Rivers, Streams, & Groundwater
advertisement

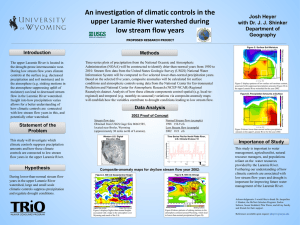
Surface Water UNIT 6 STANDARDS: NCES 2.3.2, 2.4.1, 2.4.2 LESSON 1 Lesson Objectives In this lesson, you will learn about: – What landscape features on earth are formed and changed by water • Floodplains • Deltas – How surface water moves materials • Load vs Capacity – How surface water impacts humans • Benefits and Hazards Surface Water Movement Water Cycle The continuous recycling of the planet’s water. Evaporation, condensation, precipitation, collection The sun’s energy drives the water cycle Overall Water Cycle *know steps Steps in the Water Cycle Precipitation Run Off Accumulation Evaporation Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Snow, Rain, Sleet, Hail Surface flow of water Collection of surface water Liquid to Gas state Water from Plants Gas back to liquid state (REPEAT CYCLE) Runoff What is runoff? Water that flows on the surface, down slope, and may accumulate. Vegetation .slows the flow Influencing of runoff Factors Rate of Precipitation Soil Composition Slope…Angle of land Stream Systems Tributaries carry water to collection points. Types of tributaries – – – – Brook Stream Creek River Precipitation that does not enter the ground runs off the surface. All streams flow downslope to a lower elevation. Stream Load Definition 3 Ways of Transport All materials carried in the water are known as stream load. Solution: Material dissolved – Dissolved soil or minerals Suspension – Parts carried along in the water Bed Load – Sand and pebbles pushed along on the bottom of the flow Flood Plain Why Floodplain definition A flood occurs when the water spills over the sides of the river onto land. The broad flat area surrounding the stream bank where flooding normally occurs. Great farmlands Floods Nature Monitoring Floods are a natural occurrence. Caused by heavy accumulations in areas Man monitors river depths, rainfall, and accumulation areas to issue flood warnings US Dept of Geological Survey monitors rivers for floods. Major Floods in the Last 20 Years New Orleans North Carolina Cause: Hurricane Katrina Hurricane Floyd Hurricane Fran Human Influences Harm – – – – – – – – Removal of topsoil Clearing land Building dams Pollutants Industry Waste Water Pesticides Storm Water Benefits Can help remove pollutants Can clear river ways Can be used to increase cities Increased sanitation “River Keepers” Lesson Review 1. Explain 3 ways a stream carries its load. 2. Why does little water seep into the ground on steep slopes? 3. Why do people live in floodplains? 4. What is the cost associated with living in a flood plain? 5. How does a hurricane cause flooding in North Carolina so far from the coast?