Networking I
advertisement

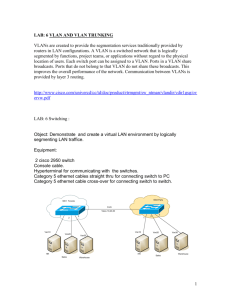
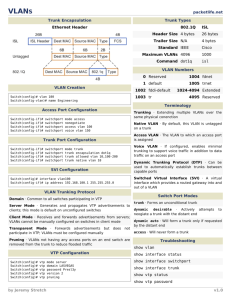
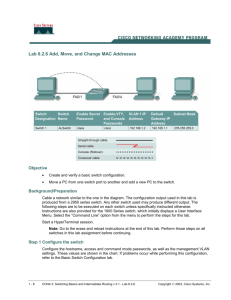
Computer Networks I By: Ing. Hector M Lugo-Cordero, MS What is a network? • Collection of computers interconnected to share resources • A network does not mean Internet access • Exposes security issues OSI Model Layers • • • • • • • Physical (repeaters/hubs): signals Data Link (bridges/switches): frame Network (routers/L3switches): packet Transport: segment Session Presentation Application: data Signals • • • • • • • • Duplex Bandwidth Throughput Delay/Latency Cyclic Redundancy Check Manchester Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing Spectrum Analyzer Parameters • Duplex: communication channel direction – Half-duplex: communication can flow in one direction at a given time – Full-duplex: communication can flow in both directions at the same time • Bandwidth: theoretical capacity of the communication channel • Throughput: actual capacity of the communication channel • Delay/Latency: the time that takes the network to deliver a packet from source to destination CRC • Detects the presence of errors so that a retransmission can be asked for • Ethernet uses a fixed polynomial for the CRC computation known as CRC32 – x32 + x26 + x23 + x22 + x16 + x12 + x11 + x10 + x8 + x7 + x5 + x4 + x2 + x + 1 Manchester OFDM Spectrum Analyzer • Allows to study signals – Frequency domain – SNR measures Physical Layer • Signals are sent through the chosen medium • Fiber Optic • Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) • Wireless • Hubs Hubs • Work the physical layer • Built with pure hardware • Amplify the signal and retransmit it to all ports except the one that sent the data • Expand collision domain and broadcast domain UTP Fabrication • Straight cable: used to communicate different devices • Cross-over cable: used to communicate devices of the same nature – PC and Routers are the exception • Rollover cable: used to communicate with the devices using the console UTP Fabrication SRC Straight Cross-over Rollover 1 1 3 8 2 2 6 7 3 3 1 6 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 4 6 6 2 3 7 7 7 2 8 8 8 1 Data Link Layer • Translates bits to signals and schedules the access to the medium • Composed of two sub-layers – Logical Link Control (LLC – IEEE 802.2) – Medium Access Control (MAC) • IEEE 802.3 – Ethernet • IEEE 802.11 – Wireless • IEEE 802.15 – Bluetooth • Switches work at this layer with MAC address MAC Addresses • Identifies uniquely a node in the network • This address should be private (unknown to other users, but not nodes) • 48 bit number – MM:MM:MM:SS:SS:SS (hex) • M is manufacturer’s id • S is serial number Switches • Able to create virtual circuit • Break collision domains but enlarge the broadcast domains • Have more intelligence than hubs • Can create network segments for privacy • Ports can be access or trunk Virtual Local Area Networks (VLAN) • Segmentation of the network • Breaks broadcasts domains • Needs a router for different vlan communications • Increase in security Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) • Creates a spanning tree of the switches topology • Breaks loops to prevent broadcast storms • Should be always enabled Switch Configuration (Cisco) • Connect rollover cable from serial in PC to console at the switch • Open hyper terminal connection with 9600 baud, data bits 8, parity none, stop bits 1, flow control none • Tipically known as: 96008N1 Switch Configuration (Cisco) • This steps erase everything to factory defaults • SW>enable #enter from user to privileged • SW#show running-config • delete vlan.dat • erase startup-config • reload Switch Configuration (Cisco) • • • • • • • • • • • This steps configure the ports of the switch SW#configure terminal SW(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/0 SW(config-if)#switchport mode access SW(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10 SW(config-if)#exit #end goes to begin SW(config)#interface range FastEthernet 0/0-15 SW(config-if)#switchport mode access SW(config-if)#switchport access vlan 20 SW(config-if)#end SW# Switch Configuration (Cisco) • This steps configure a trunk (multi vlans) • SW(config-if)#switport mode trunk • SW(config-if)#switport trunk allowed vlan add 10 • SW(config-if)#switport trunk allowed vlan add 20 Switch Configuration (Cisco) • This steps configure port security • SW(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum 1 • SW(config-if)#switchport port-security violation shutdown • SW(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address 001f.453a.1234 Switch Configuration (Linksys) File: /etc/config/network #### VLAN configuration config switch eth0 option vlan0 "0 1 2 3 5*" option vlan1 "4 5" Wireless Networking • Channels allowed by the FCC (default 6) • Authentication and association – WEP – WPA • Add-Hoc vs Infrastructure Infrastructure Networks • Access networks are wired LAN with access points • Nodes connect to access points to access the wired distribution system • A bridge from IEEE802.11 to IEEE802.3 is needed Ad-Hoc Networks • • • • • Interconnected fully wireless Multi-hop network Nodes can either be client or server Extend the range of normal WLAN Can reach places were wires can’t Setting a Wireless Access Network • What you need – Access point (IEEE802.11 to IEEE802.3 bridge) – Wireless internet card – The right technology • • • • IEEE802.11a IEEE802.11b IEEE802.11g IEEE802.11n • Security – – – – IEEE802.11i WPA No SSID broadcast MAC filtering Wireless Configuration (Linksys) File: /etc/config/wireless config wifi-device wl0 option type broadcom option channel '6' option disabled '0' config wifi-iface option device wl0 option network 'wlan' option mode 'adhoc' option ssid 'OLSR' option encryption none option hidden '0'