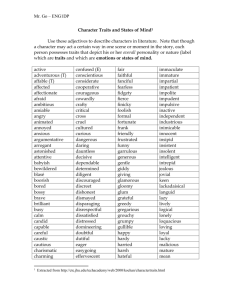
Types of Character and Character Traits
advertisement

• The people, animals, or imaginary creatures in a work of literature. • The most important character in a piece. • It’s also referred as a protagonist. • Less important character, helps move the action forward and helps readers learn about the main character(s). • A complex, highly developed character with different sides to his or her personality. • They have both strengths and weaknesses. Cassie Logan Ponyboy Katniss • A character that is NOT highly developed. • They usually have ONE distinguishing trait or one specific role in the story, and exist mainly to advance events in the plot. Voldermort Mrs. Everdeen • A character who exists to provide a contrast with a main character. • For example: if the main character is timid, a foil who is daring can highlight the timidity. • Flat characters worn out from overuse, that writers usually avoid; stereotypes may serve as a foil and provide humor, but they can also be offensive. • Examples: cold unfeeling banker or the absent-minded professor. • Static characters do not experience basic character changes during the course of the story. • Dynamic characters experience changes throughout the plot of a story. Although the change may be sudden, it is expected based on the story’s events. • The qualities of a character, such as his or her personality. • Think of adjectives for character traits. • Writers use four main methods to reveal character’s traits: 1. 2. 3. 4. Direct Comments Physical Description Speech, Actions, or Thoughts How others React • About the character’s personality by the narrator. • Example: All summer Judd had worked, saving money in a mature, responsible way. (Character traits: maturity, responsibility) • Of a character’s appearance. • Example: Judd kept his room and his attire neat and tidy, but his eyes held a pacing wildness that begged to be let go. (Character traits: conflicted, controlled, inner turmoil) • Of a character • Example: Secretly Judd dreamed of joining a rock band. With money in his pocket, he swaggered into a store and asked about the fancy guitar. He learned it was very expensive- fit for a professional. “Well, I’m not at that level yet,” said Judd, not admitting that he didn’t even know how to play. (Character traits: imagination, insecurity, pretense) • To the Character. • Example: The clerk showed Judd an affordable guitar. Judd pretended to finger the strings. As Judd paid for the guitar, the clerk took pity on him. “I see you really want to play,” he said. “I teach lessons. If you’re willing to start at the beginning and practice. I’ll give you a discount.” (Character traits: determination, inability to pretend convincingly) 1. How well do you understand the major ideas of this lesson? 2. Do you have specific questions about today’s lessons?