Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 1
CHAPTER
7
BUSINESS PLAN
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 2
Objectives
The objectives of this chapter are to:
provide and understanding of preparing a systematic,
effective and viable business plan
provide a better understanding of the difficulties and
challenges of preparing a good business plan
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 3
Learning Outcomes
At the end of this chapter, students should be able to:
apply a systematic business planning methodology which can
be applied to many other tasks or undertakings
learn the various scopes and disciplines of business planning
such as marketing operation, finance, organization and human
resources management, many of which involve generic
planning skills that can be applied in their working careers and
their life.
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 4
Learning Outcomes (cont.)
use and enhance their communication skills through business
plan presentation
develop their creativity, innovativeness and critical thinking skills
when they work out their business plan.
improve their social skills by working in teams effectively and
harmoniously on the business planning project.
prepare a good business plan that is effective, practical and
viable.
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 5
Business Plan
A business plan is a written document that outlines the
detailed execution plan of the business. It will include
details of the:
organization, administration and human resource plan
− marketing plan
− production plan
− financial plan
The business plan should enable an entrepreneur to determine
whether the project is viable, needs to be modified or whether
the project is not feasible and should be abandoned altogether.
−
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 6
Key Planning Elements
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 7
Purposes of Preparing a Business
Plan
The business plan is normally written for the following purposes:
– it is used as a feasibility study to ascertain the viability of the project
– it is a guide for project implementation
– it is used as a document to justify and support loan application or to
entice and convince a partner or investor to invest in the business
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 8
Project Preliminary Screening
Before you prepare the business plan of the project, an
entrepreneur should do a preliminary screening on the suitability
of the project. At least he should have a general idea that the
proposed business is fairly satisfactory on the following issues.
– The viability, sustainability and growth potential of the business
concept, model and strategy
– Overcoming initial start up hurdle or chasm: The provision of
adequate capital, skill manpower and the ability to achieve early
break even sale volume
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 9
Business Plan Format
A basic business plan should include:
executive summary
table of content
introduction
company background
owner/partner background
location
organization, administration and human resource plan
marketing plan
operation plan
financial plan
conclusion
appendices
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 10
Example of a Simple Business
Plan
Introduction
The following is an example on how to prepare a simple business
plan for a burger kiosk. It shows important planning elements that
must be worked out, i.e.
organization, administration and human resources
market planning
operation planning
financial planning
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 11
Organization, Administration
and Human Resources Plan
for Burger Kiosk
Basic issues that need to be resolved for man power planning are:
Manpower requirement and the organization structure for the
company.
Manpower planning also includes planning for their job
qualifications, job specification, recruitment and their
remunerations budget.
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 12
Organization Chart
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 13
Employee’s Salary, EPF and SOCSO
contribution
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 14
Administrative Budget
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 15
Marketing Plan for Burger Kiosk
Basic marketing issues that need to be resolved are:
What is your product and its special attraction or quality?
Who is your target market?
What is the market size?
Who are your competitors and what are their competitive
strengths?
What is your market share and your sale forecast?
What are your marketing strategies?
What is your marketing budget and plan?
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 16
Marketing Strategies
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 17
Target Market Profile
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 18
Target Market Profile (cont.)
Based on the issues as outlined in the above table, the
following are issues for the burger kiosk.
What is your product range?
– burgers, hot dog, kebab, etc.
Where are you going to do your business?
– It should be at strategic location where there is sizable market or
traffic and accessible. The market growth potential is good.
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 19
Target Market Profile (cont.)
Who is your target market?
−
−
−
−
−
Let’s say the purchases expected from the main group of customers
in the area of operation are as follows:
College students
Factory workers
Local residents
Tourist and others
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 20
Target Market Profile (cont.)
What is the total market size?
The estimation of the total purchase of similar products in the
locality including those purchased from your competitors.
Let’s say daily market size is as follows:
−
−
−
−
−
College students 100@RM3.00
Local residents 50@RM3.00
Factory workers 30@RM3.00
Tourist and others 20@RM3.00
Total daily market size
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
RM300.00
RM150.00
RM 90.00
RM 60.00
RM600.00
All Rights Reserved
1– 21
Target Market Profile (cont.)
Who are your competitors?
Let’s say you only have one competitor in the area.
What is your market share and your daily sale forecast?
−
−
−
−
−
Let’s say, your market share is 50 per cent, thus sale forecast is
RM300.00 per day
What is your promotion strategy?
Roadside banners and signboard only.
What is you selling price?
RM3.00 per burger
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 22
Target Market Profile (cont.)
What is your marketing Budget
Let’s say, you are going to promote your burger through
pamphlet and roadside banner:
−
−
Pamphlet—Printing and distribution RM200.00
Banner—Printing and permit RM200.00
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 23
Operation Plan for Burger Kiosk
Basic production plan issues that need to be resolved are:
− What products do you want to produce and what are its quality
specifications and characteristics? Does this quality meet the target
customers’ needs and wants?
− What is the cost of production per unit and what is the possible
selling price the market can absorb?
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 24
Operation Plan for Burger Kiosk
(cont.)
How many do you need to produce per day/week / month so that
you can cater for your sale forecast?
Based on quality and quantity required, what is the best
production plan for the job; you will have to decide whether it is
going to be fully mechanized, semi-mechanized or totally
manual?
You will have to outline your material, machines, tools, space
and lay out needs based on the production process flow chart.
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 25
Operation Plan for Burger Kiosk
(cont.)
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 26
Operation Plan for Burger Kiosk
(cont.)
Based on your production schedule, you will have to plan and
calculate the following items:
– Product: chicken and beef burgers
Let’s say your operation is quite simple. Your material input cost
per burger is only RM1.00 and your selling price per burger is
RM3.00.
– Estimated sale per day RM300.00
– Cost of raw material for one day RM140, therefore for 5 days (one
week) RM700/week
– Sale for five days/week RM300 ×5 days = RM1,500/week
– Salary:
• RM20.00 /person for 2 persons
• 5 working days/ week, RM20 × 2 persons × 5 days = RM200/week
Let’s say your asset equipment cost is only RM1,500.00
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 27
Process Flow Chart
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 28
Process Flow Chart (cont.)
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 29
Financial Plan for Burger Kiosk
Basic financial plan includes the following:
project implementation cost
sources of fund for the project
financial schedule for asset depreciation and loan amortization
cash flow projection
income statement projection (profit and loss)
balance sheet projection
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 30
Project Implementation Cost
Example of project implementation cost of burger kiosk:
Project implementation cost is as follows:
Assets (equipment)
RM1,500
Working capital for one week i.e. salary and raw material:
RM100@5 days + RM40@5days=
RM 700
Registration cost
RM 100
Banner and pamphlet (one time)
RM 400
Total project implementation cost
RM2,700
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 31
Sources of Funds
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 32
Project Implementation Cost
Table
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 33
Depreciation Table
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 34
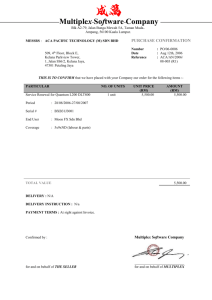
Loan Amortization Table
Example of loan amortization table for the proposed burger kiosk
project: Let’s say, the loan amount is RM1,000, duration 4 weeks,
interest at RM10.00 per week.
Period
Principal
Interest Loan balance
1st week
2nd week
3rd week
4th week
250
250
250
250
10
10
10
10
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
750
500
250
0
All Rights Reserved
1– 35
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 36
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 37
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 38
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 39
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 40
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 41
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 42
Social Entrepreneurship Project
As an alternative, students can also do a social entrepreneurship
project for their practicum.
Students can look into the internet to gain some ideas on the
types or themes of the social entrepreneurship project that can
be undertaken.
For instance, some non-governmental organizations (NGOs)
organize efforts to help the urban or rural poor, orphans, single
mums, ex-drug addicts, HIV or cancer patients, etc.
There are NGOs that work on environmental causes, animal
protection or organize to fight child labour, pollution, etc.
Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship
© Oxford Fajar Sdn. Bhd. (008974-T), 2013
All Rights Reserved
1– 43