Today's Objectives 9/9/09
advertisement

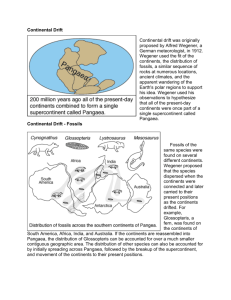
• Update your grade sheet. For the Earth’s Layers WS if you followed directions you got 10/10. If you didn’t answer the question on the back or color the diagram you got 8/10. If you didn’t do either you got 6/10. Write down your assignments. Assignment 1. Signed Rules & Procedures 2. All About You Points TotalPoints Received Possible 10 5 3. Brain Pop Sci. Meth. WS 10 4. Observation vs. Inference Unit1 Section 2 Notes 10 5. Sci. Meth Quiz 21 6. Tootsie Pop Lab 10 7. Science Pre-Test 10 8. Earth’s Layers WS 10 9. Ch. 7 Section 1 Quiz 15 • Turn in your Pangaea Lab. Find your seat and get your half sheet of paper out from yesterday. On your paper, answer the following questions: Do not open your book • 1. What is the title of Ch. 7 Section 2 • 2. What were the Terms to Learn for Ch. 7 Section 2? • 3. In 3-5 sentences, explain the main idea of Ch. 7 Section 2. • 1. Ch. 7 Section 2 Discussion and Demonstrations. • 2. Plate Tectonics WS? Restructuring Pangaea Lab Question of the Day • Besides the shape of the continents, what other evidence shown in the map below supports the Pangaea theory? QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. What was Pangaea? • Has the world always looked as it does today? What was Pangaea? • Pangaea means ‘all land’ in Greek • 245 million years ago Earth’s continents were joined together to form a supercontinent known as Pangaea. Reconstructing Pagaea Lab • 1. Label the 6 continents, including Greenland, before cutting them out. • 2. When you are cutting, cut as close to the edge of the continents as possible. Don’t cut out the islands. • 3. Outline the edge of each continent with a different color. • 4. There will not be enough scissors for everyone to cut out at the same time, so if you do not have scissors do step 3 first. Ch. 7 Section 2 Restless Continents • What do we mean when we say Restless Continents? • Continental drift- theory that continents can drift apart and have done so in the past. I. Drifting Continents • Why did Alfred Wegener believe in continental drift? • 1. continents fit together like a puzzle • 2. Fossils of the same species were found on different continents • 3. evidence of rocks and climatic conditions were found on the same continents. II. Breakup of Pangaea • What did Wegener infer based on his evidence? • Millions of years ago there was one supercontinent that over time slowly broke apart III. Wegener’s Theory Rejected • Why? • Wegener could not conclude how or why the continents moved. • What discovery provided clues that Wegener was right? III. Mid-Ocean Ridge • 1960’s underwater worldwide mountain chain was discovered • What happens at the mid-ocean ridge that moves the continents? • Sea-floor spreading III. What is sea-floor spreading? • As plates diverge magma rises up to form a mid-ocean ridge. As more magma continues to rise and harden it spreads the sea-floor apart III. Evidence of Sea-floor Spreading • How do we know sea-floor spreading is happening? Seafloor Spreading Interactive • Rock samples taken from the sea-floor show that the oldest rocks are further from mid-ocean ridges. IV. Magnetic Reversals • Throughout history Earth’s magnetic fields will switch. Meaning the north pole goes to the south pole and vice versa. • Magnetic minerals in magma align with Earth’s magnetic field. When the poles switch this creates stripes or bands that can be seen on the sea-floor.