Simple Electric Circuits
advertisement

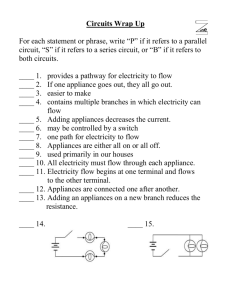
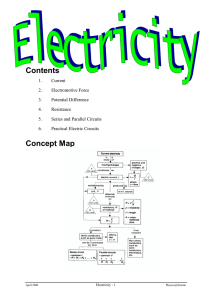
Simple Electric Circuits To know how to set up simple electric circuits, and represent these using symbols and explain the energy transfers taking place Energy & Money There are many ways a house can be made more energy efficient, however some of these techniques are more cost-effective than others Complete the saving energy and money worksheet Energy & Money Payback time – eventually the money saved per year on reduced heating bills will equal the initial cost of the insulation Insulation Type Cost Saving Made In 1 Year Payback Time Double Glazing £3000 £150 20 Years Loft Insulation £400 £200 2 Years Cavity Wall Insulation £1000 £100 10 Years Draught Excluders £50 £10 5 Years Hot Water Tank Blankets £25 £10 2.5 Years Energy There are 10 types of energy: Light energy - from the sun; a light bulb etc… Sound energy - from a loudspeaker; a drum etc… Kinetic (movement) energy - anything which moves! Nuclear energy - transferred during a nuclear reaction Thermal (heat) energy - transferred from hot objects to colder ones Radiant heat (infra red) energy - transferred as electromagnetic radiation by hot objects Gravitational potential energy - possessed by anything with the ability to fall Elastic potential energy - stretched springs; elastic and rubber bands etc… Chemical energy - possessed by food; fuels; batteries etc Electrical energy - a current in a circuit etc… Electricity Energy can never be created or destroyed, it can only ever be converted from one form to another Energy is only useful when it is converted from one form to another Electricity is so useful because it can be easily transferred… Electricity Electricity is the flow of electrical power (charge) in the form of electrons Electricity is a useful secondary energy source – most energy sources (like coal, oil, nuclear, wind etc…) can be converted into electricity Circuits A bulb in the circuit is like a radiator – an electrical device uses electrical energy, supplied by the circuit The wires are like pipes - they carry the flow of electricity (current) around the circuit Cell + Wires The electrical current is pushed by the cell (battery) – this is the voltage The electrons flow from –ve to +ve Lamp Electrical Circuits An electric current needs two things: Something to make the electricity flow (battery or power pack) A complete circuit Without these two basic things, an electric current will not flow Cell + Wires forming a complete circuit - Component Diagrams Circuit symbols are used to show the components in an electrical circuit (wires are represented by straight lines) Symbols Complete the simple electric symbols worksheet Symbols Task – to set up simple circuits Draw the circuit diagram in your book Explain what energy transfers are taking place e.g. bulb energy transfer: electrical heat & light (if there is a bulb in your circuit)) Cell + Wires Switch Lamp Quiz