IEOR 170 Design Project - UC Berkeley Industrial Engineering and
advertisement

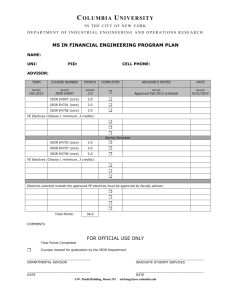
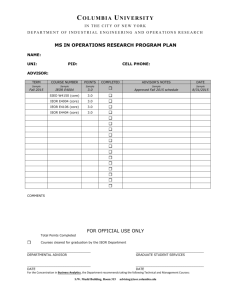
A New Engineering Direction Security Engineering Proposed by: IEOR 170 Group 3 Mohsen Ashraf Alice Chen Jake Gessin Milan Lee Angela Lu Wade Lu Jenny Wang Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Agenda Problem statement Design process Top 3 choices Survey methodology Survey analysis & result Refined major Curriculum Pros & Cons Conclusion Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Problem Statement To design a unique engineering major and a rich academic curriculum for the University of California, Berkeley. Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Design Process Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Top Three Majors Design Engineering (Conservative) Social Engineering (Radical) Combining art, creativity, and technology Enhancing social experiences and social interaction between people. Security Engineering (Intermediate) Focusing on all aspects of informational and physical security. Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Survey Methodology Three user groups Sample size = 45 people High school students = 16 Undergraduates (tech and non-tech) = 21 Professional (faculty members and employers) = 8 Characteristics of Questions Scenario-driven Quantifiable Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Survey Results – High School Question: Rank the following activities according to your interest (1=least interested, 3=most interested): ___ Create a new design for a blender ___ Arranging the homecoming sports game ___ Using intelligence to find terrorists Average Ranking 3 2.5 2.5 2 2 1.8 1.5 1 0.5 0 Design Engineering Social Engineering Security Engineering Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Survey Results – High School Question: Rank the following companies you would like to work with: (1=least preferred, 3=most preferred) __ IDEO __ Lockheed Martin __ Match.com Company Environment 29% 31% Security Engineering Design Engineering Social Engineering 40% Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Survey Results – High School Other conclusions The technical-oriented high school students favor security engineering because of the dynamics and scope of work. There’s a consensus that security engineering offers a more stable and concrete career. Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Survey Results – Undergraduates When asked which major to choose, Social Engineering has twice as many votes as Design Engineering, and four times more votes than Security Engineering. Preferred Major 14 12 12 10 8 6 6 4 3 2 0 Design Engineering Social Engineering Security Engineering Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Survey Results – Undergraduates Question: Do you think businesses, corporations, and public facilities would be safer if schools offered a major in Security Engineering. Security Engineering = Safer America Yes No Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Survey Results – Undergraduates If you wanted to design automobiles and blenders, which major would you choose? ___ Mechanical Engineering ___ Design Engineering Mechanical Engineering Design Engineering 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 “I would choose Design Engineering only because I want to focus on the design aspect of things. Yet, Mechanical Engineering would probably be my choice if I want to know more than design.” -IEOR fellow student Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Survey Results - Undergraduates Other Conclusions: The consensus is that design engineering and security engineering are more likely to be implemented into an engineering school than social engineering. “Security Engineering sounds very interesting, and it would probably have wide career potential in the future, especially in an age of terrorism.” -IEOR fellow student Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Survey Results – Professionals Question: Rate Potential the potential need in the job Need in Job Market market. (1 = least demanded, 5 = most demanded) 35% Security Engineering Design Engineering 39% Social Engineering 26% Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Survey Results - Professionals Professionals They feel that design engineering is the most demanded in the existing job market. Most of them feel that security engineering is the most practical and realistic. Quotes “Security Engineering requires technical expertise in computer and physical security (cryptography, electronic keys and locks), and understanding of legal issues surrounding information/intellectual property. Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers The Refined Major Security Engineering Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Security Engineering Focuses Computer security Security systems design Goal To improve all aspects of security Governmental agencies Private organizations Individuals Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Security Engineering Pros: Every large corporation has a need Most people are aware of the need for better security, which is in high demand Cons Issue for international students Background checks Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Security Engineering Competition No Universities offer a major in Security Engineering Some agencies and vocational schools offer classes for professional certification CISSP SSCP Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Curriculum – Web Security Emphasis Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Curriculum – Design Security Emphasis Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers New Major Courses Material Usage for Security Engineers – 4 units Security Design & Testing – 4 units Application of materials that are used for security product, involving an examination of quality, benefits, and shortcomings of the material, as well as research on material improvement. Application of design skills on designing mechanical devices, involving the testing of student designed products geared towards real-life situations. Intelligence & Security Engineering – 4 units Study of human thought, with specific regard to human intelligence in committing and preventing crime. Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers New Major Courses (Con’t) Failure of Security Systems – 4 units An examination of why security systems fail and how security systems can be broken. Some of the topics examined are the mechanisms of viruses, worms and Trojans, network attack, database, electron information and communication systems hacking. Security Systems Engineering – 4 units A study of the design, maintenance and protection of security systems. Topics include passwords, building firewalls, cryptography and encryption algorithms and network defense. Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Conclusion Security engineers will be trained to design and maintain systems of security Students majoring in security engineering are not limited to jobs in the security industry Security engineers learn practical skills that apply to many other fields Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers Questions & Answers http://ssoar.org/ieor170/se Spring 2003, IEOR 170 - Experience and Interface Design For Engineers