What are the trends in global forest production?
advertisement

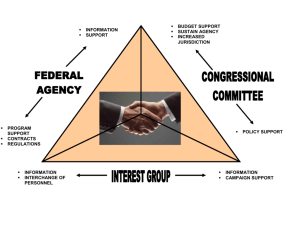
What is this map showing? What are the trends in global forest production? 1. What are the advantages of plantations over wild harvesting of forest products? 2. What are the differences in consumption of forest products in different societies? 3. What are the sources of UK timber and timber products? What are the advantages of plantations over wild harvesting of forest products? For timber and paper, tress are often grown in plantations TASK Why do harvest from wild communities produce lower yields than from plantations? Outline 3 reasons Natural woodland Plantation Irregular shape & tree density varies Edges are straight lines, even, high tree density Multi-species Monoculture Trees of all ages Trees all same age Variable light levels Low light levels once canopy has closed Contains open areas No open areas Native species May consist entirely of exotic species Accessible Inaccessible High wildlife value Low wildlife value Answers • fewer productive plants • more competitors • no genetic selection Plantations have a simpler ecological structure than natural forests. Explain the following 4 differences. 1. Species diversity 2. Age structure 3. Stratification 4. Interspecies relationships Answers Plantations have a simpler ecological structure than natural forests. Explain the following 4 differences. 1. Species diversity- small range of species selected for economic productivity 2. Age structure - large areas often planted at the same time 3. Stratification - fewer vegetation layers due to low species diversity and simple age structure 4. Interspecies relationships - Tree species are often exotic and don't support indigenous wildlife 2. What are the differences in consumption of forest products in different societies? Wood and Paper Imports TASK What are the key differences in forest product consumption between LEDCs and MEDCs Forest production Consumption of forest products in MEDCs and LEDCs MEDCs: • import huge volumes of hardwood as roundwood (tree stems) and then convert them into high value products e.g. furniture • They also import softwood for paper – making LEDCs: • export roundwood and import more expensive, finished products. • But as LEDCs develop, they are improving their capacity to manufacture and then export high-value goods • Huge volumes of wood are used as fuelwood in LEDCs Imports The UK imports over 50 million tonnes of wood and wood products annually 60 UK imports 50 Millions of m3 40 30 20 UK exports 10 0 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 Year Research Q: Why are we importing at the same time as exporting? Forest Cover How does our forest cover compare with other countries? Country Finland Sweden Russian federation Latvia Estonia Austria Portugal Italy Germany Switzerland Norway Greece France Spain UK Ireland % of land forested 72 65 50 47 48 47 40 34 30 30 29 28 27 27 11 9 3. What are the sources of UK timber and timber products? TASK. Display the following data on UK timber graphically. Imported wood and wood products (85% of total consumption) • 45% pulp and paper • 40% sawn wood • 15% wood panels UK production (15% of total consumption) 95% softwood • 40% for paper Ideas • 30% wood panels Divided bars • 25% sawn wood 5% hardwood • 3% fuel • 2% sawn wood