Carbon Fiber Composite Material Property Determination
advertisement

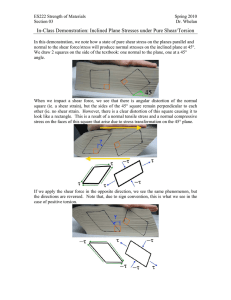
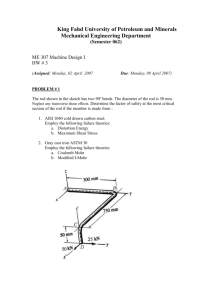
Carbon Fiber Composite Material Property Determination: Required Material Constants: E1, E2, v12, v21, G12 Calculation of E1 and E2: - Open the file ‘Carbon Fiber E1 and E2 Data.xls’ - Provided is the load and displacement data for the 1 and 2 direction in Newtons and mm, respectively - Use the included specimen geometry measurement to create stress/strain plots and calculate E 1 and E2. v12 and v21: - Use: v12 = 0.27 - Calculate v21 from your measured values of E1, E2, and v12. G12: - - Import the file ‘ten degree shear test.raw’ in excel, this is the raw Instron file. Use the Load and Displacement data from this file and the dimensions of the beam to calculate the uniaxial stress (σx): o Width = 25.25 mm o Thickness = 1.27 mm o Gauge Length = 162 mm Shear stress (τ) is calculated as 𝝉 = −𝝈𝒙 𝐬𝐢𝐧 𝜽 𝐜𝐨𝐬 𝜽, where θ=10 degrees Open the file ‘ten degree strain gage data.xlsx’. This is a recording shear strains (εA and εB) of two strain gages (A and B) which were mounted on the 10 degree offset test specimen. Shear strain (γ) for this test is 𝜸 = 𝜺𝑨 − 𝜺𝑩 Note: Gage recordings started prior to the start of the Instron test and carried on after the Instron stopped. Omit the data which is not changing (slope = 0). This should be relatively clear. Create a plot of shear stress vs. shear strain (τ vs γ). The slope of this line is shear modulus (G12).