photoelectric effect
advertisement

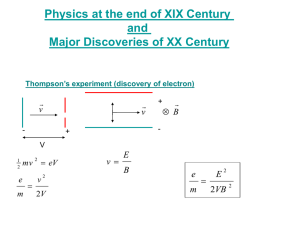
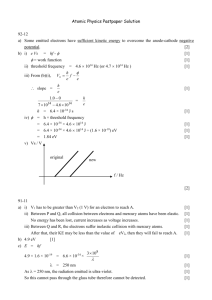
REVISION PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT the process whereby electrons are ejected from a metal surface when light of suitable frequency is incident on that surface.. IT PROVES ... the particle nature of light THRESHOLD FREQUENCY fo, as the minimum frequency of light needed to emit electrons from a certain metal surface. WORK FUNCTION Wo, the minimum energy that an electron in the metal needs to be emitted from the metal surface hfo WEo hf E Energy (Joule) h Planck's constant (6.63 1034 ) f frequency (Hertz) E Wo Ek E hf 1 2 Ek mv 2 Different metals have different work functions, because they have different ionization energies Ionization energy is the energy required to remove valence electrons from outer orbitals 3 SCENARIOS E hf Photo electrons are NOT emitted E Wo Photo electrons are emitted E Wo Photo electrons are emitted and move away using kinetic energy E Wo E Wo Ek A learner, who wants to demonstrate the photoelectric effect, uses a zinc plate fitted to the top of a gold leaf electroscope. The work function of zinc is 6.9 10 19 J a Define the concept work function b Calculate the maximum wavelength of light that will emit electrons from the zinc plate 2.88 107 m The electroscope is negatively charged and UV light is shone on it. One of the wavelengths of the light is 260nm. c Calculate the kinetic energy of a photoelectron emitted from the surface of the zinc plate 7.5 1020 J When the learner tries to replicate the experiment with a positively charged electroscope, he finds that the UV light has no noticeable effect d Explain this observation a Wo 6.9 1019 J ? h 6.63 1034 E hf Wo hf o 6.9 1019 6.63 1034 f o c 3 108 b 260 109 Ek ? Wo 6.9 1019 c f 3 108 1.04 1015 2.88 107 m f o 1.04 1015 Hz c f 3 108 f 260 109 f 1.15 1015 Hz E Wo Ek 7.65 1019 6.9 1019 Ek Ek 7.5 1020 J h 6.63 1034 c 3 108 E hf 6.63 1034 1.15 1015 7.65 1019 J c The positive zinc plate attracts the electrons and prevents the emision of photo electrons INTENSITY & FREQUENCY EXPERIMENT • http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/photoelectric INTENSITY & FREQUENCY • To increase the CURRENT the rate of flow of current must be increased Q I t FREQUENCY • Frequency depends on the wavelength of light. • Frequency influences the amount of energy of the photons. • To increase the CURRENT • The photons require more energy in order to increase the electrons kinetic energy • Therefore we INCREASE the FREQUENCY • (or DECREASE the WAVELENGTH) INTENSITY • Intensity depends on the number of light sources • Intensity influences the number of photons that are released • To increase the CURRENT • More electrons need to be release per time • Which means that more photons need to reach the surface • Therefore we INCREASE the INTENSITY • Increasing the INTENSITY does NOT change the kinetic energy of the photo-electrons • (because the energy of the photons didn’t change) • So if there AREN’T any photo-electrons released at a specific frequency, it will not help to increase the intensity, because the photons will still lack sufficient energy • To change the speed of the photo-electrons, the frequency (energy) of the photons needs to change ABSORPTION & EMISSION SPECTRA ABSORPTION & EMISSION SPECTRA • An atomic absorption spectrum is formed when certain frequencies of electromagnetic radiation that passes through a medium, e.g. a cold gas, is absorbed • An atomic emission spectrum is formed when certain frequencies of electromagnetic radiation are emitted due to an atom's electrons making a transition from a high-energy state to a lower energy state. HYDROGEN ABSORPTION vs EMISSION An automatic camera has an inbuilt light sensor. When light reaches the sensor, it falls on a metal object that emits electrons and produces a current. a What phenomenon is decribed above? A metal plate is irradiated with electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength of 200 nm The work function of the metal is 7.57 10 19 J . b Show, by calculation, that photoelectrons will be emitted. E>Wo The intensity of the radiation is increased, while the wavelength is kept constant. State and explain the effect this change will have on c the energy of the emitted photoelectrons d the number of photoelectrons emitted same increase a Photo electric effect b 220 109 Wo 7.57 1019 J E ? c f 3 108 f 220 109 f 1.363 1015 Hz E hf 6.63 10 34 1.363 1015 9.04 1019 J c 3 108 E Wo h 6.63 1034 Energy of the photons is more than the work function, photo electrons are emitted c The energy of the emitted electrons stays the SAMEm because the frequency did not change d The number of photo electrons INCREASE An increase in intensity increases the amount of photons that can transfer energy to the electrons