Chapter 14
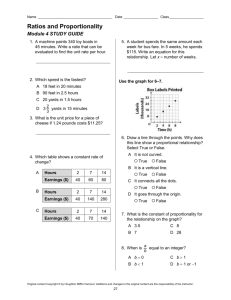
Sales Force
Performance Evaluation
PowerPoint presentation prepared by
Dr. Rajiv Mehta
New Jersey Institute of Technology
Chapter Outline
• Sales Force Performance Appraisal
• A Contemporary Approach to Sales Force
Performance Evaluation
• Providing Feedback and Improving Sales Force
Performance
• Emerging Perspectives in Twenty-First Century
Sales Force Performance Appraisals
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 2
Learning Objectives
After reading this chapter, you should be
able to do the following:
1. Carry out the sales force performance evaluation process using the
outcome-based, behavior-based, and professional development
measures.
2. Establish different types of sales goals and objectives, and develop
the sales plan.
3. Set sales force performance standards.
4. Allocate resources and efforts through sales quotas.
5. List the major steps in the sales force performance evaluation
monitoring system (PEMS).
6. Provide feedback and evaluation and improve sales force
performance.
7. Apply twenty-first century sales force performance appraisal
methods.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 3
Sales Force Performance Appraisal
• A salesperson performance appraisal is a
systematic process for establishing whether the
salesperson’s job behavior contributes to the fulfillment
of a firm’s sales objectives and for providing specific
feedback to the individual.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 4
Sales Force Performance Appraisal
• Performance appraisals can help
managers accomplish the
following:
– increase/decrease compensation
and awards to high/low performers
– identify training needs of
salespeople
– mentor salespeople about their
careers
– revise sales performance and
evaluation process
– develop a top notch sales team
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 5
Challenges in Salesperson
Performance Appraisals
• Evaluating salespeople is
challenging because they
encounter the following hurdles:
– mostly work alone in the field
– engage in a multitude of
activities
– have differences in territory
potentials
– have physical disparities in
their territories
– face intense, varying
competition
– have to allocate their time
between account development
and account maintenance
– need sufficient time to adjust
to their assigned territories
Source: © Jack Hollingsworth/Corbis
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 6
Timing of Salesperson
Performance Appraisals
• Performance appraisals are
usually conducted over these
intervals:
– once a year
– sometimes semiannually
– sometimes quarterly
• Evaluations include two kinds
of criteria:
– objective (quantitative) criteria
– subjective (qualitative)
measures
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Source: © Jack Hollingsworth/Corbis
14 | 7
A Contemporary Approach to Sales
Force Performance Evaluation
Establish sales goals
and objectives.
Develop the sales plan.
Set sales force
performance standards.
Allocate resources
and sales force efforts.
Measure sales force
performance against standards.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Take corrective action.
14 | 8
Establish Sales Goals and Objectives
• Formulate sales goals,
such as these:
Source: Flying Colours Ltd
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
– increasing sales by 5
percent each year over the
next five years
– increasing market share by
4 percent by the next five
years
– reducing customer
defections by 12 percent
– increasing the new
customer base by 10
percent each year
14 | 9
Articles on Sales Force
Performance Evaluation
• Read various articles on sales performance at
– http://www.salesmanagermag.com/archive.html#Sale
sPerformance
– http://www.successfactors.com/talentmanagement/articles/
– http://www.successfactors.com/performancemanagement/downloads/#
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 10
Develop the Sales Plan
“How much progress are we making
toward our destination?”
• set standards of performance
• evaluate actual performance
versus planned standards
• take corrective action on
variances from plan
3.
Action
programs
“What’s the best way to get
there?”
• strategies and tactics
4.
Performance
evaluation
systems
Sales
Plan
2.
Opportunities and
problems
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
“Where are we now?”
• market situation and
competitive environment
• product sales situation
1.
Situation analysis
“Where do we want to go?”
• internal environment
• external environment
• planning assumptions and
constraints
• sales forecasts
• contingency planning
14 | 11
Sales Force Performance Evaluation
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 12
Sales Force Performance Standards
• To coach your sales team to improved
productivity and learn about guidelines and
various criteria that can be used in conducting
sales performance evaluations visit
– http://www.justsell.com/salestools/salesevaluationtool
.aspx
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 13
Types of Sales Quotas
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 14
Administration of Sales Quotas
1.
Set realistic
quotas.
5.
Maintain control
(performance
evaluation).
Administration of
sales quotas
4.
Keep the sales
force updated.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
2.
Create
understandable
quotas.
3.
Include salespeople
in quota setting.
14 | 15
Sales Force Performance
Evaluation Using Sales Quotas
• To see a video on sales quota management, go
to
– http://www.sellingpower.com/video/index.asp?date=1
0/5/2007
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 16
Measure Sales Force
Performance Against Standards
1.
3.
Performance
review:
Performance
planning
Conduct
overall performance
evaluation.
“Where am I going?”
“How will I get there?”
“How will I be measured?”
Performance
evaluation
monitoring system
stages
2.
Performance
appraisal
Provide immediate feedback
(praise, or correction) on each
task accomplished.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 17
Websites of Firms Specializing in
Sales Force Performance Evaluation
• Peruse the websites of various firms that
specialize in conducting sales force appraisals,
at
– http://www.performance-appraisal.com/intro.htm
– http://www.achieveglobal.com/Solutions/Sales_Measurem
ent
– http://www.synygy.com/solutions/Performance_managem
ent/perfrevmgt.html
– http://www.360-degree-evaluations.com/360-demo.asp
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 18
Types of Performance
Appraisal Techniques
4.
Management by
objectives
3.
Behaviorally
anchored
rating scales
Types of
performance
appraisal
techniques
1.
Descriptive
statements
2.
Graphic rating
scales
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 19
Graphic Rating Scales
Semantic differential graphic rating scale
product knowledge
poor ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ _X_ ___ excellent
1 2 3 4 5 6
7
Likert-type graphic rating scale
product knowledge
____________ _______ ___X__
unsatisfactory below
average
average
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
______
__________
above
outstanding
average
14 | 20
Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scales
Cooperation with sales team members
Categories of performance
Observed behavior
10
Very high
indicates strong willingness
to cooperate with other
members of the sales team
Moderate
indicates an average amount
of cooperation with other
team members
8
Salesperson will always cooperate in any
way with other sales force team members,
even if such effort is personally inconvenient
or requires self-sacrifice.
7
Salesperson can be expected to go out of his
9
6
5
4
3
Very low
indicates generally no team
effort, which often hurts
group performance
2
or her way to help other team members with
any work-related problem.
Salesperson is usually willing to help other
team members on field sales problems.
Salesperson will occasionally help team
members with field sales problems
Salesperson seldom helps others and tends
to resent contributing to group effort.
1
Salesperson is generally antagonistic toward
0
other team members and frequently
undercuts group efforts.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 21
Management by Objectives
Modify and adjust
MBO cycle
Planning phase
Step 1
Step 2
Set sales objectives.
Develop sales plans and
implement them.
Step 4
Step 3
Conduct annual
performance evaluation
of salespeople.
Periodically monitor
performance and alter
sales tactics to stay on
track.
Control phase
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 22
Limitations of Sales
Force Evaluation Systems
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
stereotyping
contrast error
similar-to-me error
first-impression error
leniency or harshness error
central tendency error
escalation of commitment error
fundamental attribution error
self-serving bias
central tendency
Source: Stockbyte
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 23
Limitations of Sales
Force Evaluation Systems
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
political concerns
fear of reprisal
varying evaluation standards
interpersonal bias
questionable personality traits
organization use
recency bias
no outcome focus
inadequate sampling of job
activities
Source: Stockbyte
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 24
Sales Force Performance Evaluation
• To see a video on tools for salespeople to
individually manage their own sales
performance, go to
– http://www.sellingpower.com/video/index.asp?date=1
1/7/2007
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 25
Emerging Perspectives in Twenty-first Century
Sales Force Performance Appraisals:
360-Degree Performance Evaluation
Sales
manager
Other
departmental
coworkers
Purchasing
managers
(clients)
360-degree
salesperson
performance
appraisal
Accounts
payable
managers
Sales team
peers
External customers
Internal customers
Sales
subordinates
Selfappraisal
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 26
Effective Sales Performance Evaluation
• To see a video on evaluating sales force
performance by measuring customer
satisfaction—an aspect of 360-degree
performance—and employee satisfaction, which
are drivers of financial performance, go to
– http://www.sellingpower.com/video/index.asp?date=1
1/20/2007
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 27
Software for Conducting
Sales Force Performance Evaluations
• Peruse the following website to learn about
software for sales force performance evaluations
at
– http://www.callidussoftware.com
– http://www.varicent.com
– http://www.einsof.com/about_us.jsp
• Test drive Solution Selling Software, a sales
performance assessment tool, at
– http://www.salesforce.com/appexchange/detail_overv
iew.jsp?id=a0330000002VYILAA4&NavCode__c=&ta
b=publisher
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 28
Sales Force Performance Appraisals:
Performance Evaluations of Team Selling
• In cooperation,
sales managers
and sales force
team members
select relevant
performance
criteria and
appraisal methods.
• Each team
member rates all
the other members
on the following:
Source: Stockbyte
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
–
–
–
–
teamwork
leadership
productivity
team relations
14 | 29
Emerging Perspectives In Twenty-First Century
Sales Force Performance Appraisals:
Performance Review Ranking System
• Evaluate salespeople on performance using a
scale, such as this:
– A = excellent
– B = above average
– C = average
– D = satisfactory performance
– E = sub-par performance
• Then rank each salesperson and place them in
performance categories:
– top 20 percent
– middle 70 percent
– bottom 10 percent
Source: Stockbyte
• Move out the bottom performers with new talent,
thus creating meritocracies.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 30
Ethical Situation: What Would You Do?
Discussion Question
You are one of six regional sales managers for a large manufacturer of consumer
products. About ten district sales managers report to each one of the regional sales
managers. This year, your national sales manager is requiring all the company’s sales
managers to use a Likert-type performance evaluation scale to rate each of their
subordinates on various dimensions. The evaluation scale has five performance blocks or
segments labeled: outstanding, above average, average, below average, and poor.
Knowing that these evaluations will be used for current raises and bonuses, and
promotions over the longer run, you plan to rate all the district sales managers reporting
to you as at least “above average” and some “outstanding.” In all honesty, you know that
four of your district managers should be rated no better than “average,” but you don’t
want to hurt their chances for raises, bonuses, and promotion, so you just don’t use the
bottom three segments of the evaluation scale. By rating your people higher than they
should be, you feel that you retain their loyalty and support while keeping morale higher
than it would be if your performance evaluations were more accurate. You rationalize this
evaluation approach to yourself by asking: “Who gets hurt if I rate my people on the high
side? Other regional sales managers probably do the same thing.”
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
14 | 31