Suicidality & Substance Abuse
advertisement

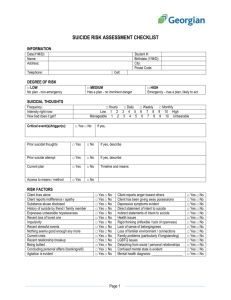
Suicidality & Substance Abuse Bruce Michael Cappo, Ph.D. Clinical Associates, P.A. Quo Vadis Intro Statistics Causality Substance factors Risk Factors What we know What to do 2 The Three Hs: Hopelessness Helplessness Haplessness 3 Hopelessness Strongest predictor of suicide Stronger even than depression Only people who have lost all hope kill themselves. Do whatever you can to build hope - however small it may be. They want to have hope in the future. 4 Helplessness The person views him or herself as being absolutely unable to make any changes to the situation or to his/her life This characteristic should signal a high risk situation for you. 5 Haplessness These people often have very sad lives 25% have a family history of successful suicidal behavior in a relative Higher percentage who have histories of mental illness, depression, abuse, divorces, frequent moves and periods of unemployment in their family Often there are multiple problems at the same time which just become too overwhelming. 6 Suicide is a tragic and potentially preventable public health problem 8th leading cause of death in the U.S. 10.6 out of every 100,000 persons died by suicide 7 The total number of suicides was approximately 31,000, or 1.3 percent of all deaths. Approximately 500,000 people receive emergency room treatment as a result of attempted suicide each year 8 Substance Use and the Risk of Suicide Among Youths Approximately 3 million youths were at risk for suicide during the past year 9 Substance Use and the Risk of Suicide Among Youths Youths who reported past year alcohol or illicit drug use were more likely than youths who did not use these substances to be at risk for suicide 10 Substance Use and the Risk of Suicide Among Youths Only 36 percent of youths at risk for suicide during the past year received mental health treatment or counseling 11 12 Underestmated Numbers? Authorities agree that many suicides are not reported, but the National Center for Health Statistics records between 25,000 and 30,000 self-inflicted deaths in the U.S. annually. 15 Attempts vs Completions For every death from suicide, experts estimate that eight other suicide attempts are made. Suicide is now the second leading cause of death among persons 15 to 24 years of age. It is increasingly a problem among adolescents and elderly people. 16 Statistical Indicators of Risk Previous suicide attempts The verbalizing of suicide threats The giving away of prized personal possessions The collection and discussion of information on suicide methods 17 Statistical Indicators of Risk The expression of hopelessness, helplessness, and anger at oneself or the world Themes of death or depression evident in conversation, written expressions, reading selections, or artwork 18 Statistical Indicators of Risk Statements or suggestions that the speaker would not be missed if he or she were gone Physical symptoms such as eating disturbances, sleeplessness or excessive sleeping, chronic headaches or stomachaches, menstrual irregularities, apathetic appearance 19 Statistical Indicators of Risk Use or increased use of substances Look for sudden changes in behavior that are significant, last for a long time, and are apparent in all or most areas of his or her life (pervasive). 20 Often occur prior to acts of self-harm The scratching or marking of the body, or other self-destructive acts Recent loss of a friend or a family member (or even a pet) through death or suicide; other losses (for example, loss of a parent resulting from divorce) 21 Often occur prior to acts of self-harm Acute personality changes, unusual withdrawal, aggressiveness, moodiness, or new involvement in high-risk activities. Sudden dramatic decline or improvement in academic performance, chronic truancy, tardiness, or running away 22 Who is at highest risk for suicide in the U.S.? Common misperception that suicide rates are highest among the young Elderly, particularly older white males have the highest rates Among white males 65 and older, risk goes up with age 23 Who is at highest risk for suicide in the U.S.? White men 85 and older have a suicide rate that is six times the national rate White males are more deliberate in their suicide intentions They use more lethal methods (firearms) & don’t tell of their plans Older persons are less likely to survive attempts because they are less likely to recuperate 24 "They [researchers] cite a wide range of potential suicide triggers, from loss of employment or loved ones, to aging and physical impairment. But, in almost all cases, they agree there is an underlying psychiatric illness-primarily depression, followed by alcoholism and substance abuse." "The Mystery of Suicide," Newsweek, April 18, 1994 Causality No cause-and-effect relationship between use of alcohol and/or other drugs and suicide has been established Substances often identified as a contributing factor 26 Possible Explanations Drinking, use of other drugs, or both may reduce inhibitions and impair the judgment of someone contemplating suicide, making the act more likely Use may also may aggravate other risk factors for suicide such as depression or other mental illness. 27 Alcohol/other drug problem prevention in reducing suicides: High rates of alcohol involvement have been found among suicide victims who use firearms. Recent studies suggest that alcohol tends to be associated with impulsive rather than premeditated suicides 28 Alcohol/other drug problem prevention in reducing suicides: Between 20 and 35 percent of suicide victims had a history of alcohol abuse or were drinking shortly before their suicides 29 Alcohol/other drug problem prevention in reducing suicides: Nearly 24 percent of suicide victims had blood alcohol concentrations (BACs) of .10 or greater Similarly, an analysis of 100,000 deaths in 1989 found positive BACs in 35 percent of suicide fatalities 30 Alcohol/other drug problem prevention in reducing suicides: In one study of youthful suicide, drug and alcohol abuse was the most common characteristic of those who attempted suicide Fully 70 percent of these young people frequently used alcohol and/or other drugs 31 Alcohol/other drug problem prevention in reducing suicides: In 1989, the cost of providing health care for people who had attempted suicide was estimated at $116.4 million annually 32 Alcohol/other drug problem prevention in reducing suicides: Prevention works, and preventing alcohol, tobacco, and other drug problems also can help prevent suicide. 33 Does alcohol and other drug abuse increase the risk for suicide? A number of recent national surveys have helped shed light on the relationship between alcohol and other drug use and suicidal behavior. A review of minimumage drinking laws and suicides among youths age 18 to 20 found that lower minimum-age drinking laws was associated with higher youth suicide rates 34 Does alcohol and other drug abuse increase the risk for suicide? In a study of all non-traffic injury deaths associated with alcohol intoxication, over 20 percent were suicides. 35 Does alcohol and other drug abuse increase the risk for suicide? Lower minimum-age drinking laws are associated with higher youth suicide rates For particular groups at risk, such as American Indians and Alaskan Natives, depression and alcohol use and abuse are the most common risk factors for completed suicide 36 Does alcohol and other drug abuse increase the risk for suicide? In a large study of adults who drink alcohol, suicidal ideation was more likely reported among persons with depression Persons who had made a suicide attempt were more likely to have had a depressive disorder and many also had an alcohol and/or substance abuse disorder 37 Other Risk Factors Aggressive behavior doubled suicide risk among boys Panic attacks nearly tripled suicide risk for girls Being a teenage runaway nearly tripled suicide risk Perfectionism has also been linked to suicide in some studies 38 Substance Abuse May Escalate Suicidal Ideas to Attempts in Teens A study in the September issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry provides important insights into the relationships between psychiatric disorders and adolescent suicide, suggesting that teens who abuse drugs or alcohol are more likely to progress from suicidal thoughts to 39 suicide attempts Substance Abuse May Escalate Suicidal Ideas to Attempts in Teens The research assessed the links among suicidal ideas, suicide attempts, and adolescent psychiatric disorders in a random sample of nearly 1,300 children aged 9 to 17 years. Of these, 67 had had suicidal thoughts 42 had made suicide attempts. Adjusted for age and gender 40 Substance Abuse May Escalate Suicidal Ideas to Attempts in Teens suicide attempts were significantly more likely for youngsters with mood disorders (depression and bipolar disorder), anxiety disorders, and substance abuse or dependence issues. 41 In order to find it you must look Recognition and appropriate treatment of mental and substance abuse disorders also hold great suicide prevention value Most elderly suicide victims --70 percent -have visited their primary care physician in the month prior to their suicides Recognition and treatment of substance abuse and depression in medical settings can help prevent suicide in older adults 42 Risk factors among people who have completed suicide For particular groups at risk, such as American Indians and Alaskan Natives, depression and alcohol use and abuse are the most common risk factors for completed suicide. Substance use & abuse occurs more frequently among youth and adults, compared to older persons. 43 Alcohol and substance abuse problems contribute to suicidal behavior Persons who are dependent on substances often have a number of other risk factors for suicide. In addition to being depressed, they are also more likely to have social and financial problems. 44 Alcohol and substance abuse problems contribute to suicidal behavior Substance use and abuse can be common among persons prone to be impulsive, and among persons who engage in many types of high risk behaviors that result in self-harm 45 What are the most common methods of suicide? Firearms For men and women 60 percent of all suicides Nearly 80 percent of all firearm suicides are committed by white males 46 Common Methods The second most common method for men is hanging The second most common method for women is self-poisoning including drug overdose 47 Common Methods The presence of a firearm in the home has been found to be an independent, additional risk factor for suicide. Thus, when a family member or health care provider is faced with an individual at risk for suicide, they should make sure that firearms are removed from the home. 48 Male - Female Differences More than four times as many men as women die by suicide Women attempt suicide more often during their lives than do men Women report higher rates of depression. 49 Why the Gender Differences? Completed suicide is associated with aggressive behavior that is more common in men Men and women use different suicide methods 50 Why the Gender Differences? Women in all countries are more likely to ingest poisons than men In countries where the poisons are highly lethal and/or where treatment resources scarce, rescue is rare and hence female suicides outnumber males 51 If someone tells you they are thinking about suicide Take their distress seriously Listen non-judgmentally Evaluate & get them to appropriate treatment People consider suicide when they are hopeless and unable to see alternative solutions to problems 52 If someone tells you they are thinking about suicide Suicidal behavior is also more likely to occur when people experience stressful events (major losses, incarceration) If someone is in imminent danger of harming himself or herself, do not leave the person alone. Limit access to firearms or other lethal means of committing suicide. 53 Are African American youth at great risk for suicide? Historically, African Americans have had much lower rates of suicides Rising at a faster rate for African American male youth Trend is for a decrease in suicide across all gender and racial groups Increase in suicide by firearms for all young males ‘Victim precipitated homicide’ in Black Males? 54 Is suicide related to impulsiveness? The mental disorders with impulsiveness most linked to suicide include borderline personality disorder among young females, conduct disorder among young males and antisocial behavior in adult males, and alcohol and substance abuse among young and middle-aged males 55 Is suicide related to impulsiveness? Impulsiveness appears to have a lesser role in older adult suicides ADHD is not a strong risk factor for suicide Impulsiveness has been linked with aggressive and violent behaviors Impulsiveness without aggression or violence present has also been found to contribute to risk for suicide. 56 What biological factors increase risk for suicide? Depression and suicidal behavior can be linked to decreased serotonin Low levels of a serotonin metabolite, 5HIAA, have been detected in CSF in persons who have attempted suicide, as well as by postmortem studies of suicide victims 57 Can the risk for suicide be inherited? Growing evidence that familial and genetic factors contribute to the risk for suicidal behavior Major psychiatric illnesses, including bipolar disorder, major depression, schizophrenia, alcoholism and substance abuse, and certain personality disorders, which run in families, increase the risk for suicidal behavior 58 Can the risk for suicide be inherited? This does not mean that suicidal behavior is inevitable for individuals with this family history Such persons may be more vulnerable and should take steps to reduce their risk, such as getting evaluation and treatment at the first sign of mental illness. 59 Does depression increase the risk for suicide? The majority of people who have depression do not die by suicide Major depression does increase suicide risk compared to people without depression 60 Does depression increase the risk for suicide? The risk of death by suicide may be related to the severity of the depression About 2% of persons ever treated for depression in an outpatient setting will die by suicide Among those ever treated for depression in an inpatient hospital setting, the rate of death by suicide is twice as high (4%) 61 Does depression increase the risk for suicide? Those treated for depression as inpatients following suicidal ideation or suicide attempts are about three times as likely to die by suicide (6%) as those who were only treated as outpatients 62 Gender Differences There are significant gender differences in lifetime risk of suicide in depression 7% of men with a lifetime history of depression will die by suicide 1% of women with a lifetime history of depression will die by suicide. 63 ”Suicide Contagion" Exposure to suicide or suicidal behaviors within one's family, peer group, or through media reports of suicide Can result in an increase in suicide and suicidal behaviors 64 Contagion Direct and indirect exposure to suicidal behavior has been shown to precede an increase in suicidal behavior in persons at risk for suicide, especially in adolescents and young adults. The risk for suicide contagion as a result of media reporting can be minimized by factual and concise media reports of suicide 65 Contagion Reports of suicide should not be repetitive, as prolonged exposure can increase the likelihood of suicide contagion Family members, friends, peers, and colleagues of the victim should be monitored and possibly evaluated by a mental health professional 66 Do school-based suicide awareness programs prevent youth suicide? Few programs have been evaluated to see if they work Of the programs that have been evaluated, none has proven to be effective Some programs have had unintended negative effects by making at-risk youth more distressed and less likely to seek help These programs present suicide as an option and ‘normalize’ it 67 Is it possible to predict suicide? No definitive measure to predict suicide or suicidal behavior Factors can identify individuals at higher risk for suicide Very few persons with these risk factors will actually commit suicide 68 Prediction Risk factors include mental illness, substance abuse, previous suicide attempts, family history of suicide, history of being sexually abused, and impulsive or aggressive tendencies Suicide is a relatively rare event and difficult to predict statistically 69 What to do... Promote overall mental health among schoolaged children by reducing early risk factors for depression, substance abuse and aggression Detect youth most likely to be suicidal by confidentially screening for depression, substance abuse, and suicidal ideation If a youth reports any of these, further evaluation takes place by professionals, followed by referral for treatment as needed 70 Treatment Strategies - Meds Antidepressants Cyclic antidepressants including tricyclics. MAO inhibitors SSRIs 71 Treatment Strategies - Therapy Psychodynamic /Interpersonal Psychotherapy Behavior Therapy Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT) Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) 72 Attempted Suicides No annual national data on attempted suicide are available; reliable scientific research, however, has found that: There are an estimated 8-25 attempted suicides to one completion; the ratio is higher in women and youth and lower in men and the elderly 73 Attempts More women than men report a history of attempted suicide, with a gender ratio of 3:1 The strongest risk factors for attempted suicide in adults are depression, alcohol abuse, cocaine use, and separation or divorce 74 Attempts The strongest risk factors for attempted suicide in youth are depression, alcohol or other drug use disorder, and aggressive or disruptive behaviors 75 Risk of Suicide Attempt 3% Overall 22% children with major depression 25 % in those with substance abuse or dependence. with two or more disorders, the rate of suicidal ideation was eight times higher than normal, rate of suicide attempts was 18 times higher than normal. 76 Findings Substance abuse or dependence is specifically related to suicide attempts Substance abuse appeared to play a key role in the transition from suicidal thoughts to actual suicide attempts. Certain psychiatric symptoms raise the risk of suicide. 77 Time for Your Questions 78