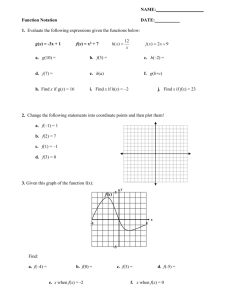
Influenza - Jessica Holttum
advertisement

Jessica Holttum and Jordan Standlee Statistics Molecular Biology Symptoms Transmission Treatment Infamous Strains Conclusion 5-20% of U.S. infected 3-5 million severe cases worldwide 200,000 hospitalized 250,000-500,000 deaths 300 million doses of vaccine administered worldwide Source: cdc.gov Enveloped virus HA and NA proteins 3 Hemagglutinin Neuraminidase “H1N1” subtypes A – animals/humans B – humans only C - asymptomatic Source: www.micro.magnet.fsu.edu (-) ssRNA genome ~14,000nt total; 8 segments Source: www.virology.ws Last 1-2 day incubation May about a week include: Fever/chills Cough Sore throat Runny/stuffy nose Muscle/Headaches Fatigue Vomiting/diarrhea Source: newshealth.net Bacterial pneumonia Ear/sinus infections Bronchitis Worsening of preexisting conditions Asthma Diabetes Congestive heart disease Link to schizophrenia Inhalation of infected fluid particles Hand-to-mouth contact Flu “season” Not due to temperature Bad weather people stay indoors extended close contact with others Source: shanghaiist.com Rest Vitamin C&A Fluids Hot drinks/soup OTC Medication Antivirals Prevention Avoid crowds Cover coughs, sneezes Wash hands Skip school/work Source: recipesfromhomeonline.com 2 types TIV Injection Dead virus LAIV Nasal spray Attenuated virus Cold-adapted Source: IFPMA H1N1 1/3 world population infected 30-50 million dead 675,000 in U.S. Over half were age 20-40 Transmission linked to high humidity 3 waves in one year Spring 1918 Fall 1918 Winter 1918-1919 “Mother of all pandemics” Source: 1918.pandemicflu.gov H5N1 First detected 1996 Human detection 1997 Outbreak begins 2003 Rare in humans; common in birds Attacks lower respiratory tract ~60% mortality Expected to remain in circulation Source: hogueprophecy.com H1N1 Less virulent Quadruple reassortant First case 2009, California Public Health Emergency expired 6/23/10 Likely to continue seasonal spread Source: freewebs.com http://www.cdc.gov/flu/professionals/vaccination/vax-s http://www.cdc.gov/flu/about/viruses/types.htm http://www.cdc.gov/flu/keyfacts.htm http://www.cdc.gov/flu/weekly/ http://www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu/cdcresponse.htm http://www.cdc.gov/flu/about/qa/hospital.htm http://www.cdc.gov/media/pressrel/2010/r100224.htm http://www.cdc.gov/flu/about/qa/fluvaccine.htm http://www.cdc.gov/flu/avian/outbreaks/current.htm http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/eid/vol12no01/05-0979.htm http://virus.stanford.edu/uda/ http://1918.pandemicflu.gov http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/viruses/influenzavirus.html http://biology.kenyon.edu/BMB/Chime2/2005/CerchiaraHolsberry/FRAMES/start.htm http://www.pdb.org/pdb/static.do?p=education_discussion/molecule_of _the_month/pdb113_1.html http://www.ifpma.org/Influenza/index.php?id=4234 http://health.nytimes.com/health/guides/disease/theflu/treatment.html http://www.who.int/csr/disease/swineflu/notes/h1n1_vaccine_20090806 /en/index.htmlummary.htm http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs211/en/index.html http://www.who.int/csr/don/2009_04_24/en/index.html http://www.who.int/csr/disease/avian_influenza/2011_01_24_h5n1_avia n_influenza_timeline_updates.pdf http://www.virology.ws/2009/05/01/influenza-virus-rna-genome/ http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2004/08/040803100609.htm http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/142829.php http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21307188 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000080.htm http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/flu.html