Nash Equilibrium
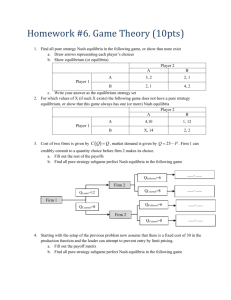
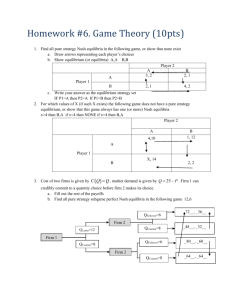
advertisement

Monte Hall Problem
Let’s Draw a Game Tree…
Problem 6, chapter 2
Information sets in Monte Hall game
• In last move, contestant knows which door he
chose and which Monte opened. The door
that Monte opened is neither the one that
contestant opened nor the one with the good
prize.
• Six things contestant might see.
1/ 2, 1/ 3, 2/ 1, 2/ 3, 3/ 1, 3/ 2.
Finding information sets
• If contestant sees 1/ 2, then the node might
be 1/ 1 /2 or it might be 3/ 1/ 2. Why couldn’t
it be 2/ 1/ 2?
• So one information set is {1/1/2,3/1/2}.
• What are the others?
HW Problem 2.11
Perfect Recall?
Nash Equilibrium
Clicker Question 1:
Strategy A2 Stategy B2 Strategy C2
Strategy A1
Strategy B1
Player 1
Strategy C1
6,0
2,3
1,1
3,2
2,3
2,0
4,1
2,8
5,2
Is the outcome where Player 1 plays B1 and Player
2 plays C2 a Nash equilibrium?
A) Yes
B) No
Clicker Question 2:
Strategy A2 Stategy B2 Strategy C2
Strategy A1
Strategy B1
Player 1
Strategy C1
6,0
2,3
1,1
3,2
2,3
2,0
4,1
2,8
5,2
Is the outcome where Player 1 plays A1 and Player
2 plays B2 a Nash equilibrium?
A) Yes
B) No
Definition
A strategy profile is a Nash Equilibrium if each
player’s strategy maximizes his payoff given the
strategies used by the other players.
Best response mapping
Best response for a player is a mapping from
actions by the others to the action (or actions)
that maximizes the player’s payoffs given the
actions of the others.
In Nash equilibrium, every player is doing the
best response to what the other players are
doing.
Prisoners’ Dilemma Game
Player 2
Cooperate
P
L
A Cooperate
y
E
R
1
Defect
Defect
10, 10
0, 11
11, 0
1, 1
Battle of Sexes
Bob
Movie A
Movie A
Alice
Movie B
BRA(A)=A
BRA(B)=B
Movie B
2,1
0,0
0,0
1,2
BRB(A)=A
BRB(B)=B
Best Responses and Nash Equilibria for this game?
BR2(a)=z
BR2(b)={w,x,z}
BR2(c)=y
BR2(d)={y,z}
BR1(w)=b
BR1(x)=b
BR1(y)=b
BR1(z)={a,d}
Find Nash equilibria for these games
• Chicken
• Pure coordination (Driving Game)
How many Nash equilibria
(in pure strategies)?
There might be just one.
There might be more than one.
There might not be any.
Rock, Paper Scissors,
Where is Nash equilibrium?
The Gingrich-Santorum game?
Textbook example.
3 candidates. Winner takes all.
Strategy positive effort +1 for self or negative
effort -2 for smeared candidate.
Starting point. Candidate 1 has initial score 2,
candidates 2 and 3 have initial scores 0.
Nash equilibria. All positive.
Candidates 2 and 3 both smear 1.
Other Nash equilibria?
When is Nash equilibrium
“the right answer”?
1. Players are “rational”. Each player’s strategy
maximizes his payoff, given his beliefs about
the strategies used by the other players.
2. Each player’s beliefs about the other players’
strategies are correct.
When is 2) a reasonable assumption?
3-Hunter Stag Hunt
Hunter 3 does Hare
Hunter 3 does Stag
Hunter 2
Hunter 2
Stag
2,2,2
0,1,0
Stag
Hunter 1
Hare
Stag
Hare
1,0,0 1,1,0
Find the Nash equilibria
Stag
Hunter 1
Hare
Hare
0,0,1 0,1,1
1,0,1 1,1,1
Weakly dominated strategies?
• Nobody will use a strictly dominated strategy
in Nash equilibrium.
• If there is a strictly dominant strategy for all
players, it is a Nash equilibrium. (example
Prisoners’ Dilemma.)
• Nash equilibrium does not exclude possibility
of using a weakly dominated strategy. (A
voting example with unanimous preferences.)
Nash and domination
Every Nash equilibrium survives the iterated
elimination of strictly dominated strategies.
Not every outcome that satisfies the iterated
elimination of strictly dominated strategies is a
Nash equilibrium.
Clicker Question 3:
Strategy A2 Stategy B2 Strategy C2
Strategy A1
Strategy B1
Player 1
Strategy C1
6,0
2,3
1,1
3,2
2,3
2,0
4,1
2,8
5,2
Does this game have more than one Nash
equilibrium?
A) Yes
B) No
Clicker Question:
What are the Nash Equilibria for this game?
4,1
A) Player 1 plays a and Player 2 plays z.
B) Player 1 plays d and Player 2 plays z.
C) Player 1 plays b and Player 2 plays y.
D) Both outcomes A) and B) are Nash equilibria.
E) There are no Nash equilibria