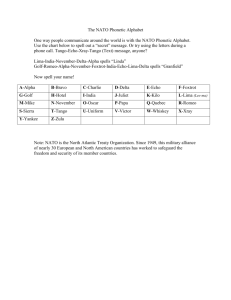
JWAC Meetings
advertisement

+ JWAC Meeting October 29, 2015 + Speaker Event Date November 18 (Wednesday before Thanksgiving break) After 8th period We will talk to APUSH, WHAP, and IB teachers to see if they will offer extra credit for attending The topic is: Life as a Refugee (or something similar depending on Dallas WAC availability) + Trick or Treating for Cans Current planned date is October 31 from 3-6 pm. Location: Whichever neighborhood you want. Basically, we just want to try to collect as many canned goods as possible You can count this as NHS service hours or CAS for IB. + Dues $15 Get a JWAC pin! What are they used for? Food Buying study material Applying for Dallas WAC membership + Officer Presentations First 4 articles in the study guide http://tinyurl.com/2016JWACStudyGuide + US Department of State on NATO Sarah McDonald + US Department of State on NATO Sarah McDonald North Atlantic Treaty Organization (1949) under the Truman administration Remains the world’s largest peacetime military alliance Created by US, Canada, and several Western European nations to provide collective security against the Soviet Union First peacetime military alliance US entered into outside Western Hemisphere US were already helping European nations (who accepted the aid) under the Marshall Plan, but communist threats on the borders of Italy and Germany concerned the US. US looked to form a European-American alliance that would commit the US to bolstering the security of Western Europe due to increasing tensions with the Soviet Union + US Department of State on NATO Sarah McDonald Brussels Treaty (1948) signed by Great Britain, France, Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg to create Western Europe collective defense Before the signing of the NATO treaty, European nations wanted assurances that the US would intervene automatically in event of attack, but the US’s power to go to war rested with Congress The United States, Canada, Belgium, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxemburg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, and the United Kingdom agreed to collective security (does not include attacks on colonial territories) 1952, Greece and Turkey admitted into NATO, and Federal Republic of Germany in 1955 Soviet version of NATO Treaty: The Warsaw Treaty Organization, which includes Eastern European nations and Soviet satellite states + NATO Jin Lee + Members BELGIUM (1949) CANADA (1949) THE UNITED KINGDOM (1949) THE UNITED STATES (1949) DENMARK (1949) FRANCE (1949) GREECE (1952) ICELAND (1949) TURKEY (1952) ITALY (1949) GERMANY (1955) LUXEMBOURG (1949) SPAIN (1982) NETHERLANDS (1949) CZECH REPUBLIC (1999) NORWAY (1949) HUNGARY (1999) PORTUGAL (1949) POLAND (1999) BULGARIA (2004) ESTONIA (2004) LATVIA (2004) LITHUANIA (2004) ROMANIA (2004) SLOVAKIA (2004) SLOVENIA (2004) ALBANIA (2009) CROATIA (2009) + Basic Points Political/Military Alliance Political-promotes democratic values and encourages consultation/cooperation on defense and security issues Military-peaceful resolution of disputes, military capacity to undertake crisis-management operations-article 5 of Washington Treaty or UN mandate Collective Security (Collective Defense) – 9/11 2010 Strategic Concept-Collective defense, crisismanagement + Decisions and Consultations Decisions by consensus – no voting Crisis Management Afghanistan, Kosovo, Counter-piracy, Mediterranean, African Union Partnerships-countries that work with NATO but are not a part of NATO, 41 partner countries + Key Events 1949-Birth of NATO through the Washington Treaty 1989-Fall of the Berlin Wall 1991-Partnerships with some former USSR states First crisis-management operation in Bosnia Herzegovina 2001-9/11 2003-NATO takes command of ISAF in Afghanistan 2010- 2010 Strategic Concept- “Active Engagement, Modern Defense” + Working Structures Each country has permanent delegation North Atlantic Council-decision makers Sub-committees Secretary General Military Committee + Bookings Institution Gordon Li The Purpose of NATO Bookings + Institute Gordon Li Problems arise regarding the purpose of NATO The fall of the Soviet Union caused a loss of purpose in the organization NATO has opened membership to many former Soviet satellites Some support extending the organization beyond military alliances There is a lot of uncertainty in the future organization of NATO + Council on Foreign Relations Eric Sun + Introduction NATO is a cornerstone of transatlantic security Founded in 1949 against Soviet aggression Evolved to confront thrats from piracy off the Horn of Africa to Taliban in Afghanistan + A Post-Cold War Pivot After the demise of the Soviet Union in 1991, the future of NATO was debated. Pres. Clinton wanted to expand NATO to the east and consolidate democratic gains, while some US officials wanted to peel back Pentagon commitments in Europe European nations were also conflicted about alienating Russia by accident + Beyond Collective Defense Article V of North Atlantic Treaty basically stated that an attack on one member of NATO was an attack on all of them. This collective defense ideology was shifted to confront instability outside its membership The breakup of Yugoslavia became a turning point. Operation Deny Flight (UN sanctioned a no-flight zone) in April 1994 meant that NATO took combat operations by shooting down four Bosnian Serb aircrafts violating this no-fly zone. + Sharing the Burden Primary financial contribution made by member states is cost of deploying armed forces for NATO operations. In 2014, NATO members spent $850 billion on defense and US account for 70%. In 2006, member states wanted to spend 2% GDP on defense, but only US, UK, Greece, and Estonia met that goal. NATO acknowledges that there is an over-reliance on the United States for everything. + Afghanistan and ISAF NATO invoked Article V (collective defense) after September 11 attacks. NATO assumed command of International Security Assistance Force to support a new Afghan government in 2003. January 2015, NATO and more than a dozen partner countries began a non-combat support mission of about 12,000 troops + Relations with Russia Moscow view NATO with concern since they believe that it breaks the alleged guarantees to not expand eastward after German reunification in 1990. NATO and Russia have taken significant steps towards reconciliation with signing of the 1997 Founding Act, which established official forum for bilateral discussions. NATO’s Bucharest summit in the spring of 2008 deepened distrust. Delayed Membership Action Plans for Ukraine and Georgia, it vowed support for Ukraine and Georgia and give them full membership in the future. Russia’s annexation of Crimea and destabilization of eastern Ukraine in 2014-2015 and poison relations. NATO’s ballistic missile defense shield worries the Kremlin since it may tip the strategic balance to the West. + A Revived Alliance NATO put new command centers six eastern periphery states: Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, and Romania. Develop Very High Readiness Joint Task Force NATO augment direct security collaboration with Ukraine. US and UK send troops to train Ukrainian Personnel In the longer term, analysts believe Finland and Sweden will join (even though they are two Partnership for Peace countries with a history of avoiding military alignment) + A Revived Alliance NATO put new command centers six eastern periphery states: Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, and Romania. Develop Very High Readiness Joint Task Force NATO augment direct security collaboration with Ukraine. US and UK send troops to train Ukrainian Personnel In the longer term, analysts believe Finland and Sweden will join (even though they are two Partnership for Peace countries with a history of avoiding military alignment) + Practice Kahoot