Market Structure at school
advertisement

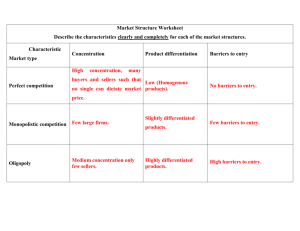
Turn to your partner and tell them three words you think of when you hear the word COMPETITION Competition and Markets Every business firm operates in a MARKET STRUCTURE Copy this chart on a full sheet or 2 of paper: Market Structure Perfect Competition Monopoly Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly # of Sellers Types of Products Barriers to Control Entry Over Price Examples Perfect Competition • Many buyers and many sellers • The market is perfectly transparent – Everyone has access to all relevant information Perfect Competition • All firms sell identical products. Perfect Competition • It’s easy to get into and out of the market. Perfect Competition • Sellers are price takers. They must sell their product at the equilibrium price and not one penny more Perfect Competition • A market may not satisfy one or more of the four conditions and still be perfectly competitive • What determines whether a market is perfectly competitive or not is if firms (sellers) in the market are price takers. Perfect Competition • Wheat Market, Corn Market, Stock Market, other agricultural markets Critical Thinking • Some of the 200 firms in Market X, a perfectly competitive market, are incurring losses. How will these losses influence…. – seller’s entrance/exit to the market? – the supply of the good produced in the market? – the price of the good? • How can a seller determine whether or not they are a price taker? • Can he/she sell any of the product for even one cent more than equilibrium price? Turn to your partner and tell them three words you think of when you hear the word MONOPOLY Monopoly • there is 1 seller. Monopoly • The product sold is UNIQUE – there are no close substitutes Monopoly • Extremely high barriers to entry…it’s hard to get into a monopoly market. • Legal Barriers “government monopolies” – public franchise – patents – copyrights • Extremely Low Per-Unit Costs – a natural monopoly “market monopoly” • Exclusive ownership of an essential resource Monopoly • • • • US postal service 1st class mail Vista Irrigation District Cox Cable historically: – Alcoa – DeBeers – Standard Oil – AT&T Monopoly • Monopolists are price searchers. They can sell some of their product at various prices. • The demand curve will determine how much they can sell and at what price. • Price will be determined based upon their decision on how much to produce. Market Structure # of Sellers Perfect Competition many identical Low or Price none takers 1 Unique Extremely Price Monopoly Types of Products Barriers to Control Entry Over Price high Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly searchers Examples OXYMORON ??? • • • • • • • • CONSTANT VARIABLE TERRIBLY GOOD VEGETARIAN MEATBALL THUNDERING SILENCE GOING NOWHERE JUMBO SHRIMP ANTI-MISSILE MISSILE HOPELESSLY OPTIMISTIC Monopolistic Competition • shares characteristics of both perfectly competitive and monopoly markets. Monopolistic Competition • there are many buyers and sellers Monopolistic Competition • Firms sell slightly differentiated products Monopolistic Competition • Easy entry and exit from the market Monopolistic Competition • Price Searchers • They can sell some of their products at various prices because they sell slightly differentiated products. • They decide how much to produce by searching for the price where they can sell all of their output Monopolistic Competition • • • • • • • Burgers Clothing Coffee Houses Gas Stations Cosmetics Movie Theaters Auto Mechanics Competitors and Monopoly • Many businesses would like to become a monopoly – they advertise perceived differences • Competition depends on two factors: 1. How close to unique the product is 2. How easy it is for sellers to enter the market With your neighbor… • Think about a monopolistically competitive company from which you have made a recent purchase. – What are the substitutes’ prices? • Why can there be a range of prices? – Why did you purchase the one you did? Oligopoly •Name five American car manufacturers Oligopoly • There are few sellers. • A few sellers account for a large percentage of sales Oligopoly • Firms produce identical or slightly differentiated products. Oligopoly • Entry into the market is difficult. • low per-unit costs • patents • control of resources Oligopoly • Price Searchers • slightly differentiated products • difficult to get in the market • the few sellers may be able to control price through agreement or cooperative action – cartel agreements (illegal) Oligopoly • • • • cars cereal airlines entertainment Identifying Oligopoly Industries • Economist determine whether a market is an oligopoly by looking at the percentage of sales accounted for by the top four firms in the industry – 6 major film studios = 90% of revenue • 20th century, Warner Brothers, Paramount, Columbia, Universal, Walt Disney • Dreamworks (Viacom bought—owned by Paramount) – 2008 became independent again but distributed by Disney • Leading Indies: Lionsgate, Summit Entertainment, MGM (former Biggie!) – 4 music companies = 80% of revenue • Sony, EMI, Universal, Warner – 6 book publishers – 3 television networks (1950-1970) • • • • ABC/Disney CBS NBC Universal 2 added since – Time Warner – News Corporation (FOX) – Food processors: Kraft, Nestle, PepsiCo Market Structure # of Sellers Perfect Competition many identical Low or Price none takers 1 Unique Extremely Price Monopoly Types of Products Monopolistic Competition Many Slightly differentiated Oligopoly Few sellers Identical or slightly differentiated Barriers to Control Entry Over Price high searchers Easy entry Difficult entry Price searchers Price Searchers Examples Review • Firm A is a perfectly competitive firm. Why can’t it sell its product for one penny higher than equilibrium price? • Buyers would know that they could buy that identical product for the cheaper price. Why would they pay one penny more? Review • To become an attorney, a lawyer must pass the bar examination. Is the bar examination a barrier to entry in the law market? • Yes Review • Firms in a monopolistic competitive market produce slightly differentiated products. How might these products be differentiated? • Besides differences in product, they could be sold in different locations, by different people, in a store, online or by phone. They can be bundled with different services or sales conditions. Review • How can profits be “competed away” in a perfectly competitive market? • It’s an easy market to enter. When businesses see the high profits, they enter the market. More supply lowers the price… Review • What are the two major factors that decide how much competition a firm faces? • How close to unique is the product? • How easy is it to get into the market for this product? “Stupid is as stupid does.” As you watch the clip from “Forest Gump,” note the process related to Bubba Gump Shrimp’s position in the shrimping market. 1. Before the hurricane, how does the shrimping industry resemble a perfectly competitive market? 2. How does the hurricane change the market price and quantity of shrimp? (Use supply & demand graphs to illustrate.) 3. How did the hurricane create a monopoly for Bubba Gump Shrimp? Use the characteristics of a monopoly to support your answer. 4. Do you think Forest can maintain his monopoly status over time? (In other words, are there barriers to entry?) Explain. Homework MyVote California • Research your assigned topic. – Be prepared to develop a short 2-3 minute presentation with your group outlining the five parties on the gubernatorial and senatorial race. • Select one: » » » » American Independent Green Peace and Freedom Libertarian • Democratic and Republican--all • Company Analysis Sheets (Stock Market Part I) due Friday, October 22.