Predicting Products of Reactions

Drill #4B 2/10/15
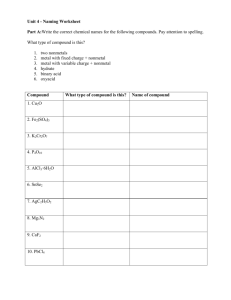
Predict the products and balance the equation for the following double-replacement reaction:
Na
2
CrO
4
(aq) + Ba(OH)
2
(aq) →
Drill #3 2/10/15
• Translate and predict products for the following reactants:
• calcium hydroxide + phosphoric acid
• FeCl
3
+ NH
4
OH
Answer
1 Na
2
CrO
4
(aq) + 1 Ba(OH)
2
2 NaOH (aq) + 1 BaCrO
4
(s)
(aq) →
BaCrO
4 is the precipitate (solid) we know this? Solubility Rules
– how do
Agenda
• Pass fwd 9-2 Practice Problems.
Drill # 4A 2/9/15
Write the balanced chemical equations for the following:
aluminum bromide + chlorine yield aluminum chloride + bromine
Potassium chlorate when heated yields potassium chloride + oxygen gas
Hydrogen + nitrogen monoxide yield water
+ nitrogen
Agenda
• Predicting Products
• Precipitation Reactions and Solubility
Rules
Lab on Wed
Predicting
Products of
Reactions
Synthesis Reactions:
A + B AB
• Element + Element Compound
– There are other forms, but for your test, it will always be an ionic compound
• To predict the products of a synthesis reaction, just cross the charges of the elements
• Example:
– Li + Br
2
– Li + Br
2
– 2Li + Br
2
?
LiBr
2LiBr (balanced)
Synthesis Practice
• Mg + N
2
?
• Mg + N
2
• 3Mg + N
2
Mg
3
N
2
Mg
3
N
2
• Mn + Cl
2
• Mn + Cl
2
? (Use Mn 2+ )
MnCl
2
(already balanced)
•
• K + O
2
K + O
2
• 4K + O
2
?
K
2
O
2K
2
O
Decomposition Reactions
AB A + B
• Compound Element + Element
– There are other forms, but for your test, we will always end with two elements.
• To predict the product, just separate the compound into elements.
DON’T FORGET THE
• Example:
DIATOMIC ELEMENTS!
– CaO ?
H
2
, N
2
, O
2
, F
2
, Cl
2
, Br
2
, I
2
– CaO Ca + O
2
– 2 CaO 2 Ca + O
2
Decomposition Practice
• PbI
2
?
• PbI
2
Pb + I
2
(already balanced)
• NH
3
?
• NH
3
N
2
• 2 NH
3
N
+ H
2
2
+ 3 H
2
• Li
2
S ?
• Li
2
S Li + S
• Li
2
S 2 Li + S
• AlF
3
?
• AlF
3
• 2AlF
3
Al + F
2
2Al + 3F
2
Single Replacement Reactions
• Element + Compound
New Element + New Compound
• 2 forms:
– A + BC AC + B (A is a metal)
• OR
– X + YZ YX + Z (X is a nonmetal)
Single Replacement Rxns.
Cont.
• You must use an Activity Series to determine if there is a reaction.
– If the free metal is above the bonded metal on the Metal Activity Series (on the back of your
Periodic Table), the free metal will take the place of the bonded metal. (If it is below, then
NR – no reaction)
– If the free nonmetal is above the bonded nonmetal on the Periodic Table, the free nonmetal will take the place of the bonded nonmetal. (If it is below, then NR.)
Single Replacement Practice
• Fe + CuSO
4
? (use Fe 2+ )
• Fe + CuSO
4
FeSO
4
+ Cu
(already balanced)
– Why? Fe is above Cu on the Activity Series
• Ca + HgO ?
• Ca + HgO CaO + Hg (already balanced)
– Why? Ca is above Hg on the Activity Series
Single Replacement Practice
• Ni + Mn
2
O
3
? (Use Ni 2+ )
• Ni + Mn
2
O
3
NR (no need to balance!)
– Why? Ni is below Mn on the Activity Series
• Al + FeCl
2
?
• Al + FeCl
2
Fe + AlCl
3
– Why? Al is above Fe on the Activity Series
• 2 Al + 3 FeCl
2
3 Fe + 2 AlCl
3
Single Replacement Practice
• MnCl
3
+ F
2
?
• MnCl
3
+ F
2
MnF
3
+ Cl
2
– Why? F is above Cl on the Periodic Table
• 2 MnCl
3
+ 3 F
2
2 MnF
3
+ 3 Cl
2
• S + Na
2
O ?
• S + Na
2
O NR (no need to balance!)
– Why? S is below O on the Periodic Table
Double Replacement Reactions
AB + CD AD + CB
• Compound + Compound
New Compound + New Compound
• To predict, swap ion pairs and re-cross charges.
• Example:
– Fe(OH)
2
– Fe(OH)
2
– Fe(OH)
2
+ H
2
SO
4
?
+ H
+ H
2
SO
2
SO
4
4
FeSO
4
FeSO
4
+ HOH (H
2
O)
+ 2 H
2
O
Double Replacement Practice
• KI + PbCl
2
?
• KI + PbCl
2
• 2 KI + PbCl
KCl + PbI
2
2
2 KCl + PbI
2
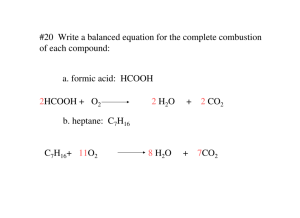
Combustion Reactions
C x
H x
+ O
2
CO
2
+ H
2
O
• Any reaction between a compound of carbon and hydrogen (C x
H x
) and oxygen will produce the same two products – carbon dioxide and water!
• Example:
– CH
4
– CH
4
– CH
4
+ O
2
?
+ O
2
+ 2 O
CO
2
2
+ H
CO
2
2
O
+ 2 H
2
O
Combustion Practice
• C
6
H
6
+ O
2
?
• C
6
H
• 2 C
6
6
H
+ O
6
2
CO
2
+ 15 O
2
+ H
2
O
12 CO
2
+ 6 H
2
O
• C
2
H
5
OH + O
2
?
• C
2
H
5
OH + O
2
CO
2
• C
2
H
5
OH + 3 O
2
+ H
2 CO
2
2
O
+ 3 H
2
O
Precipitation Reactions
• No ionic compound is entirely insoluble in water, however compounds of low solubility can be considered insoluble for most practical purposes.
• There are some general guidelines to help predict whether a compound made of a certain combination of ions is soluble.
Solubility Rules Table
Use this table to determine if precipitation will occur.
Precipitation occurs when the attraction between the ions is greater than the attraction between the ions and surrounding water molecules.
Precipitate = solid
Assignment
Complete the “Double Replacement
Reactions and the Solubility Rules” worksheet
Directions: use the solubility rules handout to determine the correct phase for each product
• Review WS