Modes of Disease Transmission
advertisement
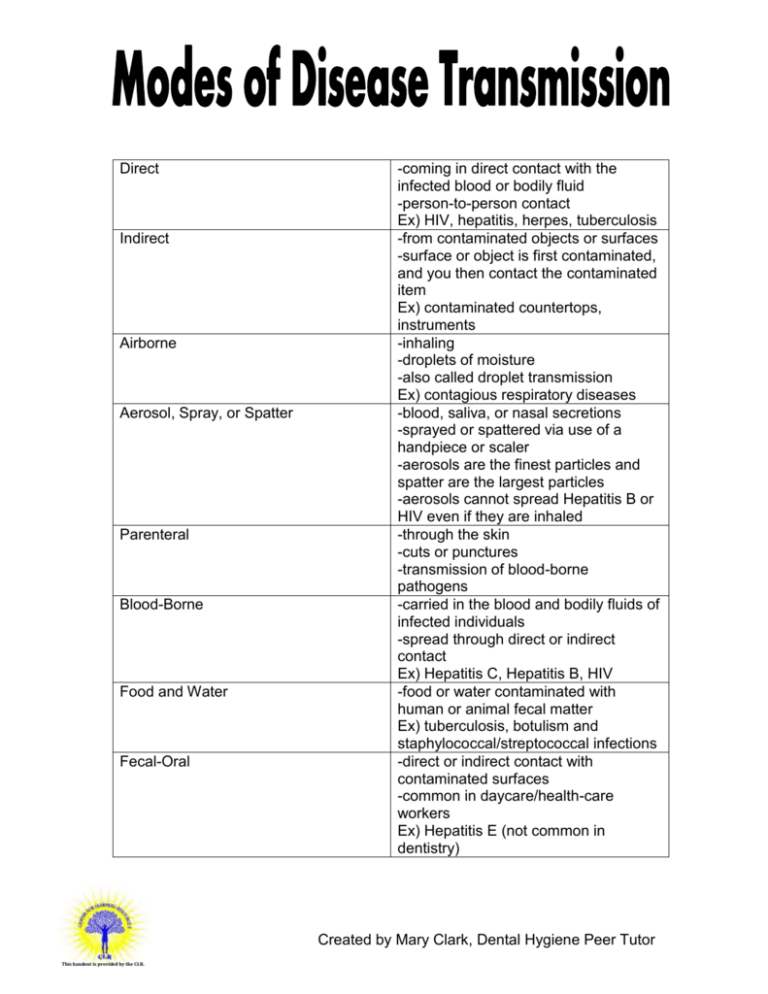
Direct Indirect Airborne Aerosol, Spray, or Spatter Parenteral Blood-Borne Food and Water Fecal-Oral -coming in direct contact with the infected blood or bodily fluid -person-to-person contact Ex) HIV, hepatitis, herpes, tuberculosis -from contaminated objects or surfaces -surface or object is first contaminated, and you then contact the contaminated item Ex) contaminated countertops, instruments -inhaling -droplets of moisture -also called droplet transmission Ex) contagious respiratory diseases -blood, saliva, or nasal secretions -sprayed or spattered via use of a handpiece or scaler -aerosols are the finest particles and spatter are the largest particles -aerosols cannot spread Hepatitis B or HIV even if they are inhaled -through the skin -cuts or punctures -transmission of blood-borne pathogens -carried in the blood and bodily fluids of infected individuals -spread through direct or indirect contact Ex) Hepatitis C, Hepatitis B, HIV -food or water contaminated with human or animal fecal matter Ex) tuberculosis, botulism and staphylococcal/streptococcal infections -direct or indirect contact with contaminated surfaces -common in daycare/health-care workers Ex) Hepatitis E (not common in dentistry) Created by Mary Clark, Dental Hygiene Peer Tutor This handout is provided by the CLR.