19.2 Hydrogen Ions and Acidity
advertisement

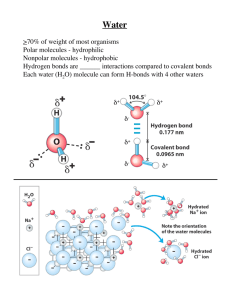
19.2 Hydrogen Ions and Acidity Self-Ionization of Water Water is very polar When the water molecules collide too fast a proton can break off and two ions form H2O → H+ + OH Usually the H+ ion reacts with an intact H2O molecule to form an hydronium ion H3O+ H+ + H2O → H3O+ Algebra Review 10000 = 104 ___1___ = 10-4 10000 Which number is larger 104 or 106? 106 Which number is larger 10-4 or 10-6? 10-4 think about it what is the larger number 1/10,000 or 1/1,000,000 Acidic or basic [H+] > 10-7 solution is acidic [H+] = 10-7 solution is neutral [H+] < 10-7 solution is basic Or other way around [OH-] > 10-7 solution is basic [OH-] = 10-7 solution is neutral [OH-] < 10-7 solution is acidic H+/OH- concentrations in acids and bases H+ OH- acid H+ OH- neutral H+ OH- base Algebra What’s a logarithm? Writing exponents w/o superscript Example: log 103 = 3 log 10-3 = -3 -log 10-3 =3 How much alkalinity/acidity Easier way of expressing acidity/alkalinity Focuses only on [H+] concentration, called pH (little p, big H!!!) The pH of a solution is the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration pH = -log [H+] Artificial scale ranging from 0 to14 Example H2O A few water molecules do this H2O → H+ + OHIs water an acid or a base? How many molecules break up? 10-7 Water has [H+] = 10-7 pH = -log 10-7 pH= 7 Because water is considered neutral, pH 7 is the neutral pH pH of Household Liquids Addtl. definition of an acid/base Acid has a pH < 7 (0 - 6.9) Base has a pH > 7 (7.1 - 14)