The Skeleton
advertisement

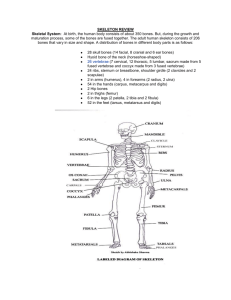
The Skeleton Bones of the Skeleton o The skeletal system consists of ______ separate bones o Two main groups, by location _____________________________________ _____________________________________ o Supports and protects the organ systems in the brain and spinal cavities, and the ventral body cavities The Axial Skeleton o Consists of 80 bones o Three major regions ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ The Skull o Two sets of bones _______________________ Enclose the brain in the cranial cavity ______________________ Framework of face Cavities for special sense organs for sight, taste, and smell Openings for air and food passage Sties of attachment for teeth and muscles of facial expression Cranial Bones o Frontal bone o Parietal bones (2) o Occipital bone o Temporal bones (2) o Sphenoid bone o Ethmoid bone Frontal Bones o ____________________________________ o Most of anterior cranial fossa o Superior wall of orbits o Contains air-filled frontal sinus Parietal Bones and Major Associated Sutures o ____________________________________ o Four sutures mark the articulations of parietal bones with frontal, occipital, and temporal bones: Coronal suture—_____________________________________________ Sagittal suture—_____________________________________________ Lambdoid suture—_______________________________________________ Squamous (squamosal) sutures—________________________________ ________________________________________ Occipital Bone o Most of skull’s posterior wall and posterior cranial fossa o Articulates with ____________________________ at the occipital condyles o ____________________________________________________________________ o Contacts the parietal bones at the lambdoid suture o Contains the ___________________________ – connects the cranial cavity and the brain with the spinal cavity Temporal Bones o Below the parietal bones and contributing to the sides and base of the cranium (___________________________________________) o Contains the external acoustic meatus which leads to the tympanum (eardrum) o Other associations with the mouth: _________________________ – point of attachment with mandible _________________________ – anchors muscles associated with the tongue and pharynx o __________________________ – cite for muscle attachment for rotation of the head Sphenoid Bone o Forms floor of the cranium o _________________________________________________ o Complex, bat-shaped bone o Sella turcica – ______________________________________________________ Ethmoid Bone o Anterior to the sphenoid bone o Superior part of __________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ o Largely associated with the nose and nasal passages Facial Bones o Mandible o Maxillary bones (maxillae) (2) o Zygomatic bones (2) o Nasal bones (2) o Hyoid bone o Lacrimal bones (2) o Palatine bones (2) o Vomer o Inferior nasal conchae (2) o Nasal complex Mandible o ____________________________________ o Largest, strongest bone of face o Temporomandibular joint: only freely movable joint in skull ______________________________ ________________________________ o ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ o Articulate with all other facial bones except for the mandible o Contain large maxillary sinuses which lighten the portion of the maxillae above the teeth Nasal Bones and Lacrimal Bones o ____________________________ Form bridge of nose between the orbits for the eyes o Lacrimal bones ________________________________________ Lacrimal fossa houses lacrimal sac Zygomatic Bones o Articulates with the frontal bone and the maxilla to complete the lateral wall of the orbit o _________________________ Palatine Bones, Vomer and Inferior Nasal Conchae o Palatine bones _________________________________________ Contributes to the floor of the nasal cavity Small part of the floor of the orbits o Vomer Plow shaped _________________________________________ o ________________________________________ Form part of lateral walls of nasal cavity Nasal Cavity (Complex) o Roof, lateral walls, and floor formed by parts of four bones (______________________) Frontal Sphenoid Ethmoid Palatine bones Maxillary bones Inferior nasal conchae o Nasal septum of bone and hyaline cartilage Ethmoid Vomer Anterior septal cartilage Paranasal Sinuses o _______________________________________________ o _______________________________________________ o Enhance resonance of voice o Found in frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, and maxillary bones Hyoid Bone o ______________________________________________ o U-shaped bone suspended below the skull o _______________________________________________ o Site of attachment for muscles of swallowing and speech Vertebral Column o Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs o _____________________________________________________ o Flexible curved structure containing 26 irregular bones (vertebrae) __________________________ (7)—vertebrae of the neck (C1-C7) __________________________ (12)—vertebrae of the thoracic cage (T1-T12) __________________________ (5)—vertebra of the lower back (L1-L5) __________________—bone inferior to the lumbar vertebrae __________________________—terminus of vertebral column Vertebral Column: Curvatures o ________________________________________________ o Has 4 curves: Two primary convex curvatures ___________________________________ Two secondary concave curvatures _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ o Abnormal spine curvatures ________________ (abnormal lateral curve) ________________ (hunchback) ________________ (swayback) Intervertebral Discs o Cushion-like cartilage pad between vertebrae composed of two parts: _______________________________ Inner gelatinous nucleus that gives the disc its elasticity and compressibility _______________________________ Outer collar composed of collagen and fibrocartilage o _______________________________________________________________________ General Structure of Vertebrae o Body or centrum ______________________________________________ o Vertebral arch Composed of pedicles and laminae that, along with centrum, enclose vertebral foramen o Vertebral foramina _______________________________________________ o Intervertebral foramina Lateral openings between adjacent vertebrae for spinal nerves o Seven processes per vertebra: _____________________________—projects posteriorly _____________________________ (2)—project laterally ______________________________ (2)—protrude superiorly inferiorly ____________________________ (2)—protrude inferiorly Cervical Vertebrae o C1 to C7: smallest, lightest vertebrae o C3 to C7 share the following features ______________________ Stumpy spinous processes Large, triangular vertebral foramen Transverse foramen in each transverse process _______________________________________________ o C1 (atlas) and C2 (axis) have unique features o ___________ (C1) ____________________________________________ Named after Atlas from the Greek myth o ___________ (C2) Dens projects superiorly into the anterior arch of the atlas Dens is a pivot for the rotation of the atlas ____________________________________________ Thoracic Vertebrae o T1 to T12 o __________________________________________ o __________________________________________ o Long spinous process o Location of articular facets allows rotation of this area of spine Lumbar Vertebrae o L1 to L5 o Vertebral body that is thicker and more oval than the thoracic o ________________________________________________ o Allowing attachment of muscles o Orientation of articular facets locks lumbar vertebrae together so as to prevent rotation o _________________________________________________ o _________________________________________________ Sacrum and Coccyx o __________________ 5 fused vertebrae (S1–S5) _____________________________ Articulates with L5 superiorly, and with auricular surfaces of the hip bones laterally ______________________________________________________ Where muscles attach that are involved in leg movement ______________________________________________________ o Coccyx _______________________________ 3–5 fused vertebrae Usually 4 Articulates superiorly with sacrum _____________________________________________________ Thoracic Cage o Composed of __________________________ _________________________ __________________________ o Functions Protects vital organs of thoracic cavity __________________________________________________ Provides attachment sites for many muscles, including intercostal muscles used during breathing o ____________________________________ First 7 ribs are true ribs because they attach directly to the sternum ________________________________________________________ 11-12 are called floating ribs because they do not attach at all Sternum (Breastbone) o Three fused bones ______________________ Articulates with clavicles and ribs 1 and 2 Body ____________________________________________________ Xiphoid process ____________________________________________________ Not ossified until ~ age 40 Appendicular Skeleton o Bones of the limbs and their girdles __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ Pectoral Girdle (__________________________) o Clavicles and the scapulae ___________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ __________________________________ o Flattened acromial (lateral) end articulates with the scapula o Cone-shaped sternal (medial) end articulates with the sternum o ______________________________________________________________ Scapulae (Shoulder Blades) o ______________________________________________________________ o Flat and triangular, with three borders and three angles o Seven large fossae, named according to location The Upper Limb o 30 bones form the skeletal framework of each upper limb Arm ______________________ Forearm ________________________ Hand 8 ___________ bones in the wrist 5 __________ bones in the palm 14 __________ in the fingers Humerus o _______________________________________________________ o Articulates at the head with the scapula o Articulates inferiorly with radius and ulna Bones of the Forearm o Ulna Medial bone in forearm ______________________________________________________________ o Radius Lateral bone in forearm (___________________________) Head articulates with humerus and with radial notch of ulna Interosseous membrane connects the radius and ulna along their entire length Hand: Carpus o Eight bones in two rows Proximal row ________________________________________________________ Distal row ________________________________________________________ o Only scaphoid and lunate articulate with radius to form wrist joint Hand: Metacarpus and Phalanges o _________________________ Five metacarpal bones (#1 to #5) form the palm o _________________________ Each finger (digit), except the thumb, has three phalanges—distal, middle, and proximal Fingers are numbered 1–5, beginning with the thumb (pollex) _________________________________________ Pelvic (Hip) Girdle o Two hip bones (each also called coxal bone or coxae) ______________________________________________________ Transmit weight of upper body to lower limbs ______________________________________________________ o Each hip bone consists of three fused bones: ilium, ischium, and pubis o ______________________________________________________________________ Hip Bone o Three regions Ilium _______________________________________________ Auricular surface articulates with the sacrum (sacroiliac joint) Ischium Posteroinferior part of hip bone _______________________________________________ Pubis ______________________________________________ Midline pubic symphysis joint Comparison of Male and Female Pelves o Female pelvis ________________________________________ True pelvis (inferior to pelvic brim) defines birth canal Cavity of the true pelvis is broad, shallow, and has greater capacity o Male pelvis Tilted less forward _________________________________________________________ Cavity of true pelvis is narrow and deep The Lower Limb o _______________________________________________ o Subjected to exceptional forces o Four segments of the lower limb Thigh: _______________ Kneecap: ___________________ Leg: ___________________ Foot: ___________________________________________________________ ______________________________________ Femur o _____________________________________________________________ o Articulates proximally with the acetabulum of the hip and distally with the tibia and patella Bones of the Leg o Tibia Medial leg bone _______________________________________________________________ o Fibula Not weight bearing; no articulation with femur _________________________________________ Connected to tibia by interosseous membrane Articulates with tibia _________________________________________ Foot: Tarsals o Seven tarsal bones form the posterior half of the foot o ______________________________________________________________ o Other tarsal bones: cuboid, navicular, and the medial, intermediate, and lateral cuneiforms Foot: Metatarsals and Phalanges o _______________________: Five metatarsal bones (#1 to #5) Enlarged head of metatarsal 1 forms the “ball of the foot” ______________________________________ o __________________________ The 14 bones of the toes Each digit (except the hallux) has three phalanges ______________________________________