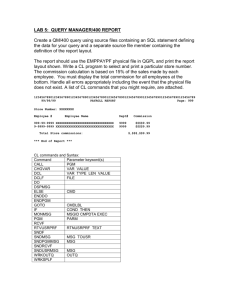
CAN 4
advertisement

EC312 CANopen mbed Intrusion
E. Zivi April 26, 2015
References:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
A CAN Physical Layer Discussion Microchip Application Note AN00228a
Controller Area Network (CAN) Implementation Guide Analog Devices Application Note AN-1123
Controller Area Network, CANPRES Version 2.0 , Siemens Microelectronics, Inc., October 98
http://www.kvaser.com/en/about-can/the-can-protocol.html
CAN physical layer ref: http://www.can-cia.org/index.php?id=systemdesign-can-physicallayer
Controller Area Network Physical Layer Requirements, TI SLLA270–January 2008
CAN Tutorial, http://www.computer-solutions.co.uk/download/Peak/CAN-Tutorial.pdf
CANopen Introduction,
ref: http://www.canopensolutions.com/english/about_canopen/about_canopen.shtml
1. Embedded Networking with CAN and CANopen, by Pfeiffer, Ayre and Keydel
2. CANopen Implementation: Applications to Industrial Networks, by Farsi and Barbosa
3. CAN in Automation, http://www.can-cia.org/
Recall CAN & ISO/OSI
Reference Model
2
CAN in Automation (CiA) CANopen &
ISO / OSI Reference Models
CiA 401
Generic I/O
Profile
CiA 402
Motion Control
Profile
IEC 61131-3
Programmable
Devices Profile
CiA 4xx Device Profiles
CiA 302 CANopen Framework for CANopen
Managers & Programmable Devices
Application
CiA 301 CANopen Application Layer &
Communication Profile
Not Implemented by CAN or CANopen
ISO 11898 CAN Data Link Layer
ISO 11898 CAN Physical Layer
High level CAN Protocols implement Application layer and skip the four intervening layers
3
CANopen Device Model
All node, network, configuration and process data is
stored in the object dictionary in pre-defined locations
CAN Lab #4 Functional Block Diagram
mbed CAN Transceiver Circuit
CAN Physical Vulnerabilities
1. Damage to CAN physical network
termination, signal integrity or continuity can
bring down network.
2. Short circuits will kill the network (MIL-STD1553 avoids this by using coupling
transformers)
3. Nodes must stay bit synchronized; one node
with the wrong bit rate will kill the system.
CAN Logical Link Vulnerabilities
1. Any node can assert an error condition at
any time
2. Highest priority messages can prevent lower
priority messages
3. At the CAN Logical Link layers, there are no
rules regarding how nodes should interact
4. All nodes are assumed to conform to the
specified rules.
CANopen Vulnerabilities
1. It is assumed that all nodes conform to the CANopen rules
and conventions.
2. Since CANopen specifies an upper level protocol based on
CAN, any CAN node (such as the mbed) can abuse the
CANopen rules.
3. There are no CANopen “hall monitors” to “police” the
system. Systems integration engineers should ensure that
all nodes are compliant with the CANopen standards.
(There are standard compliance tests).
4. All nodes are assumed to conform to the CANopen
network management specified rules.
Mbed Intrusion Lab
1. mbed controls motor, CANopen Magic monitors
experiment.
2. mbed intercepts CANopen messages and
immediately sends false messages.
a. Duty cycle command reversed (25% becomes 75%)
b. Motor speed data reversed (fast reported as slow)
3. Mbed implements PI feedback control over CAN
network. CANopen Magic sends motor speed
commands to mbed.
mbed_Maxon_steps.cpp Code Snippets
mbed CAN Initialization:
can1.frequency(500000); // set CAN bit rate to 500kbps
msg_tx.len = 8; // set data packet length (8 is default)
msg_tx.type = CANData; // CAN data messages (default)
msg_tx.format = CANStandard; // CAN 11 bit message ID )
// PWM duty cycle command to MicroMod
msg_tx.id = NODE_micromod+RPDO_2;
mbed CAN Message Transmission:
// Send PWM duty cycle sequence as MicroMod RPDO 2
...
if (can1.write(msg_tx)) // send CAN PWM command to MicroMod
led3 = 0; // clear transient CAN write error indicator
else {
led3 = 1; // set transient CAN write error indicator
led4 = 1; // set sticky CAN write error indicator
}
mbed_in_the_middle.cpp Code Snippets
if(can1.read(msg_rx)) // watch for transmitted msg
// MicroMod RPDO 2 PWM duty cycle command?
if (msg_rx.id == NODE_micromod+RPDO_2) {
// reverse duty cycle
msg_rx.data[0] = 0xff-msg_rx.data[0];
if (!can1.write(msg_rx)) // send reversed cmd
...
// MicroMod TPDO 3 tachometer motor speed?
} else if (msg_rx.id == NODE_micromod+TPDO_3) {
bad_tach = Ain4_max-(msg_rx.data[0]
+256*msg_rx.data[1]);
if (bad_tach < 0) bad_tach = 0; // lower bound
msg_rx.data[0] = 0xff&bad_tach; // load LSB
msg_rx.data[1] = bad_tach>>8;
// load MSB
if (!can1.write(msg_rx)) // send reversed speed
...
mbed_Maxon_PI.cpp Code Snippets
// Configure interrupt for RPDO2 transmission to MicroMod
ticker.attach(PI_controller,DELTA_T); // send every DELTA_T
...
void PI_controller() { // calculate & send PI command
U = (K*Omega_error+KI*I_error);
DUTY = (int)(U*1023.0/5.0); // MicroMod 8-bit duty cycle
if (DUTY > 0x00FF) // check upper bound
DUTY = 0x00FF;
// if necessary, bound
else if (DUTY < 0) // check lower bound
DUTY = 0;
// if necessary, bound
else // Calculate integral error if control is not limited
I_error = I_error + Omega_error*DELTA_T;
...
// Construct and send RPDO2 MicroMod PWM command
msg_tx_MM.data[0] = (char)(DUTY&0xFF); // unsigned 8-bit
if(can1.write(msg_tx_MM)) { // send to MicroMod
...
CANopen Magic Sample Trace Windows Part 1:
All CAN Messages:
Only Process Data Objects (PDOs) CAN Messages:
CANopen Magic Sample Trace Windows Par 2:
MicroMod Node 2 TPDO 3 (Ain4 – Ain7) Messages Only:
Mbed Node 3 TPDO 1 CAN Messages to CANopen Magic only:
Lab #4 CANopen Magic Graphical User Interface
New Closed Loop Motor Speed Command CAN Messages
Performance Expiated
Process Data Visual Display
New mbed TPDO 1 Trace Window: Messages to CANopen Magic
CAN Lab #4 Functional Block Diagram