Ms. Dong Wu
advertisement

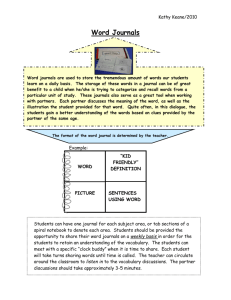
Open access and virtual science libraries Regional Preparatory Meeting for 2013 ECOSOC AMR 26 Nov 2012, Amman Commission on Science and Technology for Development 2011-2012 Priority Theme: Open Access, virtual science libraries, geospatial analysis and other complementary ICT and science, technology, engineering and mathematics assets to address development issues, with particular attention to education Definition of Open Access …its free availability on the public internet, permitting any users to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts…without financial, legal, or technical barriers other than those inseparable from gaining access to the internet itself…. (Budapest Open Access Initiative 2002) Gold OA DOAJ – Directory of Open Access Journals (www.doaj.org) eg BioMed Central (STM publisher. 220 journals) Hindawi Publishing (457 journals) Bloomsbury Qatar Foundation Journals Public Library of Science (PloS ONE, PloS Biology, Plos Medicine) Green OA OpenDOAR – Directory of Open Access Repositories (www.opendoar.org) Eg: ArXiv (Cornell University) PubMedCentral (NIH) Digital Assets Repository (Library of Alexandria) Qspace(Qatar University) Dspace (King Saud University, Saudi Arabia) No. of OA articles is increasing Source: Laakso and Björk BMC Medicine 2012 10:124 No. of articles by OA publisher type Source: Laakso and Björk BMC Medicine 2012 10:124 OA availability varies by discipline Strategies to promote OA Institutional level mandatory policies University of Southampton, UK 2002 National Institute of Technology India 2006 National level 7 UK Research Councils(2005-2011), new policy effective April 2013 US NIH 2007 Brazil, Argentina, Germany, Poland, Spain, Ukraine International and regional 7th Framework Programmes of the EU (20%) Wellcome Trust Policy Benefits of OA Improving speed, efficiency and efficacy of research Enabling interdisciplinary research Increasing impact, especially by researchers from developing countries eg Universidad de Los Andes Benefits to stakeholders outside academia eg PubMed Facilitating knowledge exchange through virtual science libraries …a library that exists, without any regard to a physical space or location (Riccio 2001) Users Virtual science library Own content Portal to distributed online content housed in other online repositories Easily search over 3000 journals in: Food Agriculture Enviro science Social science Access: Public institutions in 106 countries Free to Group A Low-cost to Affiliation Group B countries Subject related academic, research or government institutions in agriculture Set up by UN Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) Well-known founding publishers: Blackwell Publishing, Elsevier, Oxford University Press, Springer-Verlag, John Wiley & Sons, etc. Not-for-profit scholarly publishing cooperative: Bioline Toronto Brazilian Reference Center on Environmental Information University of Toronto Scarborough Provides open access to quality research journals published in developing countries Journals from Bangladesh, Brazil, Chile, China, Colombia, Egypt, Ghana, India, Iran, Kenya, Malaysia, Nigeria, Tanzania, Turkey, Uganda and Venezuela. Reduces the South-North knowledge gap Health (tropical medicine, infectious diseases, epidemiology, emerging new diseases) Biodiversity Environment and conservation International development. System of country portals providing access to over 2.5m individual S&T articles, books, etc. Reaching 500,000 S&T practitioners from affiliated institutions PPP between US Dept. of State, CRDF Global and IMIST (Morocco), CNUDST (Tunisia) and CERIST (Algeria) Funded by US Department of State and national partners Administered by CRDF Global and national partners Federation of 80 national science portals from over 70 countries Multilingual, real-time searching and translation Accessible to people from affiliated institutions in participating nations Users submit single query into search engine Multilateral 18-member partnership initiated by US and UK Governed by WorldWideScience Alliance partnership Maintained by US Dept. of Energy Challenges and trade-offs Content issues: The raw data that would allow researchers to undertake their own analyses is much harder to access Quality concerns: existence of multiple copies, information overload, bibliographic control Seen as peripheral (eg. Asia and L. America) Copyright/licensing worries: who has the right? Financial sustainability Who pays and how (users, authors publishers, universities, public institutions), impact on scholarly research and publishing Publishers must make a profit Many different business models; no best way Preservation of knowledge Who is responsible for archiving born digital journals? Which standards will allow archived material to be compatible with upgraded systems (e.g. OAI-PMH, XML) Virtual science libraries Increasing ‘openness’ Attracting and retaining users: Capacity-building, training, awareness Functionality and ease of use are two important elements of a successful virtual science library Connecting ‘openness’ Open Access: content is provided free of charge “open” educational resources Open Standards: products developed by different companies are interoperable and interchangeable Open Source: users can freely access, change and redistribute the source code of the software Benefits include: lower costs improved accessibility better prospects for long-term preservation of scholarly works Recommendations (E/2012/6) Encourage national research agencies and foundations to provide data and research results to the public domain, and make them freely available in an open and accessible format. Encourage international collaboration in disseminating digitized publications resulting from publicly-funded research, making it freely available online and easily accessible. l Recommendations (E/2012/6) Further encourage, in partnership with other stakeholders, the logistical and financial viability of virtual science libraries, in particular those that include a platform to facilitate networking among scientists across geographical boundaries and provide an integrated search capability across all available online publications Encourage the formation of national research and education networks, which promote networking among scientists, increase collective buying power for online science research services, including access to journals, and result in the l resources; sharing of scarce Thank you! Dong Wu Science and Technology Section Division on Technology and Logistics UNCTAD Dong.wu@unctad.org