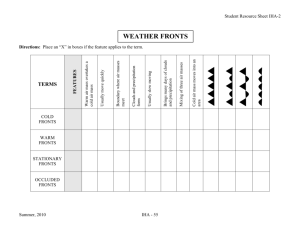
Key Idea #20 Air Masses Weather and Climate
advertisement

Key Idea #20 Weather and climate are influenced by the atmosphere and oceans. http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.kidsgeo.com/images/weather-and-climate.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.kidsgeo.com/geography-for-kids/0052-weather-andclimate.php&h=298&w=300&sz=13&tbnid=8udQUroMPUYk_M:&tbnh=115&tbnw=116&prev=/search%3Fq%3Dweather%2Band%2Bclimate%26tbm%3Disch%26tbo%3Du&zoom=1&q=weather+and+climate&hl=en&usg=__Alm3OQA8Ye70EKngAXpWocTtGA=&sa=X&ei=dorZTa7_KMrh0QG8yqn8Aw&sqi=2&ved=0CEMQ9QEwAg Weather is the mix of events that happen each day in the atmosphere and include temperature, rainfall, and humidity. Causes of Different Weather Most weather occurs at the lower portion of the atmosphere, in the troposphere, and is due to changes in the temperature of air masses (convection currents). Rising warm air eventually cools and sinks. Cool air is warmed by the Earth’s surface and rises. An air mass is a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity and air pressure throughout it. http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.fas.org/irp/imint/docs/rst/Sect14/airmasses_schem.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.fas.org/irp/imint/docs/rst/Sect14/Sect14_1b.html&h=325&w=410&sz=120& tbnid=baHgikeIJMrvaM:&tbnh=99&tbnw=125&prev=/search%3Fq%3Dair%2Bmasses%26tbm%3Disch%26tbo%3Du&zoom=1&q=air+masses&hl=en&usg=___--JyToI_vAwz09rgOSqUHtT9k=&sa=X&ei=1YfZTc75LeHr0gHr5-z8Aw&sqi=2&ved=0CC8Q9QEwAw The sun’s heat causes air masses to form and circulate in the atmosphere in the form of convection currents. This movement creates differences in air pressure. warm, moist (humid) air rises cooler, denser air sinks Differences in air pressure creates winds. Temperature changes in air masses and upper air currents cause air masses to move in the atmosphere. Air masses form mostly in tropical or polar regions. When air masses move from their regions of origin, they bring heat waves and cold spells. tulane.edu FYI: Types of Air Masses Tropical air masses (pink) are warm, low pressure air masses that form in the tropics. Polar air masses (blue) are cold, high air pressure air masses that form north of 50° north latitude and south of 50° south latitude uwsp.edu Warm air masses are forced to rise and expand over and above cold air masses because warm and cold air masses don’t mix easily. cool, dense air sinks. warm,less dense air rises. http://www.atmoz.org/img/warm-front.png FYI: Jet streams form at the boundaries of adjacent air masses that have huge differences in temperature. ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu Jet streams are concentrated, high altitude streams of fast moving wind that blow from west to east across the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. FYI located about 10-11 km above Earth’s surface (just below the tropopause). hundreds of kilometers wide and blow from west to east between 200 and 400 km/h (124-248 mph). www.merrittcartographic.co.uk/jet_streams.html The jet stream is constantly shifting. is responsible for the movement of major weather features from west to east across North America and the Earth. http://heatusa.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2009/06/jet-stream-paths.jpg Air Masses Video A front is an area where two air masses with different temperatures and densities collide. Fronts occur when huge masses of air bump into each other as they move across the land and oceans. A frontal boundary refers to the boundary that forms between warm and cold air masses. Rain or snow typically forms along fronts. As a warm, moist air mass rises above a cooler air mass it cools and the water vapor in it condenses to form clouds. Rain or snow may form if the warm air mass continues to rise, expand, and cool in the atmosphere. The type of front that develops depends on the characteristics of the air masses and how they are moving. Cold Front A cold front is a situation where a cold air mass is moving in and replacing warmer air. Cold fronts generally move from northwest to southeast. www.physicalgeography.net/.../coldfront.GIF Weather Associated with Cold Fronts Cold fronts usually move quickly causing abrupt weather changes. Thunderstorms (sometimes violent) in the summer and snowfalls in the winter are associated with cold fronts. Weather Conditions Associated with a Cold Front Weather Phenomenon Prior to the Passing of the Front Contact with the Front After the Passing of the Front Temperature Warm Cooling suddenly Cold and getting colder Atmospheric Pressure Decreasing steadily Leveling off then increasing Increasing steadily Winds South to southeast Variable and gusty West to northwest Precipitation Showers Heavy rain or snow, hail sometimes Showers then clearing Clouds Cirrus and cirrostratus changing later to cumulus and cumulonimbus Cumulus and cumulonimbus Cumulus www.physicalgeography.net Warm Front A warm front occurs when a warm air mass advances on a cold air mass. Since cold air is more dense than warm air, the warm air moves over the cold air and condenses forming clouds. www.physicalgeography.net Weather Associated with Warm Fronts Steady, long lasting rains in the summer and steady snowfalls in the winter are associated with warm fronts. Weather Conditions Associated with a Warm Front Weather Phenomenon Prior to the Passing of the Front Contact with the Front After the Passing of the Front Temperature Cool Warming suddenly Warmer then leveling off Atmospheric Pressure Decreasing steadily Leveling off Slight rise followed by a decrease Winds South to southeast Variable South to southwest Precipitation Showers, snow, sleet or drizzle Light drizzle None Clouds Cirrus, cirrostratus, altostratus, nimbostratus, and then stratus Stratus, sometimes cumulonimbus Clearing with scattered stratus, sometimes scattered cumulonimbus www.physicalgeography.net Cold Front and Warm Front Animation http://www.mesoscale.iastate.edu/agro n206/animations/05_cnWfronts.html http://www.educypedia.be/education/cli mateanimations.htm Stationary Front A stationary front is a situation where a cold air mass and a warm air mass meet and neither one is moving. When a warm or cold front stops moving, it becomes a stationary front. Once this boundary resumes its forward motion, it once again becomes a warm front or cold front. Credits and Acknowledgments for WW2010.Department of Atmospheric Sciences (DAS) at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/earth/Atmosphere/tstorm/stat_front.html Weather Associated with a Stationary Front A stationary front can last for days, producing nothing but altocumulus clouds and/or precipitation. Temperatures remain stagnant and winds are gentle to non-existent. Occluded Fronts Occluded fronts are produced when a fast moving cold front catches and overtakes a slower moving warm front. http://206.251.19.76/weather/wofront.htm Occluded Fronts An occluded front occurs when warm, cool, and cold air masses come together and the warm air is pushed above the cooler air masses. Occluded fronts are not common. http://206.251.19.76/weather/wofront.htm Air Masses and Fronts Video Predicting the Weather (FYI) Meteorologists are scientists who study the causes of weather and try to predict it. analyze data using maps, charts, and computers. prepare weather forecasts. They get their data from local weather observers. instruments carried by balloons. ocean buoys. satellites. weather stations around the world. Reading Weather Maps (FYI) Areas in the same temperature range are shown in the same color. FYI: Fronts move in the direction the symbol is pointing. The cold fronts are moving from the northwest to the northeast. The warm front is moving from the south towards the north. According to this map, what type of weather can Michigan expect in a few days? According to this map, Michigan can expect warmer temperatures and rain in a few days as a warm front moves in. According to this map, what type of weather can Michigan expect in a few days? According to this map, Michigan can expect cooler temperatures and rain as a cold front moves in. Climate is the average weather pattern in a place over many years. Weather vs Climate Weather is the mix of events that happen each day in the atmosphere includes temperature, rainfall, and humidity. Climate is the average weather pattern in a place over many years. is useful for weather forecasting. The two main factors that determine the climate of a region are temperature and precipitation. Oceans make up 70% of Earth’s surface. absorb more energy from the sun than land does. warm up and cool down much slower than land does. retain their heat better than land does. members.virtualtourist.com/m/b47ab/c57/ The temperature of the oceans affects the different climates on Earth because water in the oceans hold a large amount of heat. Oceans take a long time to warm up in the spring and summer. Oceans take a long time to cool down in the fall and winter. In the spring and summer, winds from the cooler ocean waters keep the coastal regions cooler in than inland areas. In the fall and winter, winds from the warmer ocean waters keep coastal regions warmer than inland areas. Uneven Heating of the Earth FYI: The sun is the major cause of the heating and cooling of our atmosphere. The Earth gets the same amount of light each day, but since the Earth is tilted on its axis, the light is unevenly divided into two hemispheres. More hours of sunlight = more solar heating. http://www.coryvannote.com/images/more/biology/Earth_sunlight.jpg The hemisphere that is tilted toward the sun receives more direct sunlight and experiences spring and summer. The hemisphere that is tilted away from the sun is receiving less direct light and experiences fall and winter. http://web.srv.cmes.utah.edu:8080/west/k12/EarthsTiltPic/view