Game Theory Homework: Nash Equilibria & Cournot Competition
advertisement
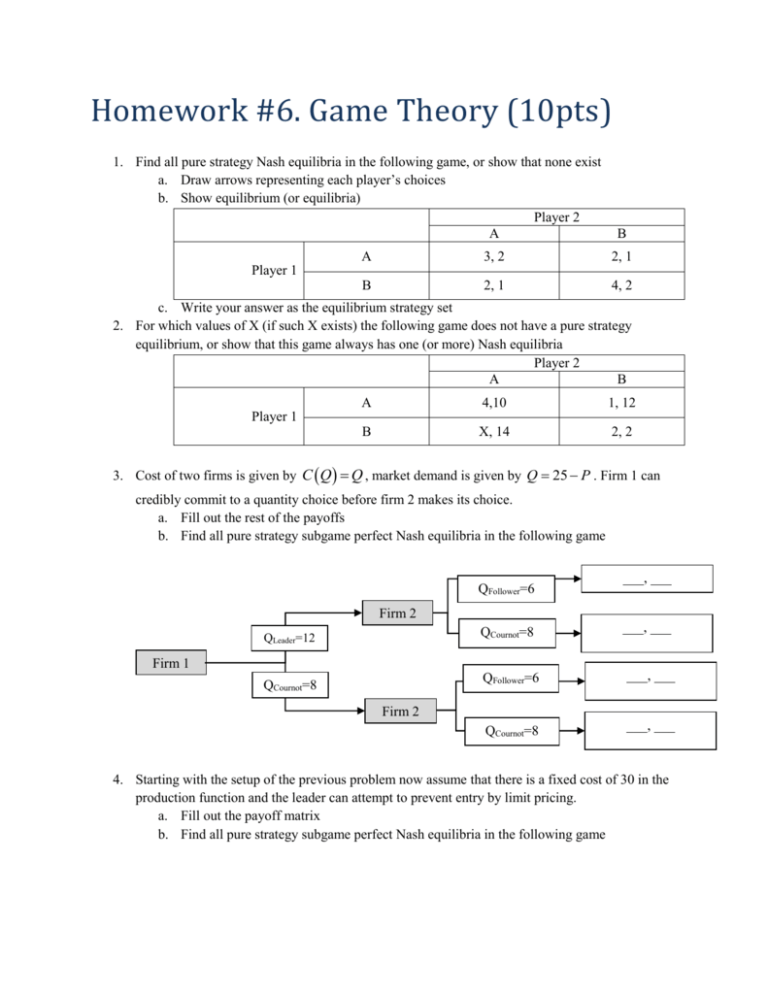
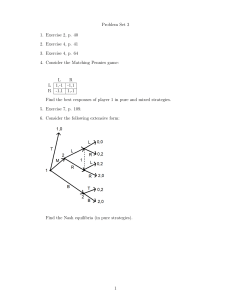
Homework #6. Game Theory (10pts) 1. Find all pure strategy Nash equilibria in the following game, or show that none exist a. Draw arrows representing each player’s choices b. Show equilibrium (or equilibria) Player 2 A B A 3, 2 2, 1 B 2, 1 4, 2 Player 1 c. Write your answer as the equilibrium strategy set 2. For which values of X (if such X exists) the following game does not have a pure strategy equilibrium, or show that this game always has one (or more) Nash equilibria Player 2 A B A 4,10 1, 12 B X, 14 2, 2 Player 1 3. Cost of two firms is given by C Q Q , market demand is given by Q 25 P . Firm 1 can credibly commit to a quantity choice before firm 2 makes its choice. a. Fill out the rest of the payoffs b. Find all pure strategy subgame perfect Nash equilibria in the following game QFollower=6 ___, ___ Firm 2 QLeader=12 QCournot=8 ___, ___ QFollower=6 ___, ___ QCournot=8 ___, ___ Firm 1 QCournot=8 Firm 2 4. Starting with the setup of the previous problem now assume that there is a fixed cost of 30 in the production function and the leader can attempt to prevent entry by limit pricing. a. Fill out the payoff matrix b. Find all pure strategy subgame perfect Nash equilibria in the following game Enter, QFollower=6 ___, ___ Firm 2 QLeader=12 Not enter, Q=0 _____, 0 Enter, Q=__ ____,_____ Not enter, Q=0 ______, 0 Firm 1 QLimit=14 Firm 2 5. Solve problem 3 at the end of chapter 6 6. Solve problem 4 at the end of chapter 6. This problem is optional but a good attempt is required. This problem demonstrates how the nature of the competition affects how firms react to changes in prices. You may use formulas from the appendix to find the answer. 7. Solve problem 7 at the end of chapter 6