What are igneous rocks?
advertisement
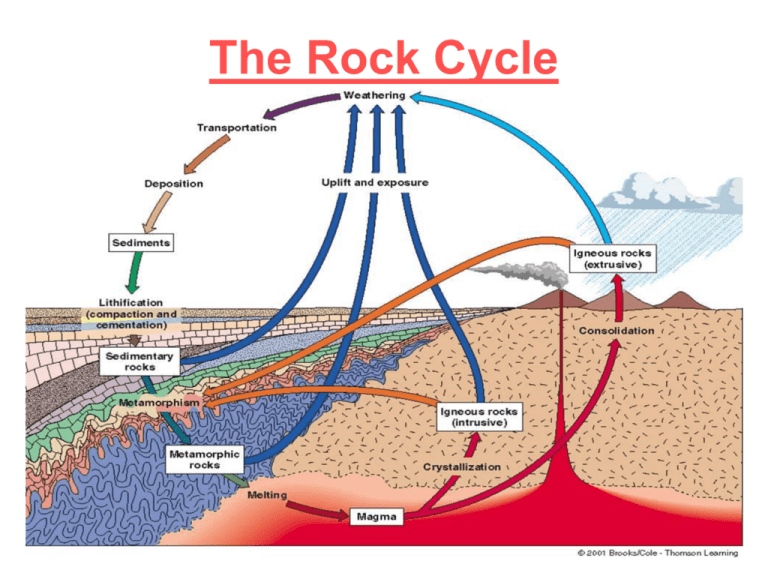
The Rock Cycle Section 3.2 • Vocabulary to know: • • • • • • • • Igneous rock Magma Lava Extrusive igneous rock Intrusive igneous rock Texture Composition Silicate What are igneous rocks? • Igneous rock– Form from molten rock deep within the Earth that has cooled… OR… – From molten rock that has reached the surface and cooled lava • Temperatures deep within the Earth are hot enough (14000F to 23000F) to melt rock Where do igneous rocks come from? • Volcanoes! • Extrusive igneous rock– Forms when lava cools on Earth’s surface • Intrusive igneous rock– Forms when magma cools within the Earth Textures of igneous rocks • Texture = size of the rock’s mineral crystals • Large crystals- slow cooling time – Intrusive rocks commonly have large crystals • Small/No crystals- fast cooling time – Extrusive rocks commonly have small or no crystals How can you tell the difference between salt and sugar? Answer = look at their composition! • Igneous rocks are mainly made up of silicate minerals Ship Rock • Formed 1km below Earth’s surface • It was once intrusive igneous rock – It is what’s left behind of magma that once fed a volcano • Through weathering and erosion, surface rock has been worn away… • …Ship Rock survives because igneous rock is usually harder than other types of rocks Section 3.3 • Vocabulary to know: • • • • • • • Sedimentary rock Sediment Cementation Coal Limestone Crossbeds Ripples What are sedimentary rocks? • Sedimentary rock– Forms from loose material (sediments) that get pressed together (cemented) into rock – Sediments• Can be pieces of rocks, minerals, plants, or animals Sedimentary rock formation… • Rainwater washes away rock particles… • Flow downhill to streams and rivers… • Eventually these sediments reach the ocean… • Settle on the bottom of the ocean… • Pressure eventually forces these sediments together… • Sedimentary rock is formed! Fossils can also make sedimentary rock • Coal– Made up of remains of plants (dead wood, bark, leaves, etc.) – Started forming millions of years ago • Limestone– Made up of remains of ocean organisms (shells, bones, etc.) – Pressure “squishes” these materials together into rock Coal formation • A- Dead pieces of plant matter collecting on lake bottom • B- sediments applying pressure on top of plant matter • C- Even greater pressure applied • D- Coal is created Limestone towers (Mono Lake) • Minerals can dissolve in water … • …and then re-form as the water evaporates • Often they form underwater… • …and as the water level drops they become visible Sedimentary rocks can teach us about the past… • Crossbeds– These layers were once moving sand dunes • Ripples– The surface of this sandstone preserves ancient sand ripples Section 3.4 • Vocabulary to know: • • • • • • Metamorphic rock Metamorphism Recrystallization Foliation Foliated rock Nonfoliated rock What are metamorphic rocks? • Metamorphic rock– Forms when heat or pressure cause older rocks to change into new types of rocks • Metamorphism– The process in which existing rock is changed by heat or pressure Metamorphic rock formation • During metamorphism rocks undergo many changes • Heat and pressure can break the bonds that join the atoms in minerals… the atoms then join together differently – Recrystallization • Rocks do not melt during this process!!! Foliation • Foliation– An arrangement of minerals in flat or wavy parallel bands • Foliated rocks– Develop under pressure – Minerals flatten out or line up in bands • Nonfoliated rocks– Develop if rock is made up of only one type of mineral – May not be under enough pressure The Rock Cycle








