Earthworm Excretory System: Nephridia & Excretion
advertisement

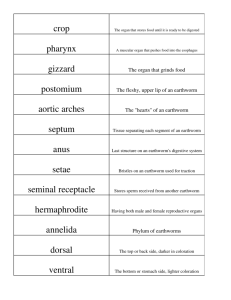
Earthworm Excretory system http://image.tutorvista.com/content/excretion-and-osmoregulation/earthworm-cross-section.jpeg New Vocabulary • Coelom – Body cavity, space • Nephridia – unit of the excretory system in earthworms • ‘stome’ – mouth like opening • Earthworm belongs to Phylum Annelida (higher invertebrates) • Excretory systems consists of nephridia which are small, coiled tubes along the body. 3 types of nephridia depending on location • Septal (behind the 15th segment) • Integumentary( along the inner side of body) • Pharyngeal(4th, 5th, 6th segments only) • A typical nephridium consists of a ciliated funnel or nephridiostome which opens into the coelomic cavity. http://shs.westport.k12.ct.us/mjvl/biology/dissect/earthworm_images/earthworm_nephridia.gif • This is followed by a short and narrow tube called the neck which is bent on itself and opens into the main body of the nephridium. • The cells lining the nephridiostome and the nephridial tube bear cilia in some lengths. The lashing movements of the cilia help in the flow of the excretory matter. Process of Excretion • Since the nephridia are richly supplied with capillaries, n_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _s wastes are removed from the blood. • The rhythmic beating of the cilia of the nephridiostomes drives a steady stream of coelomic fluid containing metabolic waste materials, such as u_ _a, a_ _ _ _ _ a and remains of dead cells, into and through the nephridial tube. • The excretory wastes are then finally discharged into the gut. Only waste matter is excreted from the capillaries with which they are richly supplied. Thus water is conserved by these nephridia. Reference: www.tutorvista.com