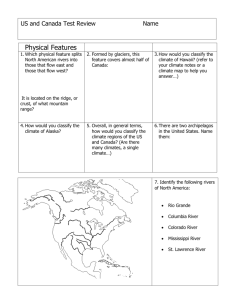
Addressing Physician Shortages in U.S. Rural Areas Policy
advertisement

NGO Code of Conduct for Health Systems Strengthening Julia Robinson, MPH MSW April 8, 2014 Outline Why a code of conduct? NGO Code of Conduct contents Research into implementation of the Code Discussion How best to use this Code? Are voluntary codes of conduct good tools for changing practices? HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL Why a code of conduct? Development aid for health quintupled since 1990, to $27.7 bn in 2011 US flows more than 50%of aid through NGOs Source: IHME/Murray et al, 2011 HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL Why a code of conduct? Fragmentation Loss of services Weak public sector health system Inefficiencies Mgmt burden Brain drain HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL Why a code of conduct? There are many factors contributing to weak public sector health systems – why focus on NGOs? HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL Why a code of conduct? Lots of them already exist …NGOs Responding to HIV/AIDS, Disaster Relief, International Philanthropy, general codes of ethics and conduct, etc. One World Trust CSO Project: http://www.oneworldtrust.org/csoproject/ HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL Why a code of conduct? Specifically, codes have been used for health workforce and recruitment efforts WONCA’s “Melbourne Manifesto” (2002) Commonwealth Code of Practice (2003) UK’s Code of Practice (2004) Voluntary Code of Ethical Conduct for the Recruitment of Foreign-Educated Nurses to the U.S. (2008) WHO Code of Practice on the international recruitment of health personnel (2010) HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL NGO Code of Conduct for HSS Coalition of organizations worked on drafting and consultations starting in 2007 Launched in May 2008 HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL NGO Code of Conduct for HSS 6 articles: Hiring practices Employee compensation practices Human resources training and support to systems Impact of management burden on ministries of health Support of MOH engagement with communities Policy advocacy for strengthening public sector ngocodeofconduct.org HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL NGO Code of Conduct for HSS 6 articles: Hiring practices Employee compensation practices Human resources training and support to systems Impact of management burden on ministries of health Support of MOH engagement with communities Policy advocacy for strengthening public sector ngocodeofconduct.org HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL First 3 articles: Human resources Hiring • Avoid hiring away from MOH • Coordinate with MOH in hiring • Hire nationals where possible (rather than expats) • Avoid creating incentives for migration Compensation • Fair monetary compensation, limit disparities • Strive for salaries not substantially greater than public sector • Avoid top-ups to MOH staff for outside work • Try to improve public sector benefits/pay Training and Support • Invest in pre-service education to increase number of workers • Build capacity of public sector workers (including mgmt) HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL Implementation so far 57 signatories today in 14 countries Thesis research by Anjali Sakhuja (MPH 2009) Questions: How are signatories implementing the Code of Conduct? What are best practices? What are challenges to operationalizing the Code? HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL Findings: Hiring Most respondents make efforts to avoid hiring from the MOH Have hired in the case of Person already resigned from MOH With permission from MOH In “after-hours” setting (also with permission) Challenges: Rural posts Project deadlines/pressure Ethics of refusing to hire due to MOH employment HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL Findings: Hiring Expatriates are hired when special expertise is needed; try to make it the exception rather than the rule Challenges Can’t hire from MOH (nationals), can’t hire expats – what if there isn’t anyone else? Bureaucracy to hire expats Expats from non-Western countries fleeing conditions in home countries HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL Findings: Compensation NGO salaries can be 10x greater, or more Challenges Low salaries make hiring and retention difficult Market pressures Finding an elusive balance Working conditions can be as important as salary considerations HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL Suggestions and promising practices Visibility of Code Post in lobby, include in orientation Improve public sector opportunities Highlight value in setting policy, broader impact Invest in career path opportunities Second staff to the MOH HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL Suggestions and promising practices Advocacy Donors should support/fund in line with Code Make signing on to the Code a condition of receiving funds Why not get the big players on board? HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL Summary Awareness, but few changes to HR policies Commitment to principles, challenges with hiring and compensation items Testing ideas in the field Importance of more preservice training Some efforts to coordinate amongst NGOs HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL Discussion How best to use the Code? Is a voluntary Code a good tool for changing practices? Other questions or thoughts? Thank you! HEALTH ALLIANCE INTERNATIONAL