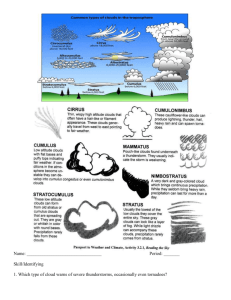
Cloud Formation: Processes & Precipitation | Earth Science
advertisement

Cloud Formation Bell-work 1. Two ways to saturate air: 1. __________________ 2. __________________ 2. As air rises, it cools rate of _____°C / km 3. As ascending air rises, it __________ and __________ Adiabatic Temperature Changes Dry and Wet Adiabatic Rates 5°C wet 10°C dry Latent Heat of Condensation The 600 calories of heat energy is released into the surrounding air by gas molecules then they condense into a water. Warms the air! 6 Cloud Formation 1. A parcel of air _______ 2. It cools to its _____ ________ 3. The water vapor ____________ into water droplets. 4. The air reaches ______________ 5. ___________ form. Cloud formation At what altitude does the air temperature cool to be the same as the dew point temperature? At that altitude and temperature, will the clouds be liquid or ice crystals? Dry air Death Valley Rain Shadow Desert 4 processes of cloud formation pg. 114- 1. Orographic lifting 2. Frontal Wedging 3. Convergence 4. Local Convection White board • • • • • Name Diagram Location Type of cloud (puffy cumulous, towering thunderstorm, or low stratus) Type of rain (sudden quick rain shower, constant rain, no rain) 1. Orographic Lifting Processes Wetter Windward Locations and Leeward Rain Shadows Heavy Precipitation in Mountains Snow Pack in the Rocky Mountains 2. Frontal Wedging: a warm front with humid air rises over a cold front. As it rises, its cools and condenses into clouds Frontal wedging clouds Cold air fronts collide with warm air Large areas of clouds and steady precipitation form all along the front 3. Convergence Clouds Converge over Southern Florida 4. Localized Convection Bell Work: Match the Location with the Type of Cloud Formation orographic lifting, convergence, frontal wedging, local convection 1 2 4 3 5 6 Global precipitation Is there a relationship between cloud formation and precipitation??