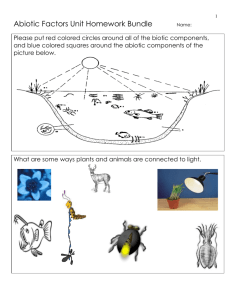
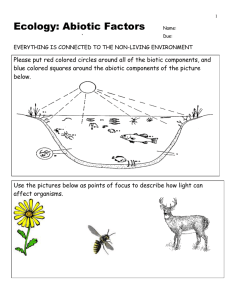
Part III: Water Cycle, Carbon Cycle
advertisement
Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link • RED SLIDE: These are notes that are very important and should be recorded in your science journal. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy -Please make notes legible and use indentations when appropriate. -Example of indent. -Skip a line between topics -Don’t skip pages -Make visuals clear and well drawn. • RED SLIDE: These are notes that are very important and should be recorded in your science journal. • BLACK SLIDE: Pay attention, follow directions, complete projects as described and answer required questions neatly. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Keep an eye out for “The-Owl” and raise your hand as soon as you see him. – He will be hiding somewhere in the slideshow Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Keep an eye out for “The-Owl” and raise your hand as soon as you see him. – He will be hiding somewhere in the slideshow “Hoot, Hoot” “Good Luck!” Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • This will be the big concept in ecology that will be addressed in this portion of the unit. – or artificial. • This will be the big concept in ecology that will be addressed in this portion of the unit. – or artificial. • This will be the big concept in ecology that will be addressed in this portion of the unit. – Note: The cycles that we will learn move between the living and non-living world. r artificial. • This will be the big concept in ecology that will be addressed in this portion of the unit. – Note: The cycles that we will learn move between the living and non-living world. r artificial. • This will be the big concept in ecology that will be addressed in this portion of the unit. – Note: The cycles that we will learn move between the living and non-living world. r artificial. New area of focus: Biogeochemical Cycles. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Biogeochemical Cycles. Bio – Life Geo – Earth Chemical – Changes in atoms / molecules Cycles – Repeated event, full turn. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Hydrosphere interacts with atmosphere (Water cycle) Hydrosphere interacts with atmosphere (Water cycle) The atmosphere interacts with the ecosphere. (Plants and animals breath -Carbon Cycle and nitrogen cycle Hydrosphere interacts with atmosphere (Water cycle) The atmosphere interacts with the ecosphere. (Plants and animals breath -Carbon Cycle and nitrogen cycle Living things change the lithosphere, become rock, erode the land. (Phosphorus Cycle) Hydrosphere interacts with atmosphere (Water cycle) The atmosphere interacts with the ecosphere. (Plants and animals breath -Carbon Cycle and nitrogen cycle The Hydrosphere, Atmosphere, Ecosphere and Lithosphere all interact within the biosphere. Living things change the lithosphere, become rock, erode the land. (Phosphorus Cycle) Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link • What’s so special about the water in this photograph? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • What’s so special about the water in this photograph? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • What’s so special about the water in this photograph? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • What’s so special about the water in this photograph? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • What’s so special about the water in this photograph? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Compare the importance of water commonly existing in all three states of matter. • Compare the importance of water commonly existing in all three states of matter. Water commonly exists in all three states of matter • Compare the importance of water commonly existing in all three states of matter. Water commonly exists in all three states of matter Water exists commonly in its solid state • Compare the importance of water commonly existing in all three states of matter. Water commonly exists in all three states of matter Water exists commonly in its solid state • Compare the importance of water commonly existing in all three states of matter. Water exists commonly in its solid state • Compare the importance of water commonly existing in all three states of matter. Water exists commonly in its solid state • Compare the importance of water commonly existing in all three states of matter. This next part helps when we study the water cycle • Solid (s) has a definite shape and volume. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Molecules form a crystal lattice. Molecules form a crystal lattice. Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link Water is being continually created by many biophysicochemical processes. As such, water can be viewed as being constantly “refreshed” or “rejuvenated.” Water is being continually created by many biophysicochemical processes. As such, water can be viewed as being constantly “refreshed” or “rejuvenated.” The water in dinosaur pee is not the same water that we drink. The H’s and O’s that make up H2O are the same ones present when the dinosaurs roamed the Earth. New Area of Focus: The Water Cycle Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy New Area of Focus: The Water Cycle AKA – The Hydrologic Cycle Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy New Area of Focus: The Water Cycle AKA – The Hydrologic Cycle Driven by the sun and gravity. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy New Area of Focus: The Water Cycle AKA – The Hydrologic Cycle Driven by the sun and gravity. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Driven by the Sun Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Driven by the Sun Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Driven by the Sun Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • What do we already know? Explain yourselves with this template. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link The hydrologic cycle (Water Cycle): Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy The hydrologic cycle (Water Cycle): The continuous movement of water on, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy The hydrologic cycle (Water Cycle): The continuous movement of water on, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy The hydrologic cycle (Water Cycle): The continuous movement of water on, above, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy The hydrologic cycle (Water Cycle): The continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the earth. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Water Cycle Available Sheet • Water Cycle Available Sheet • Step by step drawing of the water cycle. Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link Evaporation: Substance changes from a liquid state to gas state (requires energy). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Evaporation: Substance changes from a liquid state to gas state (requires energy). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Evaporation: Substance changes from a liquid state to gas state (requires energy). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link • Link! Water Cycle Flash Animation Tour – http://www.epa.gov/safewater/kids/flash/flash_ watercycle.html • Activity! Water Cycle in a Bottle. – Each group needs a standard 2 liter clear soda bottle cut in half about 10 cm from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water about 10 cm. • Add food coloring if you wish. – Slide cup into the bottle to just above the warm water with cap on. – Fill top bottle (cup) with ice cubes. • Do not overfill. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) – Visual on next slide. • Activity! Water Cycle in a Bottle. – Each Soda bottle group cut by teacher, bottle cut in needs a standard 2 liter clear soda half about 4 inches from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water. – Invert top of bottle with cap and fill with ice cubes. – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) • Activity! Water Cycle in a Bottle. – Each Soda bottle group cut by teacher, bottle cut in needs a standard 2 liter clear soda half about 4 inches from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water. – Invert top of bottle with cap and fill with ice cubes. – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) • Activity! Water Cycle in a Bottle. – Each Soda bottle group cut by teacher, bottle cut in needs a standard 2 liter clear soda half about 4 inches from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water. Next fill bottle with – Invert top of bottle with cap and fill with ice cubes. very warm water and – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the food coloring. warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit on TpT • Activity! Water Cycle on the window? – Each group needs a standard 2 liter clear soda bottle cut in half about 4 inches from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water. – Invert top of bottle with cap and fill with ice cubes. – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) • Activity! Water Cycle on the window? – Each group needs a standard 2 liter clear soda bottle cut in half about 4 inches from the top. • (Have teacher cut in advance) – Fill bottle with very warm water. – Invert top of bottle with cap and fill with ice cubes. – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) • Activity! Water Cycle on the window? – Each group needs a standard 2 liter clear soda bottle cut in half about 4 inches from the top. • (Have teacher cut in Tape advance) – Fill bottle with very warm Clear Bagwater. – Invert top of bottleWaterwith cap and fill with ice cubes. + Blue Color – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) • Activity! Water Cycle on the window? – Each group needs a standard 2 liter clear soda bottle cut in half about 4 inches from the top. Record • (Have teacher cut in Tape advance) terms – Fill bottle with very warm on bag Clear Bagwater. with – Invert top of bottleWaterwith cap and fill with ice cubes. + Blue Color Sharpie – Slide cup with ice into the bottle to just above the warm water. – Watch for evaporation, condensation, and the droplets falling back down to the warm water (precipitation) Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit on TpT • Activity! Stranded on a Desert Island. – You and your group must use the materials provided (and the water cycle) to turn salt water into freshwater over the next several days in order to survive. Use the sun as the energy source. – Each group gets a clear plastic box, glass cup, plastic wrap, marbles / pebbles, salt water mixed with sand, and a bungee cord / large elastic. – Visual of materials on next slide. – Video Link of set-up. – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4sqRvUzqDCE • Materials for the set-up. Plastic wrap Saltwater and Sand Cup Marbles Elastic • Materials for the set-up. Plastic wrap Saltwater and Sand Cup Marbles Elastic • Below is the correct set-up to use the water cycle to turn salt water into freshwater. • Below is the correct set-up to use the water cycle to turn salt water into freshwater. Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link Surface run-off: The water flow which occurs when soil is full to capacity and excess water travels over the land. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Surface run-off: The water flow which occurs when soil is full to capacity and excess water travels over the land. Capacity: ? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Surface run-off: The water flow which occurs when soil is full to capacity and excess water travels over the land. Capacity: The maximum amount that can be obtained in a body. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Storage of water in vegetation. – Plants soak up and hold water. They are very good flood preventers. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Storage of water in vegetation. – Plants soak up and hold water. They are very good flood preventers. Trees can hold enormous amounts of water.s Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Storage of water in vegetation. – Plants soak up and hold water. They are very good flood preventers. Trees can hold enormous amounts of water.s Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Storage of water in vegetation. – Plants soak up and hold water. They are very good flood preventers. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Storage of water in vegetation. – Plants soak up and hold water. They are very good flood preventers. Trees help control flooding by holding water in their tissues. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link • Activity! Not Smart Board. – Teacher on next slide to minimize out of slideshow. – Students should drag the terms to the correct position on the picture. – Answer revealed after. Possible Answer Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link 7. 8.) Which term is not shown. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Driven by the Sun 7. 8.) Which term is not shown. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Quiz 1-7 The hydrologic cycle. Please record the numbers and the correct term. 7. 8.) Which term is not shown. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Quiz 1-7 The hydrologic cycle. Please record the numbers and the correct term. 7. 8.) Which term is not shown. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. Evaporation 7. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. Evaporation 7. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Answers1-8 The hydrologic cycle. Transpiration Evaporation 7. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link • You can now complete this question on the bundled homework package on page 6 • You can now complete this question on the bundled homework package on page 6 • Please label the picture below. – Just in case on page 7. • Please label the picture below. – Just in case on page 7. New Biogeochemical Cycle: The Carbon Cycle. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Carbon is the duct tape of life. – Living things are made of carbon. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Carbon is the duct tape of life. – Living things are made of carbon. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Carbon is the duct tape of life. – Living things are made of carbon. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Carbon Cycle: The circulation of carbon into organisms (biotic) and back again (abiotic). Atmosphere, Land, Water, Oceans. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Carbon Cycle: The circulation of carbon into organisms (biotic) and back again (abiotic). Atmosphere, Land, Water, Oceans. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Where are the carbon reservoirs on our planet? – Which ones do human activities impact? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Where are the carbon reservoirs on our planet? – Which ones do human activities impact? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Where are the carbon reservoirs on our planet? – Which ones do human activities impact? Reservoirs: A large supply of something. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Where are the carbon reservoirs on our planet? – Which ones do human activities impact? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Where are the carbon reservoirs on our planet? – Which ones do human activities impact? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Where are the carbon reservoirs on our planet? – Which ones do human activities impact? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link • The energy flow of life occurs because of plants. Plants harness the energy from the sun, and pass it on to all other life forms. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • The energy flow of life occurs because of plants. Plants harness the energy from the sun, and pass it on to all other life forms. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • If a product is made of the following, it is made from plants, or old decomposed plants (oil). – Any wood. – Any fiber / other than metals. – Plastics (most are oil based). – Chemicals (most are from plants and oils). – All food. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Which of the following equations is the correct equation for photosynthesis? • A) 6O2 + 6H2O + light energy = C12H6O6 + 6O2 • • • • • • • • • B) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 C) 6CO2 + 6O2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O D) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 E) 6CO2 + H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 F) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H2O6 + 6O2 G) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 H) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O3 + 6O2 I) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6CO2 J) C6H12O6 = 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Answer! Which of the following equations is the correct equation for photosynthesis? • A) 6O2 + 6H2O + light energy = C12H6O6 + 6O2 • • • • • • • • • B) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 C) 6CO2 + 6O2 + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6H2O D) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 E) 6CO2 + H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 F) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H2O6 + 6O2 G) 6CO2 + 6H2O + sugar = C6H12O6 + 6O2 H) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O3 + 6O2 I) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6CO2 J) C6H12O6 = 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy + 6O2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Photosynthesis: Plants make sugar from sunlight. Light energy is turned into chemical energy (sugars are carbon based). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Photosynthesis: Plants make sugar from sunlight. Light energy is turned into chemical energy (sugars are carbon based). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Photosynthesis: Plants make sugar from sunlight. Light energy is turned into chemical energy (sugars are carbon based). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Respiration – The plant burns the sugar to make energy. Mitochondria Chloroplasts Respiration – The plant burns the sugar to make energy. Inside the leaf Mitochondria Chloroplasts Equation for Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 Equation for Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 Equation for Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 Carbon Dioxide Equation for Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 Carbon Dioxide Equation for Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 Carbon Water Dioxide Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link • Using M&M’s to learn the equation for photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Reactants 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy + Light Products C6H12O6 + 6O2 + Law Conservation of Mass: In any physical or chemical reaction. Mass cannot be created or destroyed. The law implies that mass can neither be created nor destroyed, although it may be rearranged in space Oxygen Carbon Hydrogen Reactants 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy + Light Products C6H12O6 + 6O2 + Law Conservation of Mass: In any physical or chemical reaction. Mass cannot be created or destroyed. The law implies that mass can neither be created nor destroyed, although it may be rearranged in space How many total atoms are in the Reactants, and how many total atoms are in the Products? Reactants 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy + Light Products C6H12O6 + 6O2 + Law Conservation of Mass: In any physical or chemical reaction. Mass cannot be created or destroyed. The law implies that mass can neither be created nor destroyed, although it may be rearranged in space How many total atoms are in the Reactants, and how many total atoms are in the Products? Answer…. Reactants 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy + Light Products C6H12O6 + 6O2 + Law Conservation of Mass: In any physical or chemical reaction. Mass cannot be created or destroyed. The law implies that mass can neither be created nor destroyed, although it may be rearranged in space How many total atoms are in the Reactants, and how many total atoms are in the Products? Answer…. Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link • Activity! Use the white boards to memorize the equation for photosynthesis. Keep writing and erasing until you can do it repeatedly. (Optional) • 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Sunlight Oxygen Carbon Dioxide Glucose Water Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Activity! Use the white boards to memorize the equation for photosynthesis. Keep writing and erasing until you can do it repeatedly. • 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Sunlight Oxygen Carbon Dioxide Glucose Water Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Which of the following equations is true of photosynthesis? Pick the correct color. – 6O2 + C6H12O6 Energy 6CO2 + 6H2O – C6H12O6 + 6O2 Energy + Chloroplasts. – 6O2 + 6CO2 + 6O2 Energy + C6H12O6 – 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 – 6O2 + 6CO2 + Energy + C6H12O6 + 6O2 – Energy + 6H2O Energy + 6O2 + 6CO2 – CO2 + 3H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + O2 – 6CO2 + 6H2O Energy + 6CO2 + 6O2 – Energy 6O2 + C6H12O6 + 6CO2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • The Answer is… – 6O2 + C6H12O6 Energy 6CO2 + 6H2O – C6H12O6 + 6O2 Energy + Chloroplasts. – 6O2 + 6CO2 + 6O2 Energy + C6H12O6 – 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 – 6O2 + 6CO2 + Energy + C6H12O6 + 6O2 – Energy + 6H2O Energy + 6O2 + 6CO2 – CO2 + 3H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + O2 – 6CO2 + 6H2O Energy + 6CO2 + 6O2 – Energy 6O2 + C6H12O6 + 6CO2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Answer: Blue – 6O2 + C6H12O6 Energy 6CO2 + 6H2O – C6H12O6 + 6O2 Energy + Chloroplasts. – 6O2 + 6CO2 + 6O2 Energy + C6H12O6 – 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 – 6O2 + 6CO2 + Energy + C6H12O6 + 6O2 – Energy + 6H2O Energy + 6O2 + 6CO2 – CO2 + 3H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + O2 – 6CO2 + 6H2O Energy + 6CO2 + 6O2 – Energy 6O2 + C6H12O6 + 6CO2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link Photosynthesis Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Photosynthesis Learn more about photosynthesis at… http://www.biology4kids.com/files/plants_photosynth esis.html Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Carbon dioxide is used. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Water is used. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Occurs in light Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Occurs only in cells with chloroplasts. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Produces sugar from light. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Produces sugar from light. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Produces sugar from light. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Oxygen is released. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Plants can get their energy from the sun by just sitting there, we have to go search for it, hunt, etc. We didn’t we evolve to be green and get our energy from the sun. – Why aren’t we green? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Plants can get their energy from the sun by just sitting there, we have to go search for it, hunt, etc. We didn’t we evolve to be green and get our energy from the sun. – Why aren’t we green? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Answer! Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Answer! Because photosynthesis only produces a small amount of energy. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Answer! Because photosynthesis only produces a small amount of energy. – We need lots of sugar to run, jump, and live our very busy and active lives. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Answer! Because photosynthesis only produces a small amount of energy. – We need lots of sugar to run, jump, and live our very busy and active lives. Plants are less active. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link • Respiration – The plant burns the sugar to make energy. Mitochondria Chloroplasts over there • Respiration – The plant burns the sugar to make energy. Mitochondria Chloroplasts • Respiration – The plant burns the sugar to make energy. Mitochondria Chloroplasts • Respiration – The plant burns the sugar to make energy. Mitochondria Chloroplasts • Respiration – The plant burns the sugar to make energy. Mitochondria Chloroplasts • Respiration – The plant burns the sugar to make energy. Mitochondria Chloroplasts • Remember: Producers create the sugars, then consumers use these sugars. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Remember: Producers create the sugars, then consumers use these sugars. – Plants harness the energy from the sun so we can live. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Remember: Producers create the sugars, then consumers use these sugars. – Plants harness the energy from the sun so we can live. “Thank you tree.” “Thank you for doing photosynthesis.” Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Remember: Producers create the sugars, then consumers use these sugars. – Plants harness the energy from the sun so we can live. “I love your sugars that you produce from photosynthesis.” Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Remember: Producers create the sugars, then consumers use these sugars. – Plants harness the energy from the sun so we can live. “I love your sugars that you produce from photosynthesis.” Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Which of the following colors is the correct color for the respiration equation. It is the opposite of photosynthesis. • • • • • • • • • 6 CO2 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 6H2O 6 CO2 + C6H12O6 + 6O2 6H2O + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 6 CO2 + 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 6O2 + 6H2O Glucose is created using respiration + Carbon Dioxide. C6H12O6 + 6CO2 6O2 + 6H2O + energy 6CO2 + 6O2 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 6H2O + energy 6CO2 6H2O + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6O2 6H2O + energy More energy + 6H2O Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Answer: • • • • • • • • • 6 CO2 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 6H2O 6 CO2 + C6H12O6 + 6O2 6H2O + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 6 CO2 + 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 6O2 + 6H2O Glucose is created using respiration + Carbon Dioxide. C6H12O6 + 6CO2 6O2 + 6H2O + energy 6CO2 + 6O2 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 6H2O + energy 6CO2 6H2O + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6O2 6H2O + energy More energy + 6H2O Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Answer: Lime Green • • • • • • • • • 6 CO2 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 6H2O 6 CO2 + C6H12O6 + 6O2 6H2O + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 6 CO2 + 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 6O2 + 6H2O Glucose is created using respiration + Carbon Dioxide. C6H12O6 + 6CO2 6O2 + 6H2O + energy 6CO2 + 6O2 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 6H2O + energy 6CO2 6H2O + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6O2 6H2O + energy More energy + 6H2O Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Video! Photosynthesis –This video will show the actual process of photosynthesis on a molecular level. – We may get just a bit but lets see the real deal. – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BK_cjd6Evc w&feature=related Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • You can now complete this question on page 8. • You can now complete this question on page 8. • Photosynthesis provides the sugar (carbon based) so animals can use that sugar and through cellular respiration make energy. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Photosynthesis provides the sugar (carbon based) so animals can use that sugar and through cellular respiration make energy. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Photosynthesis provides the sugar (carbon based) so animals can use that sugar and through cellular respiration make energy. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Cellular Respiration: Processes whereby certain organisms obtain energy from organic molecules. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Cellular Respiration: Processes whereby certain organisms obtain energy from organic molecules. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Respiration – The plant burns the sugar to make energy. Mitochondria Chloroplasts • Which of the following colors is the correct color for the respiration equation. It is the opposite of photosynthesis. • • • • • • • • • 6 CO2 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 6H2O 6 CO2 + C6H12O6 + 6O2 6H2O + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 6 CO2 + 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 6O2 + 6H2O Glucose is created using respiration + Carbon Dioxide. C6H12O6 + 6CO2 6O2 + 6H2O + energy 6CO2 + 6O2 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 6H2O + energy 6CO2 6H2O + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6O2 6H2O + energy More energy + 6H2O Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Answer: • • • • • • • • • 6 CO2 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 6H2O 6 CO2 + C6H12O6 + 6O2 6H2O + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 6 CO2 + 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 6O2 + 6H2O Glucose is created using respiration + Carbon Dioxide. C6H12O6 + 6CO2 6O2 + 6H2O + energy 6CO2 + 6O2 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 6H2O + energy 6CO2 6H2O + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6O2 6H2O + energy More energy + 6H2O Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Answer: Lime Green • • • • • • • • • 6 CO2 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 6H2O 6 CO2 + C6H12O6 + 6O2 6H2O + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 6 CO2 + 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 6O2 + 6H2O Glucose is created using respiration + Carbon Dioxide. C6H12O6 + 6CO2 6O2 + 6H2O + energy 6CO2 + 6O2 6H2O + energy 6 CO2 6H2O + energy 6CO2 6H2O + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6O2 6H2O + energy More energy + 6H2O Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • When you breath out, you are releasing water, carbon dioxide, and some heat. – These are the by products of cellular respiration in the trillions of cells in your body. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Cellular Respiration C6H12O6 + 6O2 = Released energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link • You can now complete this question on page 8. • You can now complete this question on page 8. Cellular Respiration - - - Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Burns sugars for energy. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Oxygen is used. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Oxygen is used. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Energy is released. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Energy is released. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Occurs in most cells. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • What type of cells in the human body are going to have a lot of mitochondria to do cellular respiration? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Answer! Muscle cells in the heart must always beat to keep you alive. It has a lot of mitochondria in its cells to burn sugar for energy. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Carbon dioxide produced. O2 CO2 Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link • How are these athletic events different? How does each one breath? • Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration. – What is the difference between the two? – http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/scien ce/add_ocr_gateway/living_growing/respirationa ct.shtml • Aerobic Respiration: A form of cellular respiration that requires oxygen in order to generate energy. • Aerobic Respiration: A form of cellular respiration that requires oxygen in order to generate energy. • Anaerobic Respiration: A form of cellular respiration that occurs when oxygen is absent or scarce. • In anaerobic respiration: Glucose isn’t completely broken down.. • In anaerobic respiration: Glucose isn’t completely broken down.. “Ahh, leg cramps, It hurts….” • In anaerobic respiration: Glucose isn’t completely broken down.. The waste product is lactic acid rather than carbon dioxide and water “Ahh, leg cramps, It hurts….” • In anaerobic respiration: Glucose isn’t completely broken down.. The waste product is lactic acid rather than carbon dioxide and water “Ahh, leg cramps, It hurts….” Water is released Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Water is released Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Water is released Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Water is released Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Transpiration: The evaporation of water from plants. – Plants pump water from the roots to the leaves. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Transpiration: The evaporation of water from plants. – Plants pump water from the roots to the leaves. – This pumping is driven by the evaporation of water through small pores called "stomates", which are found on the undersides of leaves. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Transpiration: The evaporation of water from plants. – Plants pump water from the roots to the leaves. – This pumping is driven by the evaporation of water through small pores called "stomates", which are found on the undersides of leaves. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Guard Cell and Stoma: Openings in leaf (stoma) controlled by guard cells that allow gasses in and out of leaf. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Guard Cell and Stoma: Openings in leaf (stoma) controlled by guard cells that allow gasses in and out of leaf. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy • Note: Stomata are small pores (openings) for gas exchange. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link The carbon dioxide oxygen balance. Photosynthesis Respiration Mitochondria in plant also do cellular respiration Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy The carbon dioxide oxygen balance. The plant Photosynthesis Respiration Mitochondria in plant also do cellular respiration Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy The carbon dioxide oxygen balance. The plant uses carbon dioxide Photosynthesis Respiration Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy The carbon dioxide oxygen balance. The plant uses carbon dioxide and produces oxygen Photosynthesis Respiration Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link • You can now complete many parts to your coloring and labeling page. – Write relevant information next to the drawings. Lightly color the objects only and not the white space. Moisture. Temperature. Wind. Light. Soil. Nutrients. Cycles, Range of Tolerance How light effects Warm organisms SPONCH. bloodedness Space and cold Thermoregulation bloodedness Physiological / Behavioral Seed Dispersal Positives and Adaptation to negatives of wind temperature Info about Isopods and Desert abiotic factors adaptation / temperature Island Biogeography Moisture. Temperature. Wind. Light. Soil. Nutrients. Cycles, Range of Tolerance How light effects Warm organisms SPONCH. bloodedness Space and cold Thermoregulation bloodedness Physiological / Behavioral Seed Dispersal Positives and Adaptation to negatives of wind temperature Info about Isopods and Desert abiotic factors adaptation / temperature Island Biogeography Moisture. Temperature. Wind. Light. Soil. Nutrients. Cycles, Range of Tolerance How light effects Warm organisms SPONCH. bloodedness Space and cold Thermoregulation bloodedness Physiological / Behavioral Seed Dispersal Positives and Adaptation to negatives of wind temperature Info about Isopods and Desert abiotic factors adaptation / temperature Island Biogeography Moisture. Temperature. Wind. Light. Soil. Nutrients. Cycles, Range of Tolerance How light effects Warm organisms SPONCH. bloodedness Space Evaporation and cold Thermoregulation bloodedness Physiological / Behavioral Seed Dispersal Positives and Adaptation to negatives of wind temperature Info about Isopods and Desert abiotic factors adaptation / temperature Island Biogeography Moisture. Temperature. Wind. Light. Soil. Nutrients. Cycles, Range of Tolerance How light effects Warm organisms SPONCH. bloodedness Space Evaporation and cold Thermoregulation bloodedness Physiological / Behavioral Seed Dispersal Positives and Adaptation to negatives of wind temperature Info about Isopods and Desert abiotic factors adaptation / temperature Island Biogeography Moisture. Temperature. Wind. Light. Soil. Nutrients. Cycles, Range of Tolerance How light effects Warm organisms Condensation SPONCH. bloodedness Space Evaporation and cold Thermoregulation bloodedness Physiological / Behavioral Seed Dispersal Positives and Adaptation to negatives of wind temperature Info about Isopods and Desert abiotic factors adaptation / temperature Island Biogeography Moisture. Temperature. Wind. Light. Soil. Nutrients. Cycles, Range of Tolerance How light effects Warm organisms Condensation SPONCH. bloodedness Space Evaporation and cold Thermoregulation bloodedness Physiological / Behavioral Seed Dispersal Positives and Adaptation to negatives of wind temperature Info about Isopods and Desert abiotic factors adaptation / temperature Island Biogeography Moisture. Temperature. Wind. Light. Soil. Nutrients. Cycles, Range of Tolerance How light effects Warm organisms Condensation SPONCH. bloodedness Precipitation Space Evaporation and cold Thermoregulation bloodedness Physiological / Behavioral Seed Dispersal Positives and Adaptation to negatives of wind temperature Info about Isopods and Desert abiotic factors adaptation / temperature Island Biogeography Moisture. Temperature. Wind. Light. Soil. Nutrients. Cycles, Range of Tolerance How light effects Warm organisms Condensation SPONCH. bloodedness Precipitation Space Evaporation and cold Thermoregulation bloodedness Physiological / Behavioral Seed Dispersal Positives and Adaptation to negatives of wind temperature Info about Isopods and Desert abiotic factors adaptation / temperature Island Biogeography Moisture. Temperature. Wind. Light. Soil. Nutrients. Cycles, Range of Tolerance How light effects Warm organisms Condensation SPONCH. bloodedness Precipitation Space Evaporation and cold Thermoregulation Surface run-Off bloodedness Physiological / Behavioral Seed Dispersal Positives and Adaptation to negatives of wind temperature Info about Isopods and Desert abiotic factors adaptation / temperature Island Biogeography Moisture. Temperature. Wind. Light. Soil. Nutrients. Cycles, Range of Tolerance How light effects Warm organisms Condensation SPONCH. bloodedness Precipitation Space Evaporation and cold Thermoregulation Surface run-Off bloodedness Physiological / Behavioral Seed Dispersal Positives and Adaptation to negatives of wind temperature Info about Isopods and Desert abiotic factors adaptation / temperature Island Biogeography Moisture. Temperature. Wind. Light. Soil. Nutrients. Cycles, Range of Tolerance How light effects Warm organisms Condensation SPONCH. bloodedness Precipitation Space Evaporation and cold Thermoregulation Surface run-Off bloodedness Infiltration Seed Dispersal Physiological / Behavioral Positives and Adaptation to negatives of wind temperature Info about Isopods and Desert abiotic factors adaptation / temperature Island Biogeography Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link • “AYE” Advance Your Exploration ELA and Literacy Opportunity Worksheet – Visit some of the many provided links or.. – Articles can be found at (w/ membership to NABT and NSTA) • http://www.nabt.org/websites/institution/index.php?p= 1 http://learningcenter.nsta.org/browse_journals.aspx?j Please• visit at least one of the ournal=tst “learn more” educational links provided in this unit and complete this worksheet • “AYE” Advance Your Exploration ELA and Literacy Opportunity Worksheet – Visit some of the many provided links or.. – Articles can be found at (w/ membership to NABT and NSTA) • http://www.nabt.org/websites/institution/index.php?p=1 • http://learningcenter.nsta.org/browse_journals.aspx?jo urnal=tst Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link Areas of Focus within The Ecology: Abiotic Factors Unit Abiotic Factors, Biotic Factors, The Big 7 Abiotic Factors, Organisms Range of Tolerance, Light, How light affects Organisms, Photosynthesis, Factors in the Environment that Affect the Amount of Light, How Organisms Movements are affected by light, Bioluminescence, How temperature affects organisms, Thermoregulation, Physiological Regulation, Behavioral Regulation, Adaptation, Hypothermia, Hyperthermia, Warm-Bloodedness (Endothermy), Cold-Bloodedness, Hibernation / Torpor, Advantages of Warm-Bloodedness, Disadvantages of Warm-Bloodedness, Advantages of Cold-Bloodedness, Disadvantages of Cold-Bloodedness, Water, Water Requirements and Plants, Adaptations of Plants and Water, Adaptations of Animals and Water, Wind, Positives and Negatives of Wind to Organisms, How animals use Wind, How Plants use Wind, Wind Dispersal, Water Dispersal, McArthur-Wilson Island Biogeography Theory, Animal Seed Dispersal, Fire Ecology, Fire Dependence, Biogeochemical Cycles, Water Cycle, Carbon Cycle, Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration, Oxygen-Carbon Dioxide Balance, Nitrogen Cycle, Phosphorus Cycle, Importance of Phosphorus, Nutrients, Nutrient Pollution and Aquatic Systems, Eutrophication. Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link • This PowerPoint is one small part of my Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit that I offer on TpT. This unit includes… • 4 Part 3,000+ Slide PowerPoint roadmap full of activities, video and academic links, review questions, and much more. • 15 page bundled homework packaged that chronologically follows PowerPoint, + modified version, answers keys. • 16 pages of unit notes with visuals. • 2 PowerPoint review games • Rubrics, Answer Keys, crossword puzzles, games, and much more. • Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Link • Please open the welcome / guide document on each unit preview. – This document will describe how to utilize these resources in your classroom and provide some curriculum possibilities. • Please open the welcome / guide document on each unit preview. – This document will describe how to utilize these resources in your classroom and provide some curriculum possibilities. • Please visit the links below to learn more about each of the units in this curriculum and to see previews of each unit. – These units take me four busy years to complete with my students in grades 5-10. Earth Science Units Extended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Geology Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Geology_Unit.html Astronomy Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Astronomy_Unit.html Weather and Climate Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Weather_Climate_Unit.html Soil Science, Weathering, More http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Soil_and_Glaciers_Unit.html Water Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Water_Molecule_Unit.html Rivers Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/River_and_Water_Quality_Unit.html = Easier 5th – 7th grade = More Difficult 6th – 8th grade = Most Difficult 8th – 10th grade Physical Science Units Extended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Science Skills Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Science_Introduction_Lab_Safety_Metric_Methods. html Motion and Machines Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Newtons_Laws_Motion_Machines_Unit.html Matter, Energy, Envs. Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Energy_Topics_Unit.html Atoms and Periodic Table Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Atoms_Periodic_Table_of_Elements_Unit.html Life Science Units Extended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Human Body / Health Topics http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Human_Body_Systems_and_Health_Topics_Unit.html DNA and Genetics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/DNA_Genetics_Unit.html Cell Biology Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Cellular_Biology_Unit.html Infectious Diseases Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Infectious_Diseases_Unit.html Taxonomy and Classification Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Taxonomy_Classification_Unit.html Evolution / Natural Selection Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Evolution_Natural_Selection_Unit.html Botany Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Plant_Botany_Unit.html Ecology Feeding Levels Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Feeding_Levels_Unit.htm Ecology Interactions Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Interactions_Unit.html Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Abiotic_Factors_Unit.html Life Science Curriculum Link Human Body Systems and Health Topics Unit Anatomy Intro, Levels of Biological Organization Lesson Bundle Skeletal System Lesson Bundle Muscular System Lesson Bundle Anatomy Intro, Skeletal, Muscular System Review Game Healthy Eating, Molecules of Life Lesson Bundle Obesity, Dangers of Fast Food, Eating Disorders Healthy Eating and Living Review Game Eating Disorders, Anabolic Steroids Digestive System Lesson Bundle Circulatory System and Respiratory System Lesson Bundle Anti-Tobacco, Dangers of Smoking Lesson Bundle Circulatory and Respiratory System Review Game Excretory System Lesson Bundle Nervous System Lesson Bundle Nervous System Review Game Endocrine System Lesson Bundle, Puberty, Hormones Human Reproductive Lesson Bundle, Fertilization Endocrine and Reproductive System Review Game Immune System, HIV, AIDS, STD's Lesson Bundle Immune System, HIV, AIDS, STD's Review Game Anatomy Crossword Puzzle DNA and Genetics Unit DNA Lesson Bundle DNA Lesson Review Game DNA Crossword Puzzle Cell Division, Mitosis and Meiosis Lesson Bundle Cell Division Review Game Mitosis and Meiosis Crossword Puzzle Genetics Lesson Bundle DNA and Genetics Crossword Puzzle Genetics Review Game Cellular Biology Unit Introduction to Cells, Cell History, Cheek and Onion Cell Lab, Cell Theory Lesson Bundle Cell Review Game Cell Transport Lesson Bundle, Osmosis, Diffusion, Active Transport Cell Transport Review Game Characteristics of Life Lesson Cellular Organelles Lesson Bundle Cellular Organelles Visual Quiz Cellular Organelles Review Game Cell Unit Crossword Puzzle Cell Unit Flash Cards Cellular Biology Unit Preview, Homework Bundle, Unit Notes, more Life Science Curriculum Link Infectious Diseases Unit Infectious Diseases Unit Intro and Virus Lesson Bundle Virus Lesson Review Game Bacteria Lesson Bundle Bacteria Review Game Parasites Lesson Bundle Immune System, HIV, AIDS, STD's Lesson Bundle Infectious Diseases Unit Crossword Puzzle Immune System, HIV, AIDS, STD's Review Game Evolution and Natural Selection Evolution and Natural Selection Lesson Bundle Evolution and Natural Selection Review Game Human Evolution Lesson Bundle Life Origins and Human Evolution Quiz Game Geologic Timescale, Earth System History Lesson Bundle Earth Geologic History Quiz Game Life Origins and Human Evolution Quiz Game Life Origins, Miller Urey Experiment Lesson Bundle Ecological Succession Lesson Bundle Ecological Succession Review Game Taxonomy and Classification Unit Taxonomy and Classification Lesson Bundle Taxonomy and Classification Review Game Bacteria Lesson Bundle Bacteria Review Game Kingdom Protista Lesson Bundle Kingdom Animal Lesson Bundle Animal Phylums Visual Quiz Class Mammalia Lesson Bundle Kingdom Animalia Review Game and Mammalia Kingdom Fungi Lesson Bundle Kingdom Fungi Review Game Kingdom Plantae Lesson Bundle Botany Unit Review Game Name the Kingdom, Phylum, Class Visual Challenge Taxonomy and Classification Crossword Puzzle Botany Unit Botany Unit Intro, Non-vascular Plants, Plate Evolution Lesson Bundle Student Botany Projects, Grow Study Lesson Bundle Botany Unit Review Game Plants, Seeds, Seed Dispersal Lesson Bundle Plants Review Game Plants, Roots, Leaves, Lesson Bundle Monocotyledons and Dicotyledons Lesson Bundle Dendrochronology, Tree Ring Dating Lesson Bundle Plant Hormones Lesson Bundle Botany Unit Crossword Puzzle Leaf Identification Lesson Bundle Botany Unit Review Game Plant Life Cycles, Flowers, Fruits Lesson Bundle Plant Life Cycles, Flowers, Fruits Review Game Life Science Curriculum Link Ecology Feeding Levels Unit Ecology Food Chain Lesson Bundle Biomagnification, Bioaccumulation of Pollution, Food Chain Lesson Bundle Ecology Feeding Levels, Pyramid of Biomass, Number Lesson Bundle Animal Dentition Lesson Bundle Ecology Feeding Levels Unit Review Game Ecology Feeding Levels Unit Crossword Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit Food Chain Board Game Ecology Non-living Factors, Light Lesson Bundle Ecology, Non-living Factor Temperature Ecology Interactions Unit Lesson Bundle Ecology Levels of Organization Lesson Bundle Photosynthesis and Respiration, Animal Habitats Lesson Bundle Biogeochemical Cycles Lesson Bundle Food Webs, Predator and Prey Cycles Lesson Bundle Ecology Non-living Factors Quiz Game Biodiversity and Population Sampling Lesson Bundle Island Biogeography Lesson Bundle Animal Competition Lesson Bundle Nitrogen Cycle Lesson Bundle Animal Camouflage and Mimicry Lesson Bundle Phosphorus Cycle and Nutrient Pollution Ecology, Camouflage, Mimicry, Population Sampling Lesson Bundle Review Game Plant Succession, Fire Ecology, Lesson Symbiosis Lesson Bundle Bundle Invasive Exotic Species Lesson Bundle Ecology Interactions Part III, IV Review Game, Symbiosis, Ecological Succession Quiz Game Ecology Flash Cards Exotic Species Ecology Interactions Unit Crossword Puzzle Physical Science Curriculum Link Laws of Motion and Simple Machines Unit Newton's Three Laws of Motion Newton's Laws of Motion Review Game Friction Lesson, Types of Friction Kinetic and Potential Energy Lesson Newton's Laws and Forces in Motion Forces in Motion Review Game Catapults and Trajectory Lesson Simple Machines Lesson Simple Machines Review Game Laws of Motion and Simple Machines Unit Flashcards Laws of Motion and Simple Machines Crossword Puzzle Laws of Motion, Forces in Motion, Simple Machines Unit Preview, Homework, Notes Atoms and the Periodic Table of the Elements Unit Science Skills Unit Lab Safety Lesson Bundle Microscopes and Magnification Lesson Bundle Metric System / SI Lesson Bundle Scientific Notation Lesson Bundle Volume and Density Lesson Bundle Scientific Method, Observation Skills Lesson Bundle Science Skills Unit Flash Cards Science Skills Unit Crossword Puzzle Science Skills Unit Review Game Science Skills Unit Preview, Homework Bundle, Notes Atoms, Atomic Number, Atomic Mass, Isotopes Lesson Bundle Inside the Atom Lesson Bundle Atoms Review Game Atomic Theory, Electrons, Orbitals, Molecules Lesson Bundle Atoms, Atomic Theory, Electrons, Orbitals, Molecules Review Game Atomic Bonding, Balancing Chemical Equations, Reactions, Lesson Bundle Atoms and the Periodic Table Crossword Puzzle and Solution Atoms and Periodic Table Unit Preview, Homework Bundle, Unit Notes Periodic Table of the Elements Unit Lesson Bundle Periodic Table of the Elements Review Game Matter, Energy, and the Environment Unit States of Matter, Physical Change, Chemical Change States of Matter, Physical Change, Chemical Change Review Game Gas Laws Introductory Lesson Bundle Gas Laws Review Game Viscosity Lesson Bundle Forms of Energy Lesson Bundle Heat Transfer, Convection, Conduction, Radiation Lesson Bundle Electromagnetic Spectrum Lesson Bundle Forms of Energy, Particles, Waves, EM Spectrum Review Game Electromagnetic Spectrum Visual Quiz Electricity and Magnetism Lesson Bundle Electricity and Magnetism Review Game Matter and Energy Crossword Puzzle and Solution Matter, Energy, and the Environment Unit Preview, Homework Bundle, Notes Environment Unit Bundle Environment Unit Bundle Review Game Earth Science Curriculum Link Geology Topics Unit Plate Tectonics, Continental Drift, Earth's Core, Plate Boundaries Lesson Bundle Dynamic Earth Review Game Plate Boundaries Visual Quiz Volcanoes Lesson Bundle Types of Volcanoes Volcanoes Review Game Earthquakes Lesson Bundle Earthquakes Review Game Rock Deformation, Compression, Tension, Shearing Minerals Lesson Bundle Minerals Review Game Rock or Mineral PowerPoint Quiz Rocks and Minerals Lesson Bundle Rocks and Minerals Flash Cards Types of Rocks Visual Quiz Rocks and the Rock Cycle Lesson Bundle Rocks and Rock Cycle Review Game Geologic Timescale, Earth System History Lesson Bundle Earth Geologic History Quiz Game Geology Unit Crossword Puzzle Geology Unit Preview, Bundled Homework, Unit Notes Astronomy Topics Unit Solar System and Sun Lesson Bundle Sun Lesson Bundle Solar System and Sun Review Game Solar and Lunar Eclipse Lesson Bundle Inner Planets Lesson Bundle Inner Planets Review Game Moon, Phases of the Moon, Tides, Seasons, Lesson Bundle Rocketry Lesson Bundle Asteroid Belt, Meteors, Torino Scale Lesson Bundle Asteroid Belt and Rocketry Review Game Mission to the Moon, Apollo Lesson Outer Planets Lesson Bundle Outer Planets Review Game Beyond the Solar System Lesson Bundle Beyond the Solar System, Galaxies, Black Holes, Constellations Review Game Galaxy Lesson, Hubble Exploration Astronomy Unit Crossword Puzzle Astronomy Unit in Spanish Earth Science Curriculum Link Weathering, Soil Science, Soil Conservation, Ice Ages, Glaciers Unit Mechanical and Chemical Weathering Lesson Bundle Mechanical and Chemical Weathering Review Game Soil Science Lesson Bundle Erosion, Soil Conservation Lesson Bundle Soil Science, Erosion, Soil Conservation Review Game Weathering, Soil Science Unit Flash Cards Weathering and Soil Science Crossword Puzzle Ice Ages and Glaciers Lesson Bundle Ice Ages and Glaciers Review Game Ice Ages and Glaciers Crossword Puzzle Ice Ages, Glaciers Unit Flash Cards Weathering, Soil Science, Soil Conservation, Ice Ages, Glaciers Unit Preview Weather and Climate Unit Atmosphere Lesson Bundle Ozone Layer, Air Pollution, Skin Cancer Atmosphere, Layers of the Atmosphere, Pollution Quiz Game Air Pressure and Winds Lesson Bundle Severe Weather Lesson Bundle, Hurricanes, Tornado, Blizzards Seasons Lesson Bundle, Axial Tilt Weather, Wind, Seasons, Quiz Game Winds, Global Winds, Wind Chill Lesson Bundle Oceans and Weather, Water Cycle, Clouds Lesson Bundle Water Cycle and Clouds Lesson Bundle Earth Science Curriculum Link Rivers, Lakes, and Water Quality Unit Rivers and Watershed Lesson Bundle Flooding Lesson Bundle Benthic Macroinvertebrate Lesson Bundle Lake Turnover Lesson Bundle Salmon Lesson Bundle Fish Lesson, Fashion a Fish, Lesson Bundle Rivers, Lakes, and Water Quality Unit Review Game Rivers, Lakes, and Water Quality Crossword Puzzle Rivers, Lakes, and Water Quality Unit Preview, Homework Bundle, Unit Notes Water Molecule Unit Water Use, Water on Earth, Water Conservation Lesson Bundle Groundwater, Groundwater Pollution Lesson Bundle Properties of Water Lesson Bundle Water Cycle Lesson Bundle Water Unit Review Game Water Unit Preview, Homework Package, Unit Notes, more • Thank you for your interest and feel free to contact me with any questions you may have. Best wishes. • Sincerely, • Ryan Murphy M.Ed • www.sciencepowerpoint@gmail.com