Chapter Topics
advertisement

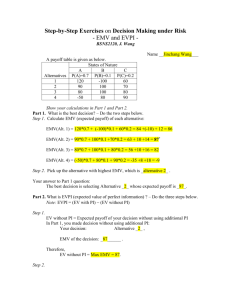
Chapter Topics •The Payoff Table and Decision Trees •Opportunity Loss •Criteria for Decision Making •Expected Monetary Value •Return to Risk Ratio Features of Decision Making •List Alternative Courses of Action (Possible Events or Outcomes) •Determine ‘Payoffs’ (Associate a Payoff with Each Event or Outcome) •Adopt Decision Criteria (Evaluate Criteria for Selecting the Best Course of Action) List Possible Actions or Events Two Methods of Listing Payoff Table Decision Tree Payoff Table Consider a food vendor determining whether to sell soft drinks or hot dogs. Course of Action (Aj) Sell Soft Drinks (A1) Sell Hot Dogs (A2) Event (Ei) Cool Weather (E1) x11 =$50 x12 = $100 Warm Weather (E2) x21 = 200 x22 = 125 xij = payoff (profit) for event i and action j Decision Tree:Example Food Vendor Profit Tree Diagram x11 = $50 x21 = 200 x12 = 100 x22 =125 Opportunity Loss: Example Highest possible profit for an event Ei - Actual profit obtained for an action Aj Opportunity Loss (lij ) Event: Cool Weather Action: Soft Drinks Profit: $50 Alternative Action: Hot Dogs Profit: $100 Opportunity Loss = $100 - $50 = $50 Note: Opportunity Loss is always positive Opportunity Loss: Table Event Alternative Course of Action Sell Soft Drinks Sell Hot Dogs Optimal Action Profit of Optimal Action Cool Weather Hot Dogs 100 100 - 50 = 50 Warm Weather Soft Drinks 200 200 - 200 = 0 100 - 100 = 0 200 - 125 = 75 Decision Criteria • • • • • • • Expected Monetary Value (EMV) The expected profit for taking an action Aj Expected Opportunity Loss (EOL) The expected loss for not taking action Aj Expected Value of Perfect Information (EVPI) The expected opportunity loss from the best decision Decision Criteria -- EMV • • Expected Monetary Value (EMV) Sum (monetary payoffs of events) (probabilities of the events) EMVj = Xij Pi N i=1 EMVj = expected monetary value of action j xi,j = payoff for action j and event i Pi = probability of event i occurring Decision Criteria -- EMV Table Example: Food Vendor Pi Event .50 Cool .50 Warm Soft xijPi Drinks $50 $50 .5 = $25 $200 $200 .5 = 100 Hot Dogs $100 $100.50 = $50 $125 $25.50 = 62.50 EMV Soft Drink = $125 Better alternative xijPi EMV Hot Dog = $112.50 Decision Criteria -- EOL • Expected Opportunity Loss (EOL) • Sum (opportunity losses of events) (probabilities of events) EOLj = lij Pi N i =1 EOLj = expected monetary value of action j li,j = payoff for action j and event i Pi = probability of event i occurring Decision Criteria -- EOL Table Example: Food Vendor Pi Event Op Loss Soft Drinks .50 Cool .50 Warm lijPi OP Loss Hot Dogs lijPi $50 $50.50 = $25 $0 $0.50 = $0 0 $0 .50 = $0 $75 EOL Soft Drinks = $25 Better Choice $75 .50 = $37.50 EOL Hot Dogs = $37.50 Decision Criteria -- EVPI Expected Value of Perfect Information (EVPI) • The expected opportunity loss from the best decision Expected Profit Under Certainty - Expected Monetary Value of the Best Alternative EVPI (should be a positive number) • Represents the maximum amount you are willing to pay to obtain perfect information EVPI Computation Expected Profit Under Certainty = .50($100) + .50($200) = $150 Expected Monetary Value of the Best Alternative = $125 EPVI = $25 The maximum you would be willing to spend to obtain perfect information. Taking Account of Variability: FoodVendor s2 for Soft Drink = (50 -125)2 .5 + (200 -125)2 .5 = 5625 s for Soft Drink = 75 CVfor Soft Drinks = (75/125) 100% = 60% s2 for Hot Dogs = 156.25 s for Hot dogs = 12.5 CVfor Hot dogs = 11.11% Return to Risk Ratio Expresses the relationship between the return (payoff) and the risk (standard deviation). RRR = Return to Risk Ratio = RRRSoft Drinks = 125/75 = 1.67 EMV j sj RRRHot Dogs = 9 You might wish to choose Hot Dogs. Although Soft Drinks have the higher Expected Monetary Value, Hot Dogs have a much larger return to risk ratio and a much smaller CV. Note: RRR is the inverse of CV