indus River Valley Ganges River Valley Huang He (Yellow) River Valley Yangzi River Valley Mesoamerica Teotihuacan Australia/Oceania Leadership: Hammurabi Qin Shi Huangdi Ramses II Genghis Khan Mansa Musa Confucius Charlemagne Competition, Conflict & Compromise: Silk Road Mediterranean Trade Routes People: Indo-European African Asian Pacific Islander Nomads Farmers Urban Dwellers Era 3 – Farming and the Emergence of Complex Societies (10,000 – 1,000 BCE) Historical Figures: Gilgamesh Sargon of Akkad Hammurabi King David King Solomon Nebuchadnezzar Confucius Laozi Invasions/Conquests: Sumerian City-States Babylonian Empire Hebrews, Israelites, and Jews Phoenicians Assyrian Empire New Babylonian Empire Egyptian Empire (Old Kingdom, Middle Place: (physical & human characteristics) Steppe Desert River Valley Growing Season Climate Zones Natural Resources: Domesticated Animals and Plants Government Structure: Authoritarian Monarchy Centralized Decentralized Economic Development Bronze Metallurgy Iron Metallurgy The Wheel Horse-drawn Chariots Shipbuilding Specialization of Labor Military Innovation: Bow and Arrow Walled Cities Trade: Trade Networks – Phoenicians & Silk Road Citizenship: Factors of Citizenship – Comparison of Ancient and Modern Citizenship Quality of Life Emergence of Social Classes Rules and Laws: Hammurabi’s Code Cultural Expression: Writing Forms – Hieroglyphics and Cuneiform Alphabet Egyptian Tombs and Mummification Pottery Values & Beliefs, Religion: Polytheism Monotheism Temple Communities Ritual Sacrifices Spirituality The Mandate of Heaven Mayan Calendar and Writing System Kingdom, and New Kingdom) Kush Kingdom Bantu Migration Harappan Society Aryan Migration Vedic Age Yangshao Society Xia Dynasty Shang Dynasty Zhou Dynasty Warring States Period Early Han Dynasty (Unification of China) Olmecs & Mayas Aztecs and Incas Native American Groups Comparisons to Today: Ancient and Modern Life Ancient and Modern Citizenship Leather Iron Wood Silver Social Structure Patriarchal Society Matriarchal Society Caste System - Varnas Role of Women Peasants Slaves Movement: Nomads/Migration Silk Road Water Routes Pastoral Nomadism Region: Southwest Asia South Asia East Asia Southeast Asia Afroerasia North Africa East Africa West Africa Sub-Saharan Africa South Africa Australia/Oceania Mesoamerica The Americas Unit 4- Classical Civilizations Essential Standards – H.1.2, H.1.3, H.2.1, H.2.3, H.2.4, G&EL.1.1, G&EL.1.2, G&EL.2.1, C&G.1.1, C&G.1.2, C&G.1.3, C&G.1.4, E&FL.1.1, E&FL.1.2, C.1.2, C.1.3 HISTORY GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY CULTURE Unit Overview In this unit, students will study the development of civilizations into city-states and then the transition to empires. Students should focus on the Persian Empire (Achaemenid, Seleucid, Parthian, Sassanid, and Classical Persia), unification of China (Confucianism, Daoism, Legalism, Qin Dynasty, Early Han Dynasty, and Later Han Dynasty), Classical India, Greek civilization, and Roman civilization in order to develop an understanding of the reasons behind the creation of city-states and then empires as well as the process (including expansion and colonization) and the effects of these developments. Students need to develop an understanding of the influence of the conqueror’s attitude and beliefs toward the conquered peoples and how that translates into the success and/or failure of the empire’s newly acquired territory (e.g., Cyrus’s respect for other cultures’ customs). Students should also examine cross-cultural exchanges (e.g., the influence of the Silk Road) and analyze the fall of the Roman Empire and the rise of religious authority. Generalizations 1. A variety of factors determines a culture’s development of city-states and then empires, including a need or desire for access to natural resources, a desire for power and control over neighboring areas, an expanding population, a need or desire for access to new trading markets, and the desire to diffuse culture and religion. 2. The structure, order, and ability of a civilization’s military has a significant impact on its success and/or failure as an empire. 3. Several early civilizations expanded and maintained their control over ever-broadening areas by encouraging peace and tolerance with the conquered peoples. 4. Early civilizations saw many notable achievements, often due to contact with other cultures and civilizations. 5. The government, leadership structures, and citizenship rules and regulations of early civilizations varied over time and across regions, but many changed and adapted as the empire expanded in order to handle the problems that arise with governing large areas. 6. Contact with new cultures and civilizations brought about many innovations and changes in art, architecture, and religion for the early civilizations. 7. Religion played an important role in the government and leadership of many early civilizations. 8. The governmental structures of Greece and Rome have significantly impacted modern forms of government. 9. Many aspects of early civilizations have contributed to modern culture. Essential Questions 1. What is the general developmental process of city-states and empires? 2. How did the military structures of different civilizations impact their success and/or failure as an empire? 3. When conquering and annexing a culture, why is it important to encourage peace, and how is that accomplished? 4. What are the notable achievements of the different civilizations? 5. What are the similarities and differences among early civilizations concerning government and leadership structures? 6. As empires expanded, how did their government and leadership structures adapt? 7. What are the similarities and differences among early civilizations regarding citizenship? 8. As empires expanded, how did regulations regarding citizenship adapt? 9. As empires expanded, how did art, architecture, and religion change for the early civilizations? 10. In what ways was religion often tied to government and leadership in early civilizations? 11. How have Greece and Rome laid the foundations for modern government? 12. How did early civilizations contribute to modern culture? Unit Vocabulary 12 Tables Han Dynasty philosophy Aristocracy Hellenes plebeian Athens hieroglyphics polis Calligraphy mercenaries polytheism caste system militia Republic Ch’in Dynasty Minoans Rosetta Stone Chou Dynasty monarchy Satrap city-state monotheism senate conscription oligarchy Shang Dynasty democracy papyrus Sparta dictator patrician T’ang Dynasty dynasty Pax Romana Trojans empire peninsula Gupta Dynasty pharaoh Key People Alexander the Great Amenhotep IV/Akhenaten Aristotle Attila Caesar Augustus Confucius Constantine Cyrus the Great Darius I Hammurabi Hannibal Hatshepsut Julius Caesar Marcus Aurelius Menes Pericles Philip II Plato Ramses the Great Socrates Wu Chao Zoroaster Unit 4- Goals What do students need to KNOW? What do students need to be able to DO? The factors that contribute to the establishment of city-states and the transition to empires Identify the factors that contribute to the establishment of citystates and the transition to empires The role of the military in the creation of empires Explain the role of the military in the creation of empires The influence of the conqueror’s attitude toward the culture and customs of the conquered people in maintaining control Analyze the influence of the conqueror’s attitude toward the culture and customs of the conquered people in maintaining control The notable achievements of several early civilizations Identify the notable achievements of several early civilizations The similarities and differences among early civilizations in relation to government and leadership structures Compare and contrast government and leadership structures in several early civilizations The similarities and differences among early civilizations in relation to citizenship Compare and contrast the rules and regulations regarding citizenship in several early civilizations The ways governments, leadership structures, and citizenship rules and regulations changed and adapted as empires expanded How the art, architecture, and religion of early civilizations changed as empires expanded Analyze the ways in which governments, leadership structures, and citizenship rules and regulations changed and adapted as empires expanded The ways religion was tied to government and leadership in several early civilizations Analyze how the art, architecture, and religion of early civilizations changed as empires expanded Explain how religion was tied to government and leadership in several early civilizations Identify the contributions of Greece and Rome to modern government Identify contributions of other early civilizations to modern cultures The contributions of Greece and Rome to modern government Contributions of other early civilizations to modern cultures I Can… Statements I Can… Identify the factors that contribute to the establishment of city-states and the transition to empires. I Can… Explain the role of the military in the creation of empires. I Can… Analyze the influence of the conqueror’s attitude toward the culture and customs of the conquered people in maintaining control. I Can… Identify the notable achievements of several early civilizations. I Can… Compare and contrast government and leadership structures in several early civilizations. I Can… Compare and contrast the rules and regulations regarding citizenship in several early civilizations. I Can… Analyze the ways in which governments, leadership structures, and citizenship rules and regulations changed and adapted as empires expanded. I Can… Analyze how the art, architecture, and religion of early civilizations changed as empires expanded. I Can… Explain how religion was tied to government and leadership in several early civilizations. I Can… Identify the contributions of Greece and Rome to modern government. I Can… Identify contributions of other early civilizations to modern cultures. Unit 4- Essential Standards HISTORY H.1.2 Summarize the literal meaning of historical documents in order to establish context. H.1.3 Use primary and secondary sources to interpret various historical perspectives. H.2.1 Explain how invasions, conquests, and migrations affected various civilizations, societies, and regions (e.g., Mongol invasion, the Crusades, the Peopling of the Americas and Alexander the Great). H.2.3 Explain how innovation and/or technology transformed civilizations, societies, and regions over time (e.g., agricultural technology, weaponry, transportation, and communication). H.2.4 Explain the role that key historical figures and cultural groups had in transforming society (e.g., Mansa Musa, Confucius, Charlemagne, and Qin Shi Huangdi). Academic Vocabulary: democracy, republic, Athens, Sparta, city-state, peninsula, polis, senate, plebeian, patrician, oligarchy, Pax Romana, 12 Tables, philosophy, empire, senate, satrap, militia GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY G&EL.1.1 Explain how the physical features and human characteristics of a place influenced the development of civilizations, societies, and regions (e.g., location near rivers and natural barriers, trading practices, and spread of culture). G&EL.1.2 Explain the factors that influenced the movement of people, goods, and ideas and the effects of that movement on societies and regions over time (e.g., scarcity of resources, conquests, desire for wealth, disease, and trade). G&EL.2.1 Use maps, charts, graphs, geographic data and available technology tools to draw conclusions about the emergence, expansion, and decline of civilizations, societies, and regions. Academic Vocabulary: resources, plague, peninsula, trade routes CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT C&G.1.1 Explain the origins and structures of various governmental systems (e.g. democracy, absolute monarchy and constitutional monarchy). C&G.1.2 Summarize the ideas that shaped political thought in various civilizations, societies, and regions (e.g., divine right, equality, liberty, citizen participation, and integration of religious principles). C&G.1.3 Compare the requirements for (e.g., age, gender and status) and responsibilities of (e.g., paying taxes and military service) citizenship under various governments. ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY E&FL.1.1 Explain how conflict, compromise, and negotiation over the availability of resources (natural, human and capital) impacted the economic development of various civilizations, societies and regions (e.g. competition for scarce resources, unequal distribution of wealth and the emergence of powerful trading networks) E&FL.1.2 Explain how quality of life is impacted by economic choices of civilizations, societies, and regions. C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations, and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices, and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism). C.1.3 Summarize systems of social structure within various civilizations and societies over time (e.g. Roman class structure, Indian caste system and feudal, matrilineal and patrilineal societies). C&G.1.4 Compare the role (e.g. maintain order and enforce societal values and beliefs) and evolution of laws and legal systems (e.g. need for and changing nature of codified system of laws and punishment) in various civilizations, societies and regions. Academic Vocabulary: city-state, pharaoh, dynasty, Great Wall of China, emperor, dictator, Hammurabi, Ramses II. 12 Tables, aristocracy, democracy, oligarchy, Alexander the Great, Hammurabi, Hannibal, Attila Academic Vocabulary: domestication, agricultural, innovation, resources, social class, irrigation, artisan, trade routes, papyrus Unit 4- Common Core Standards READING CULTURE WRITING Academic Vocabulary: cuneiform, social class, caste system, philosophy, conscription, calligraphy, architecture, polytheism, hieroglyphics, trade routes, Aristotle, Plato, Socrates, Pericles, Confucius, Akhenaten CMS CCSS Power Standards: CMS CCSS Power Standards: R.6-8.1 Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources. W.6-8.1 Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. R.6-8.10 Read and comprehend history/social studies texts in the grade 6 text complexity band independently and proficiently. W.6-8.2 Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/ experiments, or technical processes. Additional Reading Standards: Additional Writing Standards: R.6-8.2. Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of the source distinct from prior knowledge or opinions. W.6-8.4 Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. R.6-8.3. Identify key steps in a text’s description of a process related to history/social studies (e.g., how a bill becomes the law, how interest rates are raised or lowered). R.6-8.6 Identify aspects of a text that reveal an author’s point of view or purpose (e.g., loaded language, inclusion or avoidance of particular facts). R.6-8.7 Integrate visual information (e.g., in charts, graphs, photographs, videos, or maps) with other information in print and digital texts. R.6-8.8 Distinguish among fact, opinion, and reasoned judgment in a text. R.6-8.9 Analyze the relationship between a primary and secondary source on the same topic. W.6-8.5 With some guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on how well purpose and audience have been addressed. W.6-8.9 Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. Unit 4- Concepts with Subtopics Aligned to Unit Generalizations HISTORY GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY H.1.2, H.1.3, H.2.1, H.2.3, H.2.4 G&EL.1.1, G&EL.1.2, G&EL.2.1 C&G.1.1, C&G.1.2, C&G.1.3, C&G.1.4 E&FL.1.1, E&FL.1.2 Time: Era 4-5: Intensified Hemispheric Interactions Location: (absolute and relative) Fertile CrescentMesopotamia Egyptian River Valley Indus River Valley Yellow River Valley Greece Rome Persia Egypt India China Leadership: Genghis Khan Akhenaten Attila Constantine Cyrus Darius I Hannibal Marcus Aurelius Menes Philip II Ramses the Great Competition, Conflict & Compromise: Silk Road Trade routes Resources Mercenaries Militia Historical Figures: Julius Cesar Augustus Alexander the Great Pericles Socrates Plato Aristotle Constantine Invasions & Conquests: Mongol conquests of 1206-1279 Greek and Roman conquests Persian Wars China (1207-1227) Khwarizm (1218-1220) Russia (1219-1224) Comparisons to Today: Addition of Puerto Rico to the US Place: (physical & human characteristics) Desert Steppe Valley River valley mountains Natural Resources: Leather Iron Wood Silver Water Metals Movement: Nomads Silk Road Conquest & colonization Region: Southwest Asia Northeast Africa Eastern Asia Afroeurasia Mesoamerica Government Structure: Traction trebuchet – adapted from the Chinese Aristocracy Democracy Dictator Dynasty Empire Monarchy Oligarchy Pharaoh Republic Satrap senate Economic Development Rosetta Stone Silk Road Coins & money bartering Trade: Silk Road Quality of Life Access to goods from distant markets Innovations in architecture CULTURE C.1.2, C.1.3 People: Confucius Aristotle Pericles Plato Socrates Cultural Expression: Art Architecture Literature Values & Beliefs, Religion: Buddhism Confucianism Taoism Judaism Christianity Polytheism Monotheism Social Structure Caste system Plebians varnas Military Innovation: Traction trebuchet – adapted from the Chinese Strong bows Horse-drawn chariots Advanced weaponry Citizenship: The Yasa Code Aristotle’s Politics Rules and Laws: The Yasa Code Hammurabi’s Code History of the Peloponnesian War The Laws of Manu Unit 5- Religion Essential Standards – H.1.2, H.1.3, H.2.1, H.2.2, H.2.4, G&EL.1.2, G&EL.2.1, C&G.1.1, C&G.1.2, C&G.1.4, E&FL.1.1, C.1.1, C.1.2, C.1.3 HISTORY GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY CULTURE Unit Overview In this unit, students will study the development of several influential religions: Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism. Students should identify and analyze the factors that led to the development of both Eastern and Western religions and ultimately be able to compare and contrast the two. Students should also examine the effects of religious developments, including the ways in which religions were often tied to government and leadership structures in early civilizations. Students should be able to explain how religions both unite and divide humanity. Generalizations 9. Major religions such as Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism have had significant impacts on history, culture, government, and the economy. 10. The development of Eastern and Western religions stemmed from the needs, desires, and problems of a culture; often refer to the writings and/or teachings of a particular individual; and spread, changed, and adapted through contact with and conquest of other cultures. 11. Eastern and Western religions share certain similarities (e.g., reference to the writings and/or teachings of a particular individual) while still being distinct from one another (e.g., monotheistic vs. polytheistic, doctrines). 12. In many early civilizations, religious beliefs, customs, and leaders were often tied to the government and leadership structures of the culture. 13. Throughout history, religions have served to both unite and divide humanity. Essential Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. What factors led to the development of Eastern and Western religions? How have the major religions in history impacted their respective cultural histories? How have the major religions in history impacted their respective cultures? How have the major religions in history impacted their respective economies? How did religions spread, change, and adapt through contact with and conquest of other cultures? What are the similarities among Eastern and Western religions? What are the differences among the Eastern and Western religions? Are religions more similar or different in their beliefs? In what ways were the major religions in history tied to their respective government and leadership structures? 10. How does religion unite and divide humanity? Unit Vocabulary 10 Commandments Filial piety Monotheistic 4 Noble Truths Ganges River Mosque 5 Pillars Hinduism Nirvana Analects Islam Polytheistic Bible Jerusalem Reincarnation Brahmin Judaism Synagogue Buddhism Karma Temple Christianity Koran Temple Mount Church Li Torah Confucianism Mecca Vedas Dharma Messiah Dome of the Rock Moksha Key People Abraham Confucius Jesus Krishna Muhammad Siddhartha Unit 5- Goals What do students need to KNOW? What do students need to be able to DO? the impact of major religions on culture Analyze the impact of major religions on culture the impact of major religions on cultural history Analyze the impact of major religions on cultural history the impact of major religions on government and leadership structures Analyze the impact of major religions on government and leadership structures the impact of major religions on the economy Analyze the impact of major religions on the economy the factors leading to the development of Eastern and Western religions Identify the factors that led to the development of Eastern and Western religions The similarities and differences between Eastern and Western religions Compare and contrast Eastern and Western religions How major religions spread, changed, and adapted through contact with and conquest of other cultures Explain how major religions have spread, changed, and adapted through contact with and conquest of other cultures How religious beliefs, customs, and leaders were tied to the government and leadership structures of many early civilizations Explain how religious beliefs, customs, and leaders were tied to the government and leadership structures of many early civilizations The ways in which religions have united and divided humanity Analyze the ways in which religions have both united and divided humanity I Can… Statements I Can… analyze the impact of major religions on culture. I Can… analyze the impact of major religions on cultural history I Can… analyze the impact of major religions on government and leadership structures. I Can… analyze the impact of major religions on the economy I Can… identify the factors that led to the development of Eastern and Western religions I Can… compare and contrast Eastern and Western religions I Can… explain how major religions have spread, changed, and adapted through contact with and conquest of other cultures I Can… explain how religious beliefs, customs, and leaders were tied to the government and leadership structures of many early civilizations I Can… analyze the ways in which religions have both united and divided humanity Unit 5- Essential Standards HISTORY H.1.2 Summarize the literal meaning of historical documents in order to establish context. H.1.3 Use primary and secondary sources to interpret various historical perspectives. H.2.1 Explain how invasions, conquests, and migrations affected various civilizations, societies, and regions (e.g., Mongol invasion, the Crusades, the Peopling of the Americas and Alexander the Great). H.2.2 Compare historical and contemporary events and issues to understand continuity and change. GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY G&EL.1.2 Explain the factors that influenced the movement of people, goods, and ideas and the effects of that movement on societies and regions over time (e.g., scarcity of resources, conquests, desire for wealth, disease, and trade). G&EL.2.1 Use maps, charts, graphs, geographic data and available technology tools to draw conclusions about the emergence, expansion, and decline of civilizations, societies, and regions. H.2.4 Explain the role that key historical figures and cultural groups had in transforming society (e.g., Mansa Musa, Confucius, Charlemagne, and Qin Shi Huangdi). Academic Vocabulary: Monotheism, polytheism, filial piety, Koran, Bible, Abraham, Confucius, Jesus, Muhammad, Siddhartha, Krishna Academic Vocabulary: resources, trade routes, Ganges River, Mecca, Jerusalem, Temple Mount, Dome of the Rock CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT C&G.1.1 Explain the origins and structures of various governmental systems (e.g. democracy, absolute monarchy and constitutional monarchy). C&G.1.2 Summarize the ideas that shaped political thought in various civilizations, societies, and regions (e.g., divine right, equality, liberty, citizen participation, and integration of religious principles). ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY E&FL.1.1 Explain how conflict, compromise, and negotiation over the availability of resources (natural, human and capital) impacted the economic development of various civilizations, societies and regions (e.g. competition for scarce resources, unequal distribution of wealth and the emergence of powerful trading networks) C&G.1.4 Compare the role (e.g. maintain order and enforce societal values and beliefs) and evolution of laws and legal systems (e.g. need for and changing nature of codified system of laws and punishment) in various civilizations, societies and regions. Academic Vocabulary: 4 Noble Truths, 10 Commandments, 5 Pillars, Vedas, Analects CULTURE C.1.1 Analyze how cultural expressions reflected the values of civilizations, societies and regions (e.g., oral traditions, art, dance, music, literature, and architecture). C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations, and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices, and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism). C.1.3 Summarize systems of social structure within various civilizations and societies over time (e.g. Roman class structure, Indian caste system and feudal, matrilineal and patrilineal societies). Academic Vocabulary: resources, trade routes, temple, church, synagogue, mosque Academic Vocabulary: Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism, nirvana, reincarnation, Koran, Bible, Torah, Vedas, Analects, messiah, Brahmin, Moksha Unit 5- Common Core Standards READING WRITING CMS CCSS Power Standards: CMS CCSS Power Standards: R.6-8.1 Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources. W.6-8.1 Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. R.6-8.10 Read and comprehend history/social studies texts in the grade 6 text complexity band independently and proficiently. W.6-8.2 Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/ experiments, or technical processes. Additional Reading Standards: Additional Writing Standards: R.6-8.2. Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of the source distinct from prior knowledge or opinions. W.6-8.4 Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. R.6-8.6 Identify aspects of a text that reveal an author’s point of view or purpose (e.g., loaded language, inclusion or avoidance of particular facts). R.6-8.7 Integrate visual information (e.g., in charts, graphs, photographs, videos, or maps) with other information in print and digital texts. R.6-8.8 Distinguish among fact, opinion, and reasoned judgment in a text. R.6-8.9 Analyze the relationship between a primary and secondary source on the same topic. W.6-8.5 With some guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on how well purpose and audience have been addressed. W.6-8.9 Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. Unit 5- Concepts with Subtopics Aligned to Unit Generalizations HISTORY GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY H.1.2, H.1.3, H.2.1, H.2.2, H.2.4 G&EL.1.2, G&EL.2.1 C&G.1.1, C&G.1.2, C&G.1.4 E&FL.1.1 Time: Eras 3-5: this unit is a broad look into the history of religion over the ages Location: (absolute and relative) Europe Northern Africa Asia Afroeurasia Middle East China India Rome Jerusalem Mecca Dome of the Rock Leadership: Abraham Confucius Jesus Muhammad Siddhartha Krishna Competition, Conflict & Compromise: Silk Road Trade routes Spread of religious views and texts Adaptation of religious views, customs, and texts via contact Spread of religion as a by-product of empire expansion Historical Figures: Abraham Confucius Jesus Muhammad Siddhartha Krishna Invasions & Conquests: Unification of China Spread of Christianity via Rome and the Crusades Muslim conquest Jewish diaspora Catholicism vs. Protestantism Comparisons to Today: Religion and government Islam vs. Christianity Place: (physical & human characteristics) Steppe Natural Resources: Leather Iron Wood Silver Waterways Access to trade routes, travel, and expansion Movement: Silk Road Empire expansions Travel and trade Government Structure: Roles of religious leaders Divine right to rule Military Innovation: Development of weaponry that aided conquest, such as hardened steel, horse-drawn chariots, better bows Citizenship: Role of religion in citizenship Rules and Laws: 4 Noble Truths 5 Pillars 10 Commandments Analects Vedas Bible Koran Torah Economic Development Silk Road Spread of religion opened new markets for trade Trade: Silk Road Trade routes New markets from conquest CULTURE C.1.1, C.1.2, C.1.3 People: Abraham Confucius Jesus Muhammad Siddhartha Krishna Cultural Expression: Religious texts Art music Values & Beliefs, Religion: religious texts Art music Social Structure Caste system Enslaving conquered people of different religions High social ranking for religious leaders or figures Quality of Life Silk Road Influence of religious customs from other regions Unit 6- Middle Ages to Renaissance Essential Standards – H.1.1, H.1.2, H.1.3, H.2.1, H.2.4, G&EL.1.2, G&EL.2.1, G&EL.2.2, C&G.1.2, C&G.1.3, C&G.1.4, E&FL.1.1, E&FL.1.2, C.1.1, C.1.3 HISTORY GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY CULTURE Unit Overview In this unit, students will study the political, cultural, and economic changes and growth that occurred from the Middle Ages through the Renaissance with particular emphasis on art, science, language, and political thought. Students should be able to trace the conflicts that spread language, scientific theories, artistic ideologies, cultural and religious customs, disease, trade, and territorial boundaries over this time period, and they should be able to identify several specific changes that took place during these time periods. Students should ultimately be able to analyze the impact of the Middle Ages and the Renaissance and explain how these two eras helped to shape modern culture. Generalizations 14. The Middle Ages and the Renaissance brought about political, cultural and economic changes and growth in the civilizations of those eras. 15. Art, science, language, and political thought showed significant changes during these time periods. 16. Conflict and conquest spread language, scientific theories, artistic ideologies, cultural and religious customs, disease, trade, and territorial boundaries. 17. Religion and the Roman Catholic Church played an important role in the culture, economy and political thought of the Middle Ages and the Renaissance. 18. The developments of the Middle Ages and the Renaissance have helped to shape modern culture, economy, and political thought. Essential Questions for the Middle Ages 1. How did the Germanic tribes come to control such a large territory? 2. How did Charlemagne positively impact the Frankish society? 3. What are the reasons behind the conflicts between the Vikings and the Anglo-Saxons, and why did they virtually stop after 1066? 4. How does feudalism work, and what are the advantages and disadvantages of a feudalist society? 5. How did manorialism create the kind of isolation that prevented cultural growth and maintained the social status quo? 6. How did the growth and expansion of the Roman Catholic Church impact the government, art, culture, and scientific theories during the Middle Ages? 7. Although the Crusades were unsuccessful at winning the Holy Land, what were the positive effects of those conflicts? 8. How were disease, knowledge, culture, and economy accelerated by trade routes, particularly those established during inter-cultural conflicts? 9. How did the cultural, economic, and political exchanges that occurred with the Crusades serve to upset the social, political, and economic structures of Europe and Asia? 10. During the middle of the Middle Ages, how did the power and status of the aristocracy begin to trickle down to the common people? 11. How was Emperor Justinian’s rule over the Byzantine Empire different from the rule of prior Byzantine emperors? 12. What were the contributions of Constantinople to the culture of the Middle Ages? 13. How did the Byzantine Empire positively affect Russia? 14. How did the governing policies of the Mongols weaken their control over Russia until Ivan the Great reclaimed it? 15. What were the positives and negatives of the czarist rule over Russia? Essential Questions for the Renaissance 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What were the strengths and weaknesses of the Italian states during the Renaissance? What were some artistic contributions from Italy during this time period? What were some political contributions from Italy during the Renaissance? How have the humanists of the Renaissance impacted modern cultures? Why was the Gutenberg printing press a key invention during the Renaissance? What changes in language occurred during the Renaissance? What pivotal role did Dante Alighieri play in language development during the Renaissance? How did the development of the scientific method revolutionize scientific thought at the start of the Renaissance? 9. During the Renaissance, how did science come into conflict with the doctrines of the Roman Catholic Church, and what were the results? 10. How did the Scientific Revolution instigate revolutions in other fields of learning, particularly in political thought? 11. How were the rights and responsibilities of the common people bolstered during the Renaissance? 12. How did the Renaissance serve as fuel for the American and French Revolutions? 13. What is the fundamental difference between the Middle Ages and the Renaissance? Unit Vocabulary Book of Kells Byzantine Empire Canon law Cavalry Charter Chivalry Code of Justinian Crusades Cyrillic alphabet Divine right Excommunication Feudalism Fief Key People Bartolomeu Dias Cervantes Charlemagne Columbus Da Vinci Dante Descartes Galileo Henry Hudson Joan of Arc Johann Gutenberg John Cabot Keppler Locke Machiavelli Magellan Mansa Musa Martin Luther Michelangelo Montesquieu Newton Richard the Lion-Hearted Rousseau Saladin Shakespeare Vasco da Gama William the Conqueror Guild Hanseatic League Heresy Holy Land Humanism Knight Liege Lord Magna Carta Manorialism Medieval Monarchy Parliament Plague Pope Reformation Renaissance Salt-gold trade Samurai Serf Shogan Silk Road Utopia Vassal Unit 6- Goals What do students need to KNOW? A broad picture of the conflicts and wars that were integral parts of the Middle Ages The impact of Charlemagne on the Frankish society The sources of conflict between the Vikings and the AngloSaxons Why the events of 1066 curbed the conflicts between the Vikings and the Anglo-Saxons How feudalism works and its advantages and disadvantages How manorialism creates isolation and social stagnation The impact of the Roman Catholic Church on government, art, culture, and scientific theories during the Middle Ages The positive effects of the Crusades How disease, knowledge, culture, and economy were accelerated by trade routes How the cultural, economic, and political exchanges of the Crusades upset the social, political, and economic structures of Europe and Asia How the power and status previously held by the aristocracy began to be extended to the common people The influence of Emperor Justinian and the Byzantine Empire The contributions of Constantinople to the cultures of the Middle Ages The positive effects of the Byzantine Empire on Russia How the governing policies of the Mongols were ineffective in maintaining their control over Russia The positives and negatives of czarist rule over Russia The strengths and weaknesses of the Italian states during the Renaissance The artistic and political contributions from Italy during the Renaissance The impact of the Renaissance humanists on modern cultures The significance of the Gutenberg printing press The language changes that took place during the Renaissance and Dante Alighieri’s role in them How the scientific method revolutionized scientific thought The conflicts between science and the Roman Catholic Church during the Renaissance How the Scientific Revolution instigated revolutions in other fields of learning How the rights and responsibilities of the common people were What do students need to be able to DO? Outline the series of conflicts central to the Middle Ages Analyze the impact of Charlemagne on the Frankish society Identify the sources of conflict between the Vikings and AngloSaxons Explain why the events of 1066 curbed the conflicts between the Vikings and Anglo-Saxons Explain the workings, advantages, and disadvantages of feudalism Analyze the effects of manorialism Explain the impact of the Roman Catholic Church on government, art, culture, and scientific theories during the Middle Ages Identify the positive effects of the Crusades Explain how disease, knowledge, culture, and economy were accelerated by trade routes Analyze how the cultural, economic, and political exchanges of the Crusades upset the social, political, and economic structures of Europe and Asia Explain how the power and status of the aristocracy began to be extended to the common people Analyze the influence of Emperor Justinian and the Byzantine Empire Explain the contributions of Constantinople to the cultures of the Middle Ages Identify the positive effects of the Byzantine Empire on Russia Analyze the flaws in the governing policies of the Mongols that led to their loss of control over Russia Identify the positives and negatives of czarist rule over Russia Identify the strengths and weaknesses of the Italian states during the Renaissance Identify the artistic and political contributions from Italy during the Renaissance Analyze the impact of the Renaissance humanists on modern cultures Explain the significance of the Gutenberg printing press Analyze the changes in language that took place during the Renaissance and Dante Alighieri’s role in those changes Analyze how the scientific method revolutionized scientific thought Explain the conflicts between science and the Roman Catholic Church during the Renaissance Explain how the Scientific Revolution instigated revolutions in other fields of learning Analyze how the rights and responsibilities of the common people were bolstered during the Renaissance bolstered during the Renaissance How the Scientific Revolution fueled the American and French Revolutions of the 1700’s Explain how the Scientific Revolution fueled the American and French Revolutions of the 1700’s Identify the fundamental differences between the Middle Ages and the Renaissance The fundamental differences between the Middle Ages and the Renaissance I Can… Statements I Can… outline the series of conflicts central to the Middle Ages I Can… analyze the impact of Charlemagne on the Frankish society I Can… identify the sources of conflict between the Vikings and Anglo-Saxons I Can… explain why the events of 1066 curbed the conflicts between the Vikings and Anglo-Saxons I Can… explain the workings, advantages, and disadvantages of feudalism I Can… analyze the effects of manorialism I Can… explain the impact of the Roman Catholic Church on government, art, culture, and scientific theories during the Middle Ages I Can… identify the positive effects of the Crusades I Can… explain how disease, knowledge, culture, and economy were accelerated by trade routes I Can… analyze how the cultural, economic, and political exchanges of the Crusades upset the social, political, and economic structures of Europe and Asia I Can… explain how the power and status of the aristocracy began to be extended to the common people I Can… analyze the influence of Emperor Justinian and the Byzantine Empire I Can… explain the contributions of Constantinople to the cultures of the Middle Ages I Can… identify the positive effects of the Byzantine Empire on Russia I Can… analyze the flaws in the governing policies of the Mongols that led to their loss of control over Russia I Can… identify the positives and negatives of czarist rule over Russia I Can… identify the strengths and weaknesses of the Italian states during the Renaissance I Can… identify the artistic and political contributions from Italy during the Renaissance I Can… analyze the impact of the Renaissance humanists on modern cultures I Can… explain the significance of the Gutenberg printing press I Can… analyze the changes in language that took place during the Renaissance and Dante Alighieri’s role in those changes I Can… analyze how the scientific method revolutionized scientific thought I Can… explain the conflicts between science and the Roman Catholic Church during the Renaissance I Can… explain how the Scientific Revolution instigated revolutions in other fields of learning I Can… analyze how the rights and responsibilities of the common people were bolstered during the Renaissance I Can… explain how the Scientific Revolution fueled the American and French Revolutions of the 1700s I Can… identify the fundamental differences between the Middle Ages and the Renaissance I Can… identify the fundamental differences between the Middle Ages and the Renaissance Unit 6- Concepts with Subtopics Aligned to Unit Generalizations HISTORY GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY H.1.1, H.1.2, H.1.3, H.2.1, H.2.4 G&EL.1.2, G&EL.2.1, G&EL.2.2 C&G.1.2, C&G.1.3, C&G.1.4 E&FL.1.1, E&FL.1.2 Time: Eras 5-6 Location: (absolute and relative) Holy Land Russia Europe Western Asia Northwest Africa Mesopotamia India Greece Italy Leadership: Charlemagne Descartes Galileo Joan of Arc Martin Luther Saladin William the Conqueror Competition, Conflict & Compromise: Trade routes Manorialism Feudalism Salt-gold trade Historical Figures: Bartolomeu Dias Columbus Henry Hudson John Cabot Magellan Mansa Musa Richard the LionHearted Vasco da Gama Invasions & Conquests: Mongol conquests of 1206-1279 China (1207-1227) Khwarizm (1218-1220) Russia (1219-1224) Byzantine Empire Hanseatic League Crusades Muslim Conquest Vikings Anglo-Saxons Italian city-states Greece Comparisons to Today: Addition of Puerto Rico Scientific innovations Science vs. religion Religion in government Place: (physical & human characteristics) Peninsula Island Waterways Land-locked Resources Vegetation Climate Natural Resources: Leather Iron Wood Silver Waterways Metals Spices Building materials Cloth Dye Food Animals Movement: Salt-gold trade Crusades Silk Road Plague Government Structure: Monarchy Aristocracy Feudalism Manorialism Charter Parliament Canon Law Military Innovation: Cavalry Citizenship: Charter Serf Knight Vassal Lord Rules and Laws: Divine right Excommunication Canon law Heresy Code of Justinian Pope Magna Carta Economic Development Silk Road Salt-gold trade Manorialism Feudalism Fief Trade: Silk Road Salt-gold trade Quality of Life Silk Road Trade routes Scientific development CULTURE C.1.1, C.1.3 People: Pope Samurai Shogan Cervantes Da Vinci Dante Johann Gutenberg Michelangelo Shakespeare Keppler Locke Machiavelli Montesquieu Newton Rousseau Cultural Expression: Utopia Art Music Literature Humanism Book of Kells Chivalry Code of Justinian Cyrillic alphabet Values & Beliefs, Religion: Canon law Holy Land Heresy Social Structure Lord Serf Vassal Knight Guild Liege Fief Divine right