Assignment # Cellular Respiration
advertisement

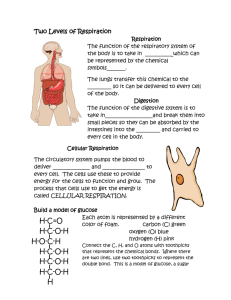
Assignment # Cellular Respiration Biology March 16, 2016 Mrs. McCarthy I. To grow, function, and reproduce, cells must: A. Create new cellular components such as cell walls, cell membranes, nucleic acids, ribosomes, proteins, etc… B. Collect energy and convert it into a form that is usable to do cellular work. II. Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms obtain energy from food. A. Glucose is the most common source of energy 1. It comes from the breakdown of complex carbohydrates B. Making a bond stores energy (dehydration synthesis) C. Breaking a bond releases energy (hydrolysis) D. The breakdown of food releases energy in the form of ATP 1. Adenosine triphosphate is a high energy molecule 2. Phosphorylation is the transfer of energy caused by the removal of a phosphate molecule 3. Adenosine diphosphate is a low energy molecule (ADP) An analogy can be made between the process of cellular respiration in our cells and a car. The mitochondria are the engines of our cells where sugar is burned for fuel and the exhaust is CO2 and H2O. III. The Energy Cycle in the Cell C6H12O6 Low Energy Breaking bonds releases energy for a cell to use. Making bonds stores energy for a cell to use later. Phosphorylation High energy IV. Types of Cellular Respiration A. Anaerobic respiration is respiration without oxygen 1. Results in little energy produced (2 ATP) 2. Takes place in the cytoplasm 3. Organisms that use anaerobic respiration are yeast & bacteria a. yeast are used to produce CO2 to make bread rise b. Yeast also makes alcohol 4. The equation for anaerobic respiration is: Yeast & Bacteria Animals 5. Lactic acid is produced in animal muscle cells when there is not enough oxygen present. This causes muscle cramps. TAKE THE LACTIC ACID CHALLENGE THE WINNER RECEIVES A WAY TO REPLENISH THE GLUCOSE USED IN THE CHALLENGE! Let’s take the lactic acid challenge!! Lean head, shoulders, lower back, and butt against a wall, with feet about 18 inches in front. Keeping knees hip-width apart, slide down the wall until you are in a chair like position. Your legs should not go any lower than a right angle to the floor. How long can YOU last? B. Aerobic respiration is respiration with oxygen 1. Results in maximum energy produced (36 ATP) 2. Takes place in the mitochondria 3. Most organisms use aerobic respiration 4. The equation for aerobic respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 ATP (food) Reactants (air) (released) (used) Products (used) V. Comparing Anaerobic and Aerobic Respiration Reaction Oxygen needed? Yes or No Location in the cell Reactants (starting materials) Anaerobic Respiration No Cytoplasm C6H12O6 2 Aerobic Respiration Yes Mitochondria C6H12O6 36 6O2 Amount of energy (ATP) produced The Glucose Song Glucose Ah, sugar, sugar You are my favorite fuel From the blood-borne substrate pool Glucose Monosaccharide sugar You’re sweeter than a woman’s kiss ‘Cause I need you for glycolysis I just can’t believe the way my muscles take you in For you, they’ll open the door All it takes is a little bit of insulin To upregulate GLUT - 4 Glucose Ah, sugar, sugar You help me make ATP When my predators are chasing me Glucose You’re an aldehyde sugar And you’re sweeter than a woman’s kiss ‘Cause I need you for glycolysis I just can’t believe the way my muscles take you in My glycogen is almost gone A few more seconds and I’ll be rigor mortis bound Acidosis done me wrong! Your sweet is turning sour, baby I’m losing all my power, baby I’m gonna make your muscles ache! I’m swimming in lactate, baby Yes, I’m swimming in lactate, baby Now I’m drowning in lactate, baby I’m gonna make your muscles ache! I’m drowning in lactate, baby Glucose Ah, sugar, sugar I used you up and you left me flat Now I’ll have to get my kicks from fat Glucose, Glucose Sugar, Sugar, Glucose, Glucose Sugar, Sugar The honeymoon is over now….. Journal Entry # March 16, 2016 Listen to the song again and think about the biology behind the words. What is this song trying to explain?