Terrestrial Biome Notes
advertisement

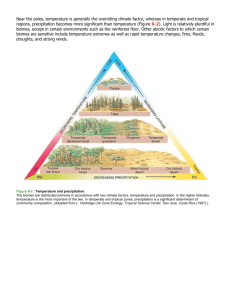
Terrestrial Biomes (3.2) State Standard SB4A. Investigate the relationships among organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, and biomes. Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems 3.2 Terrestrial Biomes EFFECTS OF LATITUDE/CLIMATE 1 Weather is the condition of the atmosphere at a specific place and time. One of the keys to understanding these communities is to be aware of latitude and climatic conditions. Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems 3.2 Terrestrial Biomes EFFECTS OF LATITUDE/CLIMATE 2 - Latitude The distance of any point on the surface of Earth north or south from the equator is latitude. Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems 3.2 Terrestrial Biomes EFFECTS OF LATITUDE/CLIMATE 3 - Climate The average weather conditions in an area, including temperature and precipitation, describe the area’s climate. The graph shows how temperature and precipitation influence the communities. Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems 3.2 Terrestrial Biomes MAJOR LAND BIOMES 1 Biomes are classified by 3 factors: plant life temperature precipitation Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems 3.2 Terrestrial Biomes MAJOR LAND BIOMES 2 - Tundra Tundra Temp: Very low Precipitation: Very low Plant Life: Treeless, short grasses, shallow-rooted shrubs Animal Life: Caribou, polar bears, birds, insects, wolves, trout, salmon Location: South of the polar ice caps in the Northern hemisphere Abiotic factors: soggy summers; permafrost; cold and dark much of the year Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems 3.2 Terrestrial Biomes MAJOR LAND BIOMES 3 – Boreal Forest Boreal Forest Temp: Low Precipitation: Low Plant Life: Spruce & Fir (Christmas) trees, decidous trees, small shrubs Animal Life: birds, moose, beavers, deer, wolverines, mountain lions Location: Northern part of North America, Europe, Asia Abiotic factors: short/moist summers long/cold/dry winters *** AKA Taiga or Northern Coniferous Forest *** Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems 3.2 Terrestrial Biomes MAJOR LAND BIOMES 4 – Temperate Forest Temperate Forest Temp: Moderate Precipitation: Moderate Plant Life: Deciduous trees (oak/maple/beech), shrubs Animal Life: squirrels, rabbits, skunks, birds, deer, foxes, black bear Location: South of boreal forest in eastern N. America, eastern Asia, Australia, & Europe Abiotic factors: well-defined seasons; hot summers, cold winters ***AKA Temperate Decidous Forest*** Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems 3.2 Terrestrial Biomes MAJOR LAND BIOMES 5 – Temperate Woodland/Shrubland Temperate Woodland/Shrubland Temp: Moderate Precipitation: Low Plant Life: Evergreens, shrubs, corn oak Animal Life: foxes, jackrabbits, birds, bobcats, coyotes, lizards, snakes, butterflies Location: surrounds Mediterranean Sea, western coasts of North & South America, South Africa, & Australia Abiotic factors: Hot, dry summers; cool, wet winters Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems 3.2 Terrestrial Biomes MAJOR LAND BIOMES 6 – Temperate Grassland Temperate Grassland Temp: moderate Precipitation: moderate to low Plant Life: grasses & herbs Animal Life: gazelles, bison, horses, lions, deer, mice coyotes, foxes, wolves, birds, snakes, grasshoppers, spiders Location: North & South America, Asia, Africa, Australia Abiotic factors: hot summers, cold winters, fires Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems 3.2 Terrestrial Biomes MAJOR LAND BIOMES 7 - Desert Desert Temp: Very High to low Precipitation: Very low Plant Life: cacti, Joshua trees, succulents Animal Life: lizards, bobcats, birds, tortoises, rats, antelope, desert toads Location: every continent except Europe Abiotic factors: dry; widely variable temperature from day to night Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems 3.2 Terrestrial Biomes MAJOR LAND BIOMES 8 – Tropical Savanna Tropical Savanna Temp: Very high Precipitation: Moderately Low Plant Life: grasses & scattered trees Animal Life: lions, hyenas, cheetahs, elephants, giraffes, zebras, birds, insects Location: Africa, South America, & Australia Abiotic factors: hot/rainy summers; cool/dry winters ***Think “Lion King”*** Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems 3.2 Terrestrial Biomes MAJOR LAND BIOMES 9 – Tropical Seasonal Forest Tropical Seasonal Forest Temp: Very High Precipitation: Moderate Plant Life: deciduous & evergreen trees, orchids, mosses Animal Life: elephants, tigers, monkeys, koalas, rabbits, frogs, spiders Location: Africa, Asia, Australia, South & Central America Abiotic factors: seasonal rainfall Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems 3.2 Terrestrial Biomes MAJOR LAND BIOMES 10 – Tropical Rain Forest Tropical Rain Forest ***Biome with the most biodiversity*** Temp: Very High Precipitation: Very High Plant Life: broadleaf evergreens, bamboo, sugar cane Animal Life: chimps, Bengal tigers, elephants, toucans, bats, orangutans, sloths, snakes, insects Location: Central & South America, southern Asia, western Africa, & northeastern Australia Abiotic factors: humid all year; hot/wet Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems 3.2 Terrestrial Biomes OTHER TERRESTRIAL AREAS 1 Mountains If you go up a mountain, temperature and precipitation will change with increasing elevation. An increase in altitude has the same effect as an increase in latitude. The highest points on a mountain will resemble the tundra. ***Be able to explain this diagram*** Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems 3.2 Terrestrial Biomes OTHER TERRESTRIAL AREAS 2 Polar Regions Border the tundra at high latitudes Polar regions are cold all year. Penguins in Antarctica