Biotechnology Lab
advertisement

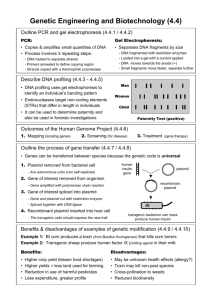
Biotechnology Lab Bio 11 Week 1 Brief Overview of Lab Objectives 1. Obtain Bacterial DNA (plasmids-pAMP and pKAN) 2. Cut DNA into specific pieces using special enzymes (restriction enzymes- BamHI; HindIII) 3. Measure size of pieces cut by enzymes (gel electrophoresis) 4. Glue pieces together using other enzymes (DNA ligase) 5. Take glued pieces and put them into another bacterium (plasmid transformation of E. coli) 6. Separate bacteria with plasmid from those without Today’s Objectives 1. Obtain Bacterial DNA (plasmids-pAMP and pKAN) 2. Cut DNA into specific pieces using special enzymes (restriction enzymes- BamHI; HindIII) 3. Extract eukaryotic genomic DNA from strawberries* * Optional (Time permitting) Prerequisites to lab • Pipette tutorial (second) • Metric system review (first) Metric conversions • • • • • 500µL = ______mL .1mL = ________µL 10mL= ________µL 10.0µL= ________mL 1000µL= ________L Micropipettors Are fragile Expensive Precise They depend on correct usage for accuracy Figure 5a: P-20 Model 6.86 ml = 0.00686 or 6.86 x 10-3 ml Figure 5b: P-200 Model 132.4 m l = 0.1324 or 1.324 x 10-1 ml Figure 5c: P-1000 Model 262 m l = 0.262 or 2.62 x 10-1 ml Steps in proper pipette usage 1. Adjust volume 2. Select tip 3. Depress plunger to first stop 4. Put tip into desired liquid 5. Release plunger slowly 6. Put tip into desired container 7. Depress plunger to second stop 8. Remove tip from container 9. Discard empty used tip 10.Repeat Lab Concepts in Detail Two Types of DNA in E. coli Chromosomal DNA – necessary for cell survival; circular, double-stranded Plasmid DNA – extrachromosomal DNA (“bonus material”) useful for experimental manipulation; circular, double-stranded Plasmids contain nonessential (but important) genes “Bonus Package” 1: origin of replication and cloning site Plasmids can be cut with restriction enzymes Enzymes homodimerize to make symmetrical cuts BamHI CGGATCCA GCCTAGGT CG GCCTAG GATCCA GT “sticky ends” Restriction Enzymes cut very specific sequences of DNA Bacterium Gene inserted into plasmid Plasmid DNA manipulation is at the heart of biotechnology Bacterial chromosome Cell containing gene of interest Plasmid Gene of interest Recombinant DNA (plasmid) DNA of chromosome Plasmid put into bacterial cell Recombinant bacterium Host cell grown in culture to form a clone of cells containing the “cloned” gene of interest Protein expressed by gene of interest Gene of interest Copies of gene Basic research on gene Gene for pest resistance inserted into plants Protein harvested Basic research and various applications Gene used to alter bacteria for cleaning up toxic waste Protein dissolves blood clots in heart attack therapy Basic research on protein Human growth hormone treats stunted growth BamHI BamHI pKAN pAMP HindIII ampR Ori BamHI kanR ampR Restriction digest Ori Ori Ori BamHI (2332 bp) HindIII (3755 bp) BamHI HindIII HindIII (784 bp) kanR Ligation (1875 bp) BamHI kanR ampR HindIII Ori HindIII