week5.attitudes

ATTITUDES: FORMING AND
CHANGING ATTITUDES
Happy hours in a bar: An attitude adjustment period.
What is your attitude toward drinking alcohol?
Attitude =
Altitude
I don’t like your attitude, Don’t give me this attitude
Attitudes: Definitions…
“Attitudes are learned predispositions to respond to an object or class of objects in a consistently favorable or unfavorable way.”
“Attitudes are lasting , general evaluations of people, products, advertisements or issues (Attitude object)”
Are all positive attitudes similar?
INTENSITY DIFFERENCES
Any neutral attitude?
NO ATTITUDES (VALENCE)
Are Attitudes Important for Marketers ?
Mainly important for 2 reasons…
Important role in explaining and predicting behavior toward products and services. Attitudes are closely related to behavioral intention.
Attitude toward a product may also help to evaluate responsiveness to communication from the company.
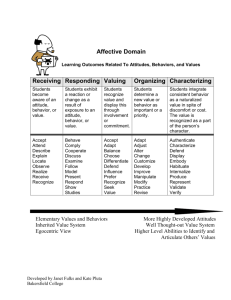
Functions of Attitudes (Katz)
Utilitarian function: support in decision making.
Value-expressive function: what does the attitude say about me.
Ego-defensive function: strengthen self aspects.
Knowledge function: fullfill need for order, structure or meaning
Attitudes Vary Along a Number of
Dimensions
THE LINGO
Favorability
Accessibility
Strength/confidence
Persistence
Resistance to attack
SAY WHAT??
“I like it a lot.”
“I can remember my attitude toward it.”
“I’m sure I like it.”
“I’ve liked it for a long time and will continue to like it.”
“I’ll like it no matter what anyone says about it.”
Preferences: represent attitudes toward one object in relation to another (way to measure attitudes)
Attitude toward the object:
How much do you like/dislike IBM computers?
Like very much 1 2 3 4 5 Dislike very much
Preference:
Compared to Apple personal computers, how much do you like IBM personal computers?
Like IBM much 1 2 3 4 5 Like Apple much more than Apple more than IBM
Cognitive
Attitudes Components
Based on the knowledge the person has about the attitude object.
Affective
Based on the feelings regarding the attitude object.
Behavioral
Based on the behavioral tendencies toward the attitude object.
What about attitudes formation?
Attitude
Component
Cognitions or
Beliefs
Affect or
Feelings
Conations or
Actions
Attitude Object
Dhl, For Shipping A
Business’s Small Packages
• DHL is very reliable in its service.
• DHL is more economical than other package carrier services.
• DHL is able to customize its service to my shipping needs.
• When I ship by DHL, I feel secure.
• I am very happy to be suing DHL for my shipping needs.
• I don’t care if DHL goes out of business.
• I use DHL for my shipping more than I use other carriers.
• I am often recommending DHL to other business associates.
• I am looking for alternative carriers.
Shopping For Airline
Tickets On The Internet
• For my airline tickets, shopping on the internet is very convenient.
• You can find the cheapest fares by shopping on the internet.
• Internet based travel agents do not offer you a comprehensive set of airline and flight options.
• Shopping on the Internet is:
(please circle as many as apply)
Totally cool Boring Confusing
A pain in the neck Enjoyable Terrible
• I have used Internet for my travel airline tickets recently.
• I often search Internet for planning my travel itinerary.
Tridimensional Approach
Cognitive
Component
Attitude
Affective
Component
Behavioral
Component
Unidimensional approach or
Hierarchy of effects
Belief Affect
Behavioral
Intention
Attitude
Hierarchy of Effects.
High- and Low-Involvement
Information-Processing Modes
Central processing route
– The customer attends to and scrutinizes message content actively and thoughtfully
Peripheral processing route
– The consumer attends to the message only cursorily, and tends to make quick inferences by simply looking at the elements in the ad
Exhibit 6.2: General Approaches to
Attitude Formation and Change
Attitudes Formation
Key Aspect: The Consistency principle
Cognitive dissonance theory (opposed cognitive information, eliminate, add or distort)
Self-perception Theory (maintain equilibrium, low implication, use my behavior to assess my attitude)
Social Judgment Theory (maintain equilibrium in reference to a framework, latitude of acceptation, assimilation-contrast)
Balance Theory (balanced triads)
The Role of Beliefs in Attitude
Formation
The Fishbein Model
Model proposes that attitude toward an object is based on the
summed set of beliefs about the
object’s attributes weighted by the evaluation of these attributes
The Role of Beliefs in Attitude
Formation
The Fishbein Model n
A o
= Σ b i
I i
i =1
A o
= attitude toward object b i
= strength of the belief that object has attribute i
I i
= Importance of attribute i n = number of salient or important attributes
USD
Attitude Model
Strategic Application of multiattribute model
Capitalize on relative Advantage.
Strengthen Perceived Product/Attribute Linkages
Add a new attribute
Influence competitors’ ratings
Communicating the Presence of
Desirable Attributes
Communicating the Absence of
Undesirable Attributes
Exhibit 6.4:
Expectancy-Valued model: The Theory of Reasoned Action
How Cognitively Based
Attitudes are Influenced
The Message
– Argument Quality
Strong Arguments
– One- Versus Two-Sided Messages
One-Sided Messages
Two-Sided Messages
– Comparative Messages
How Cognitively Based
Attitudes are Influenced
Communication Source
– Spokesperson Credibility
Credibility
– Company Reputation
Celebrity Effectiveness
Depends on Credibility
–
–
–
Trustworthiness
Expertise
Status / Prestige
The higher the credibility, the greater the attitude change (especially with opposed consumer)
Less impact on more knowledgeable consumers
Celebrity Problems
Overexposure
– When celebrity endorses too many products
(reduces effectiveness)
Celebrity Behavior
– Madonna, Mike Tyson, Michael Jackson
Cognitive Bases of Attitudes
When Consumer Effort Is Low
Simple Inferences
Heuristics
Frequency Heuristic
The Affective (Emotional)
Foundations of Attitudes
Affective Involvement
Affective Responses
Emotional Appeals
How Affectively Based
Attitudes Are Influenced
The Source
– Attractiveness
– Match-up Hypothesis
The Message
– Emotional Appeals
– Fear Appeals
Affective Bases of Attitudes
When Consumer Effort Is Low
The Mere Exposure Effect
– Wearout
Classical Conditioning
High
Involvement
Commercial and Attitudes:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Cognition Affect
Low
Involvement