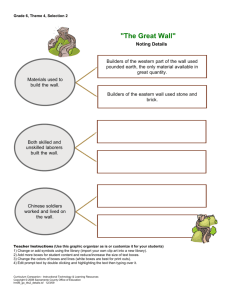
Thinking in New Boxes
You need a systematic way to identify and question old boxes…
and then create new ones
Doubt
Explore
Diverge
Creativity | Innovator
(right brain)
Converge
Reevaluate
Execution | Investor-Manager
(left brain)
Entrepreneurship
(ambidexterity)
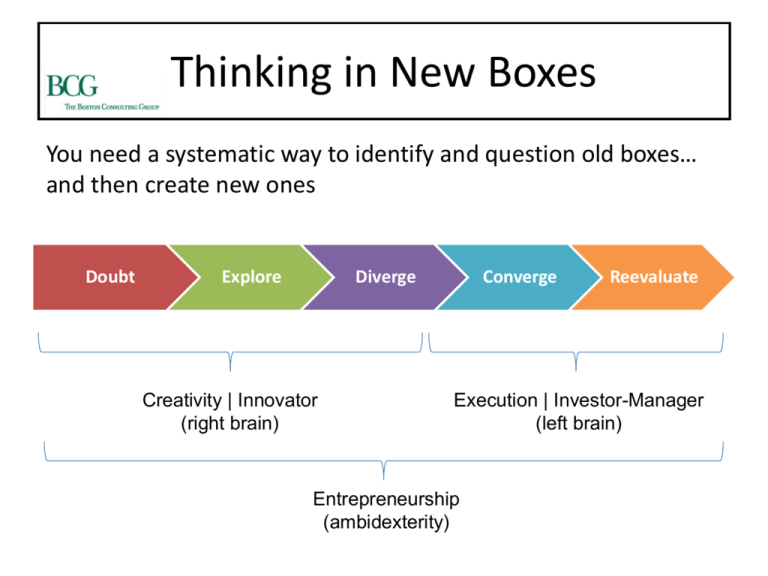
Thinking in New Boxes
You need a systematic way to identify and question old boxes…
and then create new ones
Doubt
Explore
Diverge
Converge
Reevaluate
All our ideas are only working hypotheses
• We need to identify our models and try to explore ways in
which they might be adapted
(example: Crushing exercise)
Thinking in New Boxes
You need a systematic way to identify and question old boxes…
and then create new ones
Doubt
Explore
Diverge
Converge
Reevaluate
All our ideas are from the world
• Research can help us understand the world in
front of us, using tools including trends (CH4),
customer insight (IA#2), competitive analysis, etc.
Thinking in New Boxes
You need a systematic way to identify and question old boxes…
and then create new ones
Doubt
Explore
Diverge
Converge
Reevaluate
No idea is born good—and the best way to
have a good idea is to have a lot of ideas
• Brainstorming and other exercises (CH4)
• The key is to shift perspective, reframe
the problem, and try new combinations
(example: Collective notebook of 50 ideas)
Recap
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
CH1:
CH1:
CH4:
CH4:
CH2:
CH2:
CH3:
CH3:
foundational definitions
entrepreneurial thinking
tools to floss minds
encourage creativity everywhere
implement ENT as a manager
ride corp. elevator as an employee
you’re you best critic so make it work
what investors look at
3-5
Chapter 3
Entrepreneurial Strategy:
Generating and Exploiting
New Entries
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Justin Parer
• His entrepreneurial story in one sentence…
(for example)
• Learn from failure
• Why a career jungle gym is better than a
corporate ladder
• Be your own best critic!
ENTREPRENEURIAL ACTION IS…
(CH1)
Action through the creation of new products/processes and or the entry
into new markets, which may occur through a newly created organization
or within an established organization
“New Entry” includes…
(3 elements)
• New product in an established or new market
• Established product in a new market
• A new organization
(1 more element based on the definition of ENT
action in CH1 and the purpose of CH2)
• Or a new operation within an established
organization
Entrepreneurial strategy is…
Figure 1.1 - Entrepreneurial Action
HOW CAN WE DO IT?
We need resources
“Resources”…
•
•
•
•
•
Are a source of _______________.
Inputs into the production process
Are basic building blocks to a firm’s functioning
Can be combined in different ways
Provide capacity to achieve superior performance
when they are:
• __________
• __________
• __________ (including __________)
Examples of VRIN
• What’s valuable?
• (for example) Air
• To whom is it valuable?
• (for example) Not Martians
• Can you sell it?
• (for example) Well… not if it is “rare”
Oxygen Bar
Examples of VRIN
• What about inimitable?
• What about nonsubstituable?
• “Nothing lasts forever” – Maroon 5
Know your target customers
Know yourself
Know your competitors
Know your suppliers
IS “LIGHT YEARS AHEAD” ALL
GOOD?
It depends
Now or Later (or Never)
First-mover (dis)advantages
• Environmental instability
• Demand uncertainty:
• Potential size, growth, and the key dimensions along
which a market will grow
• Technological uncertainty:
• The technology will perform
• Alternate technologies will emerge and leapfrog over
current technologies
• Adaptation:
• Persistence and determination can inhibit the ability to
adapt
First-mover (dis)advantages
• Overcome customers’ uncertainty (IA#2) by:
•
•
•
•
Informational advertising
Highlighting product benefits over substitutes
Creating a frame of reference for potential customers
Educating customers through demonstration and
documentation
3-19
First-mover (dis)advantages
• Lead time
• Is the grace period in which the first mover
operates in the industry under conditions of
limited competition
• Can be extended by:
•
•
•
•
Building customer loyalties
Building switching costs
Protecting product uniqueness
Securing access to important sources of supply and
distribution
To be or not to be
The attractiveness of a new entry opportunity
depends on (2 things):
• The level of information
• Willingness to make a decision under uncertainty
• Error of commission
• Error of omission
Indecision is a decision!