The Human Body Plan
advertisement

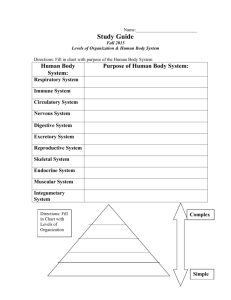
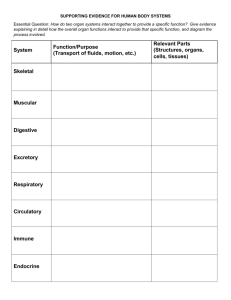
THE HUMAN BODY PLAN IMPORTANT CONCEPTS 1. There are 4 types of tissues that make up the human body 2. Tissues work together to make up an organ, organs work together to make up an organ system 3. Each organ system has a specific function in the body 4. All of the organ systems depend on each other to maintain human body functions. 5. All animals need to maintain steady internal conditions (homeostasis) to survive. 4 TYPES OF TISSUE MUSCLE TISSUE Composed of cells that can contract in a coordinated way Cardiac muscle in your heart and pumps blood Skeletal muscle moves your bones Smooth muscle in charge of functions you cannot control (ex: food going through esophagus) NERVOUS TISSUE Contains cells that receive and transmit messages in the form of electrical impulses Makes up brain, spinal cord, nerves EPITHELIAL TISSUE Contain cells that line or cover all internal and external body surfaces. Cells are tightly bound together creating a protective barrier. CONNECTIVE TISSUE • Binds, supports and protects structures in the body ORGANIZATION ORGAN SYSTEMS http://www.proprofs.com/flashcards/tableview.php?title=mcb-organ-systems BODY CAVITIES Each cavity contains 1 or more organs INTERDEPENDENCE Nutrients from the digestive system are distributed by the circulatory system. Circulatory system depends on oxygen from the respiratory system. Every system relies on the nervous system to sense changes in the environment and respond accordingly. EXAMPLE Each day, your body’s cells, tissues, and organs work together to keep you responsive to the environment. Consider the example of eating your lunch. The lunch buzzer sounds just as your stomach is making some rumbling noises. Your brain records the information that the buzzer and time of the day mean you should eat. You proceed down the hall and enter the school cafeteria. In the cafeteria, your eyes see a poster advertising the daily specials, and your nose senses the odour of freshly made pizza. The message is sent to your brain, and you decide that you should eat pizza for lunch. While in the line, you decide to reach out and select a slice of pizza from the warming oven. The muscles in your hand and arm contract and relax, which enables you to pick up the slice of pizza without dropping it. Once in your seat, you chew and swallow a bite of pizza using your teeth and tongue (Figure 2.33). As the muscles in your digestive system push the food along, a variety of glands add juices to assist in breaking down the food into the necessary nutrients. In several hours, the nutrients in the pizza are absorbed into your bloodstream and carried through your body to the cells. In this example, several organ systems, including the circulatory, digestive, and nervous systems, interact to enable you to obtain, digest, and transport essential nutrients from the pizza to all cells of your body. HOMEOSTASIS- KEEPING INTERNAL CONDITIONS STABLE A specific response amplifies until a proper level is reached, and the response is stopped (designed to push levels out of normal ranges. ) The end point of a specific process regulates the beginning of that same process. (maintain or regulate physiological functions ) HOMEOSTASIS- KEEPING INTERNAL CONDITIONS STABLE Positive feedback loops During childbirth, pressure on mother’s Uterus causes secretion of hormone oxytocin This stimulates contractions, putting Pressure on the fetus Pressure from the fetus further stimulates The hormone to be released. Negative feedback loops Blood calcium must be at proper level for muscles to function. If too low, parathyroid gland releases a hormone that pulls calcium from the bones and releases it into the bloodstream. Once at proper level, the gland stops releasing the hormone.