General Chemistry Bell Ringers
advertisement

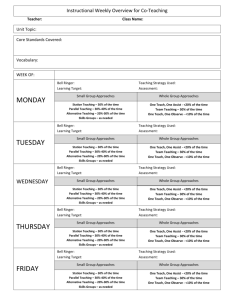
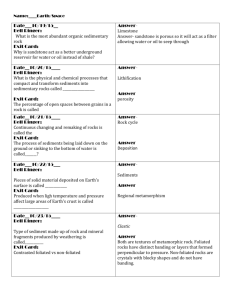
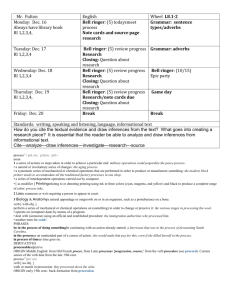
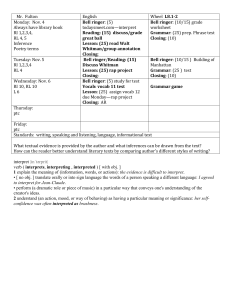
Modern Chemistry Semester 2 Bell Ringer 1-28-16 Use the kinetic molecular theory to explain each of the following properties of gases: expansion, fluidity, low density, compressibility, and diffusion. 1-28-16 Continued… Expansion: gas particles move rapidly in all directions without significant attraction between them. Fluidity: attractive forces between gas particles are too weak to hold the particles in a rigid structure. Low Density & Compressibility: gas particles are further apart than they are in another state. Diffusion: gas particles are in continuous and random motion Exit 1-28-16 Explain why liquids in a test tube form a meniscus. 1-28-16 Continued… If the liquid is attracted to the glass, it is pulled upward into the test tube creating the concave surface. This is called capillary action, and the surface is called a meniscus. Bell Ringer 1-29-16 Describe the solid state according to the kinetic molecular theory. 1-29-16 Continued… Solids consist of closely packed particles held together by intermolecular forces; these particles are able to move back and forth about in fixed positions. Exit 1-29-16 What is the vapor pressure of a liquid? How is it measured? 1-29-16 Continued… Pressure exerted by vapor in equilibrium with its corresponding liquid at a given temperature. Its is measured by introducing a liquid into an evacuated flask, allowing enough liquid to evaporate to reach equilibrium, then measuring the increase in gas pressure. Bell Ringer 2-1-16 Why is a water molecule polar? 2-1-16 Continued… The bent shape of the molecule…there is a large electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen atoms that results in overall polarity of the molecule. Exit 2-1-16 Why does ice float? Why is this phenomenon important? 2-1-16 Continued… Ice floats because it is less dense than liquid water. Due to its low density, ice forms only on the surface. The solid layer insulates the liquid water below it. This prevents a total freeze, which would kill most living things in lakes etc. Bell Ringer 2-2-16 Fe, Mn, Cr & Ni Cation Lab Day! Have your Composition Notebook out for Labs Make the entry in the Table of Contents Name Period # Honors Chemistry Lab Book 1 Page Content 1 Table of Contents 2 Measurements Lab 3-5 Separation of a Mixture 7-9 Percentage of Water 11-15 Flame Test Lab 17-19 Group IA & IIA Cations 21-24 Fe, Mn, Cr & Ni Cations Lab Bell Ringer 2-3-16 You will be continuing your lab on Fe, Mn, Cr and Ni Cation identification. BEFORE you can begin, your lab must be checked to ensure that it has the following parts: Questioning: Predicting: Procedure: (check for variables) Safety: Bell Ringer 2-4-16 This is your Unknown Identification portion of the lab on Fe, Mn, Cr and Ni Cation identification. Be seated and ready for attendance before finishing your lab. Remember that your final sections should have the following parts: Data & Observations: Calculations & Results: Qualitative!!! Discussion of Results: Additional Questions: COMPLETE SENTENCES Bell Ringer 2-5-16 This is your final day of the lab on Fe, Mn, Cr and Ni Cation identification. Be seated and ready for attendance before finishing your lab. Remember that your final sections should have the following parts: Data & Observations: Calculations & Results: Qualitative!!! Discussion of Results: Additional Questions: COMPLETE SENTENCES Additional Questions What are names of the following compounds: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) NaOH NiCl2 MnCl3 FeCl2 CrCl3 Bell Ringer 2-8-16 Please do not be pain for the substitute. Your grade will feel it…There may be calls home for students that do not come prepared. Fill out the chart below in your Learning Log: Name of the Law Formula Boyle’s Law V1 = V2 T1 T2 Gay-Lassac’s Law P1V1 = P2V2 T1 T2 Volume is directly proportion to n Ideal Gas Law Bell Ringer 2-8-16 Continued Fill out the chart below in your Learning Log: Name of the Law Formula Boyle’s Law P1V1 = P2V2 Charle’s Law V1 = V2 T1 T2 Gay-Lassac’s Law P1 = P2 T1 T2 Combined Gas Law P1V1 = P2V2 T1 T2 Avogadro’s Law Volume is directly proportion to n Ideal Gas Law PV = nRT Exit 2-8-16 To Update me on how your group work is going…I would like you to note the following for your exit: 1)Who is in charge of what parts of your presentation? 2)What do you need to work on most tomorrow? Bell Ringer 2-9-16 Finish each of the following statements: _______ Law states that if temperature decreases then volume decreases. ______ Law states that P1V1=P2V2 if the temperature remains constant ______ Law reduces Boyle’s, Charle’s, Gay-Lussac’s and Avogadro’s laws. ______ Law states that if volume increases then number of moles increases. _____ Law states that if the pressure increases then the volume decreases. _____ Law states that if volume is constant, pressure increases then temperature increases. Bell Ringer 2-9-16 Continued… Finish each of the following statements: Charle’s Law states that if temperature decreases then volume decreases. Boyle’s Law states that P1V1=P2V2 if the temperature remains constant Ideal Gas Law reduces Boyle’s, Charle’s, Gay-Lussac’s and Avogadro’s laws. Avagadro’s Law states that if volume increases then number of moles increases. Boyle’s Law states that if the pressure increases then the volume decreases. Gay-Lussac’s Law states that if volume is constant, pressure increases then temperature increases. Exit 2-9-16 Presentation update: Write 3 sentences explaining at LEAST three things you were able to do today for your groups presentation. Bell Ringer 2-10-16 Write as much of the 8 solubility rules story into your Learning Log as you know so far… Bell Ringer 2-10-16 What are the standard conditions for gas measurements? Bell Ringer 2-10-16 Continued… 0 C and 1 atm pressure Exit 2-10-16 Explain why helium-filled balloons deflate over time faster than air filled balloons do. Exit 2-10-16 Continued… The average velocity of Helium molecules is higher than that of the molecules of gases found in regular air (little guys are the fastest). Helium molecules escape through the pores in the balloon more quickly. Most people think they are smaller so they fit more easily through the pores…partially true but really it is because they crash around faster so they have more chances to get out based on their faster speed. Bell Ringer 2-11-16 Here is a check list of what you should have done while I have been out. This is a Catch Up Day. Please have all work DONE for tomorrow: Chapter 10 Learning Log is COMPLETE and Ready to Grade tomorrow Cation Fe, Mn, Cr & Ni Lab is COMPLETE and Ready to Grade tomorrow Your portion of the Team Presentation is COMPLETE and you are ready to present when your day is here… For your BR today…Write me a note as to what your are focusing on in class. Please do not be pain for the substitute. Your grade will feel it…There may be calls home for students that do not come prepared. Exit 2-11-16 State the ideal gas law equation, and tell what each term means. Exit 2-11-16 Continued… PV = nRT P=Pressure in atm V= Volume in L n = amount in moles R = is a constant we know 0.0821 Latm/mol K T = Temperature in K If they give you P, V or T in anything other than atm, L or K you HAVE to convert it! C + 273.15 = K or K - 273.15 = C Bell Ringer 2-12-16 If a student is asked to convert 1.75 atm into kPa and mmHg, is the student correct if they conclude that there are 177 kPa and 1300 mmHg? Justify your reasons… Bell Ringer 2-16-16 Exam 10 Please pick up your remote that is assigned to your name. You may use scratch paper on the test and a calculator (NO CELL PHONE). Please be ready for the exam to begin. Bell Ringer 2-17-16 The volume of a gas is 27.5 ml at 22.0 degrees C and 0.947 atm. What will the volume be at 15.0 degrees C and 0.993 atm? Exit 2-17-16 Evaluate the following problem. Then determine if the answer provided is correct or incorrect. At STP, what is the volume of 7.08 mol of Nitrogen gas? Proposed Answer: 142 L Bell Ringer 2-18-16 What volume of oxygen gas is needed to produce 0.626 L of carbon dioxide gas? Assume all volume measurements are made at the same temperature and pressure. C3H8 + O2 CO2 + H2O Exit 2-18-16 What pressure, in atm, is exerted by 0.325 mol of hydrogen gas in 4.08 L container at 35 degrees C? Bell Ringer 2-19-16 A gas sample occupies 8.77 L at 20 degrees C. What is the pressure in atm, given that there are 1.45 mol of gas in the sample? Exit 2-19-16 A 4.44 L container holds 15.4 g of oxygen at 22.5 C. What is the pressure? Bell Ringer 2-22-16 A sample of nitrogen gas occupies 1.55 L at 27.0 C and 1.00 atm. What will the volume be at -100.0 C and the same pressure. Exit 2-22-16 Convert the following pressures into pressure in standard atmospheres (atm). 151.98 kPa 456 torr Bell Ringer 2-23-16 Today is PVT Math Day Time Out! For you Bell Ringer please copy the following information: 1 torr = 1 mm Hg 1 atm = 760 torr or 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.01325 x 105 Pa 1 atm = 101.325 kPa Exit 2-23-16 Cleaning room used for sterile biological research are sealed and operate at slightly above atmospheric pressure. Explain why you would want the room above the pressure outside the room. Bell Ringer 2-24-16 Turn you book to page 384… Note that R has many values but we have only been focusing on 0.0821 Latm/molK Why are there so many other values listed and what is their purpose? Exit 2-24-16 A tank of hydrogen gas has a volume of 22.9 L and holds 14.0 moles of the gas at 12 C. What is the pressure of the gas in atm? Bell Ringer 2-25-16 Exam 11 Please pick up your remote that is assigned to your name. You may use scratch paper on the test and a calculator (NO CELL PHONE). Please be ready for the exam to begin. 2-26-16 Bell Ringer Write your 8 solubility rules story into your Learning Log… 2-26-16 Exit Classify the following as either a heterogeneous or homogenous mixture, and explain your answers. Orange Juice & Tap Water 2-29 Bell Ringer What is the molarity of a solution composed of 5.85 g of KI dissolved in enough water to make 0.125 L of solution? (Note P2…you have seen this question before) 2-29-16 Exit What are substances called whose water solutions conduct electricity? Why does a salt solution conduct electricity? Why does a sugar-water solution not conduct electricity? 3-1-16 Bell Ringer What is the molality of acetone in a solution composed of 255g of acetone, (CH3)2CO, dissolved in 200. g of water? 3-1-16 Exit Why would you expect a packet of sugar to dissolve faster in hot tea than in iced tea? 3-2-16 Bell Ringer Go back to your Bell Ringer for 226…Translate the 8 solubility rule hints we practiced in class to what they actually stand for in chemistry. 3-2-16 Exit We dissolve 5.00 grams of sugar, C12H22O11, in water to make 1.000 L of solution. What is the concentration of this solution expressed as a molarity? 3-3-16 Bell Ringer How many moles of H2SO4 are present in 0.500 L of a 0.150 M H2SO4 solution? 3-3-16 Exit You evaporate all the water from 100. ml of NaCl solution and obtain 11.3 grams of NaCl. What was the molarity of the NaCl solution? 3-4-16 Bell Ringer Exam 12 Please pick up your remote that is assigned to your name. You may use scratch paper in the test and a calculator (NO CELL PHONE). Please be ready for the exam to begin. 3-7-16 Bell Ringer Dissociation is the separation of ions that occurs when ionic compounds dissolve. How many moles of ions are contained in 1 L of a 1 M solution of KCl? Of Mg(NO3)2? Why do covalent bonds not have dissociation? 3-7-16 Exit Identify the spectator ions in the reaction between KCl and AgNO3 in an aqueous solution. 3-8-16 Bell Ringer (2 slides) Write the equation for the dissolution of each of the following in water, and then indicate the total number of moles of solute ions formed. a) 0.50 mol strontium nitrate b) 0.50 mol sodium phosphate 3-8-16 Bell Ringer Continued… Write the equation for the dissolution of each of the following in water, and then indicate the total number of moles of solute ions formed. a) 0.50 mol strontium nitrate Sr(NO3)2 Sr2+ + 2NO31.50 moles of ions b) 0.50 mol sodium phosphate Na3PO4 3Na+ + PO43- 2.0 moles of ions 3-8-16 Exit (2 slides) Write the formulas of the following compounds with BALANCED charges: Sodium Carbonate Barium Phosphate If you mix them in aq form, will there be a precipitate? 3-8-16 Exit Write the formulas of the following compounds with BALANCED charges: Sodium Carbonate Na2CO3 Barium Phosphate Ba3(PO4)2 If you mix them in aq form, will there be a precipitate? Na + PO4 = insoluble so yes precip Ba + CO3 = insoluble so yes precip 3-9-16 Bell Ringer How does the presence of a nonvolatile solute affect each of the following properties of the solvent in which the solute is dissolved? a) Vapor pressure b) Freezing point c) Boiling point d) Osmotic pressure 3-9-16 Bell Ringer Continued… How does the presence of a nonvolatile solute affect each of the following properties of the solvent in which the solute is dissolved? a) Vapor pressure (Lowers) b) Freezing point (Lowers) c) Boiling point (Raises) d) Osmotic pressure (Increases) 3-9-16 Exit Compare the effects of the nonvolatile electrolytes with the effects of nonvolatile nonelectrolytes on the freezing and boiling points of solvents in which they are dissolved? Why are such differences observed? 3-9-16 Exit Continued… Compare the effects of the nonvolatile electrolytes with the effects of nonvolatile nonelectrolytes on the freezing and boiling points of solvents in which they are dissolved? A nonvolatile electrolyte will lower the freezing point or raise the boiling point more than a nonelectrolyte at the same concentration will. Why are such differences observed? One mole of a nonelectrolyte produces 1 mol of particles in solution. A mole of nonvolatile electrolyte produces more than 1 mol of ions in solution. 3-10-16 Bell Ringer Today we start the Penny Lab…All you need is the Procedure in your own words and a “data” spot to tape your two pennies. Be prepared to answer additional questions tomorrow. 3-11-16 Bell Ringer Penny Lab Continued… Additional Questions: 1) Given one example of something in real life that is made of Brass 2) At one point pirate and old sailing vessels used to keep their cannon balls on a brass stand that looked very similar to a set of shelves for bowling balls. Brass contracts more drastically in cold then most metals. Predict what occurred when a sailing ship encountered a cold day at sea. 3-14-16 Bell Ringer Why does the actual freezing-point depression of an electrolytic solution differ from the freezing-point depression calculated on the basis of the concentration of particles? 3-14-16 Bell Ringer Continued… Why does the actual freezing-point depression of an electrolytic solution differ from the freezingpoint depression calculated on the basis of the concentration of particles? The difference is caused by the attractive forces between the ions in the solution. 3-14-16 Exit What colligative properties are represented by each of the following situations? Antifreeze is added to a car’s cooling system to prevent freezing when the air temperature is below 0C. Ice melts on sidewalks after salt has been spread on them. 3-15-16 Bell Ringer Exam 13 Please pick up your remote that is assigned to your name. You may use scratch paper in the test and a calculator (NO CELL PHONE). Please be ready for the exam to begin. 3-16-16 Bell Ringer Summarize the 5 characteristics of an acid and 5 characteristics of a base. ACTUALLY write them in your own words…you will need them later (see page 468 and 471). 3-16-16 Exit Why are strong acids also strong electrolytes? Is every strong electrolyte also a strong acid? 3-17-16 Bell Ringer What are the similarities between a binary acid and an oxyacid (look at their chemical formulas)? 3-17-16 Exit Complete and balance the following reactions: H2CO3 + Sr(OH)2 HClO4 + NaOH HBr + Ba(OH)2 NaHCO3 + H2SO4 3-17-16 Exit Continued… Complete and balance the following reactions: H2CO3 + Sr(OH)2 SrCO3 + 2H2O HClO4 + NaOH NaClO4 + H2O 2HBr + Ba(OH)2 BaBr2 + 2H2O NaHCO3 + H2SO4 Na2SO4 + 2H2O + 2CO2 3-18-16 Bell Ringer What is the difference between Bronsted-Lowry and Lewis acids/bases. 3-18-16 Exit For the reaction below, label each reactant as an electron pair acceptor or electron pair donor and as a Lewis acid or Lewis base. AlCl3 + Cl AlCl4 3-29-16 Bell Ringer Hg, Ag, Zn, & Cu Cation Lab Day! Have your Composition Notebook out for Labs Make the entry in the Table of Contents Name Period # Honors Chemistry Lab Book 1 Page Content 1 Table of Contents 2 Measurements Lab 3-5 Separation of a Mixture 7-9 Percentage of Water 11-15 Flame Test Lab 17-19 Group IA & IIA Cations 21-24 Fe, Mn, Cr & Ni Cations Lab 25-29 Hg, Ag, Zn, Cu Cations Lab 3-30-16 Bell Ringer You will be continuing your lab on Hg, Ag, Zn and Cu Cation identification. BEFORE you can begin, your lab must be checked to ensure that it has the following parts: Questioning: Predicting: Procedure: (check for variables) Safety: 3-31-16 Bell Ringer This is your Unknown Identification portion of the lab on Hg, Ag, Zn, & Cu Cation identification. Be seated and ready for attendance before finishing your lab. Remember that your final sections should have the following parts: Data & Observations: Calculations & Results: Qualitative!!! Discussion of Results: Additional Questions: COMPLETE SENTENCES 4-1-16 Bell Ringer This is your final day of the lab on Hg, Ag, Zn, & Cu Cation identification. Be seated and ready for attendance before finishing your lab. Remember that your final sections should have the following parts: Data & Observations: Calculations & Results: Qualitative!!! Discussion of Results: Additional Questions: COMPLETE SENTENCES 4-1-16 Continued… Additional Question 1) Some cations are soluble in water and others are not. We can force them to become soluble/insoluble by adding either _____________ or ___________. This either makes a precip form or dissolves one. 2) What are the names of: HCl HNO3 HOAC NaOH 3) Which are acids and bases in question #2? 4) Why did it take a ton of NaOH on the right side? 4-4-16 Bell Ringer Identify the conjugate acid and conjugate base in the equation below: HCl + H20 H3O+ + Cl- 4-4-16 Exit A classmate states, “All compounds containing H atoms are acids, and all compounds containing OH groups are bases.” Do you agree? Give examples. 4-5-16 Bell Ringer Exam 14 Please pick up your remote that is assigned to your name. You may use scratch paper in the test and a calculator (NO CELL PHONE). Please be ready for the exam to begin. 4-6-16 Titration Lab Day! Have your Composition Notebook out for Labs Make the entry in the Table of Contents Name Period # Honors Chemistry Lab Book 1 Page Content 1 Table of Contents 2 Measurements Lab 3-5 Separation of a Mixture 7-9 Percentage of Water 11-15 Flame Test Lab 17-19 Group IA & IIA Cations 21-24 Fe, Mn, Cr & Ni Cations Lab 25-29 Hg, Ag, Zn, Cu Cations Lab 31-34 Titration Lab 4-7-16 Bell Ringer You will be continuing your lab on Titration. BEFORE you can begin, your lab must be checked to ensure that it has the following parts: Questioning: Predicting: Procedure: (check for variables) Safety: 4-8-16 Bell Ringer This is your final day for data collection. Be seated and ready for attendance before finishing your lab. Remember that your final sections should have the following parts: Data & Observations: Calculations & Results: Qualitative & Quantitative!!! Discussion of Results: Additional Questions: COMPLETE SENTENCES 4-11-16 Additional Questions 1) When you added deionized water to the HCl solution in the Erlenmeyer flask before titrating, why did the addition of water not affect the results? 2) What characteristic of phenolphthalein made it appropriate to use in this titration? 3) Could you have done the experiment without it? 4) How does phenolphthalein’s end point relate to the equivelence point of reaction? 4-12-16 Bell Ringer You will need to follow your lab write up hand out to ensure that you will earn full points. You have today and tomorrow in the computer lab to complete your write up. You must have it submitted to Turnitin.com by Sunday night by midnight for full credit. Remember it tells me how much of your report is similar to others! This should be YOUR words! 4-13-16 Bell Ringer You will need to follow your lab write up hand out to ensure that you will earn full points. You have today and tomorrow in the computer lab to complete your write up. You must have it submitted to Turnitin.com by Sunday night by midnight for full credit. Remember it tells me how much of your report is similar to others! This should be YOUR words!