Infection Control
advertisement

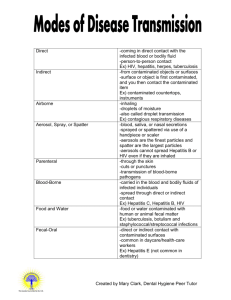
Infection Control Principles of Disease Transmission Microorganisms • Small living plant or animal • Non-pathogens – Live in or on the body – Part of the normal flora – May be beneficial to the body • Pathogens – Germs – Cause infection Types of Pathogens • Bacteria – One celled plants – Classified by shape and arrangement – Cocci – strep, staph – Bacilli – TB, tetanus – Spirilla – syphilis, cholera • Protazoa – One celled animals – Found in decayed material and contaminated water – Malaria, dysentery • Fungi – Simple plant-like organism – Live on dead matter – Yeasts, molds – Ringworm,athlet e’s foot, thrush Rickettsiae - Parasitic microorganism – Transmitted to humans through the bite of a tick,fleas, Typhus and lice, mites – Rocky Mountain spotted fever • Viruses – Smallest microorganism – Can only reproduce inside humans cells – Colds, chicken pox, warts, influenza, HIV, Hepatitis Needs of microorganisms • To Grow – – – – – – Warmth Darkness Source of food Moisture Aerobic need oxygen Anaerobic – don’t need oxygen How Pathogens Cause Infections • Poisons/toxins – Ex: tetanus • Allergic Reactions – Ex: runny nose, sneezing • Attack and Destroy cells they invade – Ex: malaria Additional Classifications • Endogenous – Originates inside the body • Exogenous – Originates outside the body • Nonsocomial – An infection acquired inside the hospital • Opportunistic – Infections that occur when the body’s immune system is weak Chain of Infection Asepsis • Absence of disease-producing microorganisms • Any area or object containing pathogens is considered contaminated Levels of aseptic Control • Antisepsis – Prevent or inhibit the growth of pathogenic organism but are not effective against spores or viruses. – Ex: Alcohol/Betadine Disinfection • Destroys or kills pathogenic organisms but not always effective against spores or viruses • Ex: Bleach, Clorox Sterilization • The process that destroys all microorganisms both pathogenic and nonpathogenic including spores and viruses. • Ex: Steam under pressure, autoclave, gas, radiation, chemicals Most Inexpensive, Quickest, and Effective way to prevent the spread of pathogens Standard Precautions Two Main Ways Pathogens Spread • Blood – HIV – Hepatitis B – Hepatitis C • Body Fluids OSHA • Occupational Safety and Health Administration • 1991 established blood-borne pathogen standard regulations Regulations • Determine employees who have occupational exposure • Provide the Hepatitis B vaccine free • Provide PPE – Personal Protective Equipment • Provide adequate hand washing facilities • Ensure the worksite is maintained in a clean and sanitary condition Regulations Cont. • Enforce NO eating , drinking, smoking, applying lip balm or lipstick, handling contact lenses or mouth pipetting in any area potentially contaminated with blood or body fluids. • Provide adequate sharps containers coded red/orange • Post signs in areas where there is occupational exposure • Provide confidential medical evaluation and follow up for any employee with an exposure • Provide free training for any new updates or changes Sharps • • • • • • all needles syringes syringe bodies scalpels lancets any glass items, such as slides or Pasteur pipettes, that are contaminated with potentially infectious material and/or human blood. PPE • Personal Protective Equipment Sterile Technique • Sterile – Free from all organisms • Contaminated – Organisms and pathogens are present – Items that touch your clothes or skin or any area below the waist are considered contaminated Sterile Field • • • • • Never reach across the top of the field Reach in from the sides to add to the field Never turn your back to a sterile field 2 inches around the border are contaminated Anything below the level of the tray is contaminated Methods to Remove Sterile Articles from Sterile Wraps • Drop Method • Mitten Method • Transfer Forceps Sterile Field • Keep Sterile field dry • Pathogens move quickly through wet surfaces • Take care when pouring solutions into a sterile field • When you put on sterile gloves, only handle sterile items Standards Precaustions • Used when contacting all patients Transmission-based Isolation • • • • Airborne Droplet Contact Protective Communicable Diseases • A disease caused by a pathogic organism that can be easily transmitted to others • Spread by – – – – Direct contact with patient Contact with blood and body fluids Droplets Discharge from wounds