Nucleic Acid Notes - Newberry Life Science
advertisement

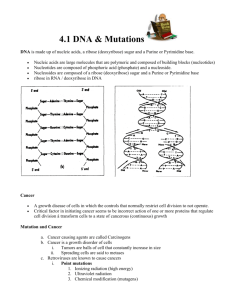
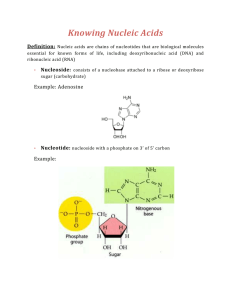
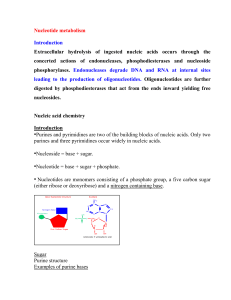
NUCLEIC ACIDS: DNA AND RNA DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid 1. Structure: A. Monomer – Nucleotide composed of 1. A nitrogen base a. adenine: a double-ring base (purine) b. guanine: a double-ring base (purine) c. thymine: a single-ring base (pyrimidine) d. cytosine: a single-ring base (pyrimidine) 2. Deoxyribose (pentose sugar) 3. Phosphate group B. Single strand of DNA 1. Phosphate group of nucleotide covalently bonds to deoxyribose of next nucleotide C. Double strand of DNA 1. Two single strands of DNA bond to form a ladder shape 2. The sides of the ladder are made up of deoxyribose and phosphate group 3. The nitrogen bases (A,G,C,T) make up the “rungs” of the ladder, connected by hydrogen bonds 4. A and T always pair together; C and G always pair together 5. Ladder twists to form a “double helix” RNA: Ribonucleic Acid Same as DNA, but with the following differences: 1. The sugar in the nucleotide is ribose (instead of deoxyribose) 2. RNA does not contain thymine. Instead, adenine (A) always pairs with uracil (U). Uracil is a pyrimidine. 3. RNA is usually single-stranded