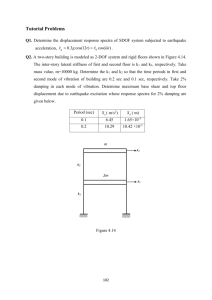
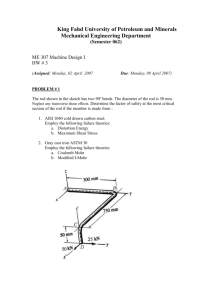
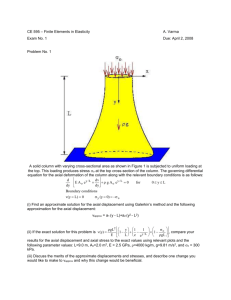
Richefeu & al., Géotech. Lett., 2, 113
advertisement

Mesure de champs cinématiques particulaires haute définition dans les milieux granulaires bidimensionnels G. Combe, V. Richefeu Présenté par O. Jenck Schneebeli** rods : a 2D granular material **G. Schneebeli, CRAS, 243(1):125-126 (1956) 2D Grains ≡ 6 cm long cylinders of various sections and different diameters PVC rods ϕ = [1,5 - 2,5 - 3,5 mm] Mixtures of discs and rectangles Wood rods ϕ = [6 - 10 - 16 - 20 mm] Hexagonal shapes 2 2000 wooden rods in 1γ2ε shear device 3 ** 1γ2ε Shear apparatus **H.A. Joer & al, Géotechnique, 48(5):605-619 (1996) Possible tests Oedometric compression Isotropic compression And Simple shear test: tilt with constant vertical stress Biaxial test: vertical compression, lateral stress constant Test with imposed rotation of the principal axes of STRAINS or STRESSES (more complex) 4 ** 1γ2ε Shear apparatus **H.A. Joer & al, Géotechnique, 48(5):605-619 (1996) What do we measure ? - Macroscopic level (sample scale): • Lengths and tilt of the boundaries ➟ Strain macroscopic tensor • Forces at the corners of the frame ➟ Stress macroscopic tensor - Microscopic level (grain scale): • Position and orientation of grains ➟ full grain kinematics ➟ Contacts list 5 Assessing kinematics using “modern” Digital Camera (2010 ➟ ...) Shear test on 2000 wooden rods 1100 pictures - 24.5 MPixels movie picture speed x 500 6 PIT : Particle Image Tracking Combe & Richefeu, Powders and Grains 2013 PIT : Digital Image Correlation technique adapted to track “automatically” full kinematics of rigid bodies Tracker PIT software Rigid-motion relation to track u, v and θ… … with a subpixel resolution using bilinear, bicubic or biquintic interpolation 7 PIT: Particle Image Tracking Combe & Richefeu, Powders and Grains 2013 Correlation works between the first and the current images (thanks to rigid motion and ZNCC) ➡ digital truncation errors are NOT cumulated. A rescue procedure that basically increase the search zone and avoid exclusion zones of well-found bodies. Body being « rescued » Exclusion zone Well-found bodies Increased search zone 8 PIT: Particle Image Tracking Combe & Richefeu, Powders and Grains 2013 Accuracy with synthetic images (from Orteu et al., 2006) Courtesy, L. Robert ➠ Same intrinsic accuracy as the codes used in the GdR CNRS 2519 9 PIT : Particle Image Tracking Combe & Richefeu, Powders and Grains 2013 Accuracy with real images that involve the whole measurement chain. Solid motion = distance and angle conservation Correction of distortion drastically improve the accuracy. 10 Fluctuations of displacement Richefeu & al., Géotech. Lett., 2, 113-118,(2012) An experimental study inspired from the numerical work of Radjaï & Roux, PRL (2002) Quasi-Static shear test 11 Fluctuations of displacement Richefeu & al., Géotech. Lett., 2, 113-118,(2012) An experimental study inspired from the numerical work of Radjaï & Roux, PRL (2002) Quasi-Static shear test 12 Fluctuations of displacement Richefeu & al., Géotech. Lett., 2, 113-118,(2012) Fluctuations are due to geometrical constraints 13 Fluctuations of displacement Richefeu & al., Géotech. Lett., 2, 113-118,(2012) ➠ Statistical analysis of the fluctuation of displacement ** **C. Tsallis, Journal of Statistical Physics 52, 479–487 (1988) 14 Fluctuations of displacement Small shear-strain increment Richefeu & al., Géotech. Lett., 2, 113-118,(2012) Large shear-strain increment 15 Fluctuations of displacement Richefeu & al., Géotech. Lett., 2, 113-118,(2012) Vortex small Δγ ➠ long range correlation large Δγ ➠ short range correlation 10<d> vortice-like structures 16 Conclusions An digital image correlation tool has been developed with a special concern with “particle tracking”. It has been shown to be as accurate as other tools used in the field of continuous materials. On a direct 2D shear test, the displacement fluctuations was defined as the measured displacements subtracted by the displacements interpolated from the boundary movements (affine field). Some specific features of the fluctuations, that play a role analogue to the dislocations in steel plasticity, have been characterized. And now… we work on how to derive a plastic model of granular material from the fluctuations of grain displacements. Thank you for your attention