The Sensory System
advertisement

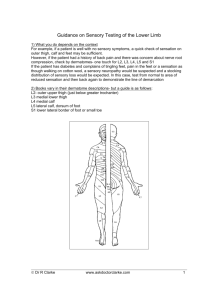
The Sensory System Examining the sensory system provides information regarding the integrity of the Spinothalamic Tract, posterior columns of the spinal cord and parietal lobes of the brain. Client preparation Examination gown Sit comfortably on bed or exam table Explain re position changes Reassure and provide with clear directions Equipment Cotton ball Objects to feel, quarter or key etc. Test tubes with hot/cold H2O Tuning fork, low pitched Screening Test Only necessary to evaluate the following Lateral aspect of upper thighs Inner aspect of upper arms Dorsal or palmer surface of hands Bottom or dorsal surface of feet Neural Pathways Sensory impulses travel to the brain via 2 ascending neural pathways 1. 2. Spinothalamic tract Posterior columns Impulses originate in the afferent fibers of the peripheral nerves, are carried through the posterior dorsal root into the spinal cord. Lateral Spinothalamic Tract Pain Temperature Crude & Light Touch Posterior Columns Position Vibration Fine touch Assessment Scatter stimuli over the distal and proximal parts of all extremities and trunk to cover most of the dermatomes. Abnormal symptoms may indicate need to test the entire body surface Pain Numbness Tingling Compare sensations on symmetric parts of the body If decrease in sensation Systematic testing From point of decreased sensation toward sensitive area Note where sensation changes Map borders of deficient area, Diagram Note if the pattern of sensory loss is “distal” Glove & stocking ( hands & feet) Dermatones C3- front of neck T4 - nipples T10 – umbilicus C6 – thumb L1 inguinal Dermatones L4 – Knee L5 – Anterior ankle & foot Dermatone = bandof skin innervated by the sensory root of a single spinal nerve. Light Touch Sensation Use wisp of cotton Ask clients to close both eyes and tell you what they feel and where Normal Findings Correctly identifies light touch In some older clients light touch and pain sensations may be decreased Abnormal findings Disorders that can alter perception of sensations Peripheral neuropathies due to: Diabetes Folic acid deficiencies Alcoholism Lesions of the ascending spinal cord, brain stem, cranial nerves, and cerebral cortex Abnormal findings to Touch Anesthesia = absent Hypoesthesia = decreased Hyperesthesia = increased Pain Sensation Pin prick Tongue blade, dull & sharp Ask to distinguish 2 sec. b/t each stimulus to avoid summation (frequent consecutive stimuli percieved as one strong stimulus) Abnormalities to pain Analgesia = absence of pain sensation Hypalgesia = decreased Hyperalgesia = increased Apply lightest pressure to obtain response Temperature Only tested when pain sensation is abnormal. Temp. & pain travel in the lateral spinothalamic tract Test tubes, hot & cold H2O Vibration Low pitched tuning fork (128Hz) Distal interphalangeal joint (finger & big toe) Ask what the patient feels. Ask to tell when the vibration stops and then touch the fork to stop it. If impaired- proceed to more proximal joints or bony prominances. Posterior Column Tract Vibration – often first sense to be lost in peripheral neuropathy. Loss = posterior column disease, lesion of peripheral nerve or root Position ( Kinesthesia) Passive movement of extremity Finger or big toe up and down Hold by sides b/t thumb and index finger If position sense is impaired, move proximally to next joint If position sense intact distally , then it is OK proximally. Tactile Discrimination Sensory cortex Eyes closed during testing Stereognosis= identification of an object by feel Astereognosis, inability to recognize objects Number identification= Graphesthesia Used when stereognosis prevented due to motor impairment for ex. In arthritis Use blunt end of pen/pencil to draw number Two-point discrimination Alternate double with single stimulus Minimal distance1 from 2 points= less than 5mm on finger pads Point Localization Touch pt’s skin Open eyes and point to where touched Useful trunk & legs Extinction Simultaneously stimulate same area both sides of body Ask how many points felt and where charting If normal Identifies light touch, dull and sharp sensations to trunk and extremities. Vibratory sensation, stereognosis, graphesthesia, two-point discrimination intact. Abnormal results in these tests indicate lesions of the sensory cortex. These tests not done on children 6 yrs and younger. 65yrs &older loss of sensation of vibration at the ankle Position sense in big toe may be lost Tactile sensation impaired Infants and toddlers Little sensory testing Hypoesthesia Responds to pain by crying General reflex withdrawal of all limbs 7 – 9mos.can localize stimulus