Name: Date:______ PowerPoint Presentation Fill
advertisement

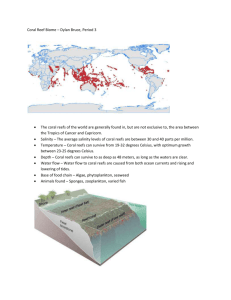
Name:____________________________ Date:_____________ PowerPoint Presentation Fill-in Sheet Coral Reefs Directions: To help you stay attentive and help you study for the chapter exam, follow the PowerPoint presentation about coral reefs and fill in the missing information. What exactly are coral reefs? Coral reefs are rocky mounds and ridges formed in the sea by marine organisms through the accumulation and deposition of limestone, otherwise known as calcium carbonate. Coral reefs are unique and rich marine ecosystems. -Hard Coral Colonies: ________________________ 1) ___________________________ 2) ___________________________ 3) ___________________________ Ecological requirements of coral reefs: warm water (17-34°C) shallow coastal waters and bays sufficient sunlight to support ______________________ Where are coral reefs located? - Pacific Ocean - Atlantic Ocean - Indian Ocean (including the _______________________ ) 3 Widely Recognized Major Coral Reef Areas: - ___________________________ - ____________________________ - ____________________________ Types of coral reefs: - ___________________- a roughly circular oceanic reef system surrounding a central lagoon - ____________________- a reef system that grows fairly close or directly from the shore, with an entirely shallow lagoon or none at all - _____________________- a reef system that is parallel to a shore and is separated from it by a wide lagoon that contains some depth in sections How are coral reefs formed? Coral reefs are formed by the accumulation of __________________ extracted from seawater. Small animals and plants help form the mounds and ridges. The following build the underlying framework: -Reef-building Corals: _________________________________ -Coralline algae: _______________________________ Types of Fish and Plant in the Coral Reef Two types of classes Vertebrates- _____________________________________ Cartilaginous- _______________________________________ Helpful fact: A majority of the fish dwelling in the coral reef are bony fish. Fish Adaptations to the reef _____________________- Torpedo like shape for speed, laterally compressed shape to make sharp turns _______________________ - Bright colors, odd patterns. This is to hide from predators and attract mates. Also, some fish have venomous spines or flesh to warn off enemies. ________________________- Special digestive tracks to digest plants/small fish. Some fish have sharp teeth to snip off coral like the butterfly fish. Finding Nemo Anemones are coral reef animals that have stinging tentacles to ward off other creatures. Anemones look like plants but are in fact sea animals. You may have herd of them from finding nemo. Clownfish (nemo) are fish that have adapted to anemones. They are able to live in them with out getting stung. Herbivores Herbivores are fish that feed mainly on plants (___________________________). -Parrotfish- _____________________________________________________________ -Surgeonfishes -Rabbitfish- _____________________________________________________________ -Damesfish Planktivores Planktivores are fish that feed on small animal plankton. - __________________________________________________ - _____________________________ – Hunt their pray while remaining close to the reef. - ______________________________- Hunt during the night. Benthic Carnivores Benthic Carnivors are fish that feed on invertebrate animals and small fish that live on or near coral reef habitats. These types of fish make up a majority of the fish associated with living in the coral reef. -____________________________________ -____________________________________ -____________________________________ Piscivores Piscivores are fish that pray on other fish. There are three different hunting strategies these fish have; pursuit, stalking and ambush - _____________________- fish that relay on speed to track down their pray - _____________________- watch and approach their pray before they strike. - _____________________- relay on their coloration to make them seem invisible, and their stillness. Their pray won’t see what's coming. Coral Reef Plants Three main types - _____________________- essential to the survival of the coral reef - _____________________- supports other forma of life. Provides a habitat. - _____________________- Shoreline plants. Grow where there are few waves. Located a far distance from hard corals. Coral Reef Conservation Quick Facts about Coral Reefs The coral reefs are home to 25% of all marine life 10% of the World’s coral reefs have been completely destroyed 70% of the reef in the Philippines is destroyed and only 5% is in good condition Coral Bleaching Colorful algae in the coral are expelled due to the ____________________________________________ caused by global warming If the algae do not return the coral will _____________. On warm days scientists are very concerned with this phenomenon. Coral Mining Live coral is removed from the reefs and used in construction as _________________________________________________. Coral is also taken from the reefs and sold as _____________________________. They are also harvested for a live rock trade. Sedimentation and Pollution Sedimentation occurs when _______________________ caused by construction, mining, logging, or farming flows into the rivers and then into the ocean. The sedimentation __________________________________________________ _____________________________________ and can get caught in the reefs. _________________________ occurs when toxins are dumped in the ocean or their runoff reaches the ocean. This can cause an overgrowth of algae, blocking sunlight to the reef. Overfishing This can cause problems in the entire food chain and cause problems beyond the reef. Destructive fishing practices can eliminate fish and the reeds themselves due to dynamite fishing or muro-ami which means banging on the reef with _______________________ so the fish will swim out. Why is this important? Coral reefs remove and recycle carbon dioxide They protect the land from harsh weather by absorbing the impact from storms Very large biodiversity in the reefs and without them many plants would die Lots of new things can be studied from reefs such as ecosystems, biodiversity, biomes, and interrelationships between organisms