Introduction
advertisement

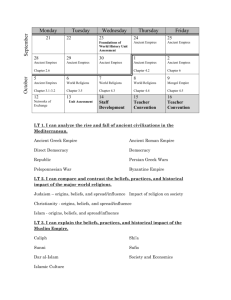
Ancient Empires An Introduction to Eight Imperial Civilizations of the Ancient World An Introduction to Eight Imperial Civilizations of the Ancient World 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires 1 Overview The Evolution of Civilization Anthropology and Archaeology in Historical Analysis The Rise and Characteristics of Empires Cities and Technologies Timelines 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires 2 The Evolution of Civilizations Definition: Civilization a culture that builds cities and has achievements in art, literature, science, and technology Civilizations don’t rise alone End product of evolution of culture within a geographic area 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires Rome 100 AD 3 Archaeology - Definition The study of human activity in the past, primarily through the recovery and analysis of the material culture and environmental data that they have left behind. 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires 4 Anthropology - Definition The study of humans, past and present, that draws and builds upon the knowledge from the social sciences and biological sciences as well as the humanities and natural sciences. 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires 5 The Importance of Archaeology Art of History Written records: • political, military, economic Bias toward rich & powerful Science of Archaeology Maya glyphs Adds accurate detail about daily life of ordinary people Changed modern view of history 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires 6 Key to History History is a gift Recreated in each generation Human mind has not changed in 200,000 years • Evolution of homo sapiens is cultural Clovis Hunter Archaeology Takes time, money Started in Europe • Heinrich Schliemann – Wealthy German businessman – Excavated Troy 1870’s 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires Heinrich Schliemann 7 Archaeology and Anthropology Science of Anthropology Archaeology Cultural anthropology Linguistics Physical anthropology Cultural history Archaeologist is anthropologist Seeing society whole • All social groups and functions • more accurate, meaningful interpretation of ancient cultures 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires 8 Hunter-Gatherers Big game hunting • Nomadic, migratory herds of land & sea mammals • Focus on one or two species First settlements River valleys on migration routes Extraction of unearned resources • Energy from other biomes • Larger families possible Archaic adaptation: scheduled collecting of seasonal foods 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires 9 The Agricultural Revolution Developed in semi-arid areas adjacent to river valleys Need to store collected cereals Impact of agriculture Chaco granary Stored surplus food • Geometric increase in population Dependence on nonfood resources • Water, fuel, stone, metal, etc. Transportation & trade • Moving scarce resources between settled villages Urbanization, industrialization Overpopulation, overexploitation of resources, pollution 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires French traders in a Huron village 10 Phases of Cultural Development 1. Hunting & gathering 2. Agriculture Domestic plants Domestic animals 3. Towns & Cities Population increase Urbanization Specialization Competition 16-Mar-16 Egyptian agriculture Mesoamerican urban centres GNED002 - Ancient Empires 11 Life in the Ancient World Populations small Local farms, villages Little change over time Hard lives Unvaried foods No medical services Poor sanitation High infant mortality rice plowing Simple joys Family and friends Games, songs, stories Faith 16-Mar-16 Seneb the Dwarf & family 6th Dynasty Egypt GNED002 - Ancient Empires 12 Cultural Growth Theory of Diffusion Culture and technologies originate with one culture and are diffused by contact with other cultures. Theory of Correspondence All humans have same mental & physical capabilities, thus invent similar culture and technology in similar environments 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires 13 Birthplace of Empires River valleys Life-giving Godlike Human innovations Development of crop species Irrigation systems Nile farming • Mesopotamia Calendars • Nile Valley flooding 16-Mar-16 Egyptian scribe GNED002 - Ancient Empires 14 The Rise of Cities Indus Valley Civilization Ecological richness of valley attracts people Cities Centre of richness Expanded areas of control Walled for protection • Repelled invaders • Attracted immigrants Emblems of Empire 16-Mar-16 Mohenjo Daro - walls and citadel GNED002 - Ancient Empires 15 The Rise of Empires Rich & fertile valleys Examples: Nile, Indus, Huang Ho Regional Cultures Centred around cities Shared trade, culture Military dominance leads to empire Alexander the Great 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires 16 Imperial Cities Dense population Urbanization processes Cultural innovation Driven by Commerce Cultural interaction 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires The Agora - Athens 17 The Elements of Empire Elements Peoples Goods Ideas Longshan pottery Existence & dynamism of elements depend on Movement Exchange Egyptian mural - transporting the grain 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires 18 City As Symbol of Wealth Struggle for control of cities Richness: ability to produce surplus goods and services agriculture pottery, metalworking commerce rice harrowing - China Supported nobility, administrative class, army Increased wealth, population by immigration First Emperor’s terracotta army 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires 19 Civilization to Empire City Agriculture means larger towns Specialized buildings, occupations City-State Metropolis and hinterland Imperial Italy • Interaction of towns and cities State Equality of cities e.g. Italy in Roman Republic Empire Subject states e.g. Aztec Empire 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires Aztec Empire 20 Culture and Expansion The Stay-at-Homes China, Egypt, Maya Little knowledge of other empires beyond their boundaries The Expansionists China - relief Rome, Greece Pursuit of trade or conquest Limited by • Natural obstacles • Opposing forces 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires Greek colonies 21 The Polynesian Case Polynesian seafarers 3000 BC on Sailed and colonized Pacific • Northwest Coast • Easter Island No empire, colonies isolated The Record Factor Key is permanent records • Written language • Maps Example: Greek knowledge of Mediterranean world 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires 22 Timelines Timeline of Ancient Egypt Framework for understanding Time sequence of development of culture Marked by dynasties, technological progress Rise-and-fall image • Spengler’s view of history 16-Mar-16 GNED002 - Ancient Empires 23